Abstract
Aims
Changes in litter chemistry and stoichiometry following N enrichment have important consequences on litter decomposition and plant-mediated nutrient cycling. Our knowledge about the responses of litter stoichiometry at different biological organization levels to N enrichment remains poorly understood. Moreover, whether the impacts of N enrichment on stoichiometric ratios in litter would depend on ecosystem management strategies remains unknown.
Methods
We examined the effects of N addition and mowing on C:N:P stoichiometry in standing litter at plant organ, species, functional group, and community levels in a semi-arid grassland of northern China, taking advantage of a field experiment that has been running for seven years.
Results
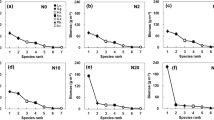
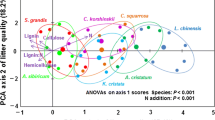
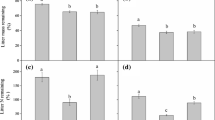
Nitrogen addition altered biomass allocation between different organs and among different plant functional groups, with consequences on litter stoichiometry at community level. N addition had no impacts on litter C concentration, increased litter N, and N:P ratio, and decreased litter C:N ratio from plant organ to community. The impacts of N addition on litter P and C:P depended on the identity of plant species and functional group. Mowing did not affect litter nutrient characters across all organization levels. Furthermore, no interactive effects between N addition and mowing on litter nutrient characters were observed from plant organ to community levels.
Conclusions
We conclude that N deposition will enhance litter quality even in the heavily-used grasslands with shifts in biomass allocation and species composition, which may contribute to the enhancement of plant-mediating nutrient cycling.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts R, Chapin FS (1999) The mineral nutrition of wild plants revisited: a re-evaluation of processes and patterns. Adv Ecol Res 30:1–67
Aerts R, De Caluwe H (1994) Nitrogen use efficiency of Carex species in relation to nitrogen supply. Ecology 75:2362–2372
Bai Y, Wu J, Clark CM, Naeem S, Pan Q, Huang J, Zhang L, Han X (2010) Tradeoffs and thresholds in the effects of nitrogen addition on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: evidence from inner Mongolia Grasslands. Glob Chang Biol 16:358–372
Bennett LT, Judd TS, Adams MA (2003) Growth and nutrient content of perennial grasslands following burning in semi-arid, sub-tropical Australia. Plant Ecol 164:185–199
Billings SA, Zitzer SF, Weatherly H, Schaeffer SM, Charlet T, Arnone JA, Evans RD (2003) Effects of elevated carbon dioxide on green leaf tissue and leaf litter quality in an intact Mojave Desert ecosystem. Glob Chang Biol 9:729–735
Bridgham SD, Pastor J, Mcclaugherty CA, Richardson CJ (1995) Nutrient-use efficiency: a litterfall index, a model, and a test along a nutrient-availability gradient in North Carolina peatlands. Am Nat 145:1–21
Clark CM, Tilman D (2008) Loss of plant species after chronic low-level nitrogen deposition to prairie grasslands. Nature 451:712–715
Collins SL, Knapp AK, Briggs JM, Blair JM, Steinauer EM (1998) Modulation of diversity by grazing and mowing in native tallgrass prairie. Science 280:745–747
Craine JM, Towne EG, Nippert JB (2010) Climate controls on grass culm production over a quarter century in a tallgrass prairie. Ecology 91:2132–2140
Frank DA, Kuns MM, Guido DR (2002) Consumer control of grassland plant production. Ecology 83:602–606
Freschet GT, Cornelissen JH, van Logtestijn RS, Aerts R (2010) Substantial nutrient resorption from leaves, stems and roots in a subarctic flora: what is the link with other resource economics traits? New Phytol 186:879–889
Fujita Y, Robroek BJM, De Ruiter PC, Heil GW, Wassen MJ (2010) Increased N affects P uptake of eight grassland species: the role of root surface phosphatase activity. Oikos 119:1665–1673
Galloway JN, Schlesinger WH, Levy H, Michaels A, Schnoor JL (1995) Nitrogen fixation: anthropogenic enhancement-environmental response. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 9:235–252
Gholz HL, Wedin DA, Smitherman SM, Harmon ME, Parton WJ (2000) Long-term dynamics of pine and hardwood litter in contrasting environments: toward a global model of decomposition. Glob Chang Biol 6:751–765
Giese M, Brueck H, Gao YZ, Lin S, Steffens M, Kögel-Knabner I, Glindemann T, Susenbeth A, Taube F, Butterbach-Bahl K, Zheng XH, Hoffmann C, Bai YF, Han XG (2013) N balance and cycling of inner Mongolia typical steppe: a comprehensive case study of grazing effects. Ecol Monogr 83:195–215
Güsewell S, Gessner MO (2009) N: P ratios influence litter decomposition and colonization by fungi and bacteria in microcosms. Funct Ecol 23:211–219
Han WX, Fang JY, GD L, Zhang Y (2005) Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol 168:377–385
Han X, Sistla SA, Zhang Y-H, Lü X-T, Han X-G (2014) Hierarchical responses of plant stoichiometry to nitrogen deposition and mowing in a temperate steppe. Plant Soil 382:175–187
van Heerwaarden LM, Toet S, Aerts R (2003) Nitrogen and phosphorus resorption efficiency and proficiency in six sub-arctic bog species after 4 years of nitrogen fertilization. J Ecol 91:1060–1070
Henry HAL, Cleland EE, Field CB, Vitousek PM (2005) Interactive effects of elevated CO2, N deposition and climate change on plant litter quality in a California annual grassland. Oecologia 142:465–473
Hiernaux P, Turner MD (1996) The effect of clipping on growth and nutrient uptake of Sahelian annual rangelands. J Appl Ecol 33:387–399
Hou S-L, Yin J-X, Sistla S, Yang J-J, Sun Y, Li Y-Y, Lü X-T, Han X-G (2017) Long-term mowing did not alter the impacts of nitrogen deposition on litter quality in a temperate steppe. Ecol Eng 102:404–410
Isbell F, Reich PB, Tilman D, Hobbie SE, Polasky S, Binder S (2013) Nutrient enrichment, biodiversity loss, and consequent declines in ecosystem productivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:11911–11916
Jia Y, Yu G, He N, Zhan X, Fang H, Sheng W, Zuo Y, Zhang D, Wang Q (2014) Spatial and decadal variations in inorganic nitrogen wet deposition in China induced by human activity. Sci Rep 4:3763
Kang L, Han XG, Zhang ZB, Sun OJ (2007) Grassland ecosystems in China: review of current knowledge and research advancement. Philos Trans R Soc B 362:997–1008
Klumpp K, Tallec T, Guix N, Soussana JF (2011) Long-term impacts of agricultural practices and climatic variability on carbon storage in a permanent pasture. Glob Chang Biol 17:3534–3545
Koerselman W, Meuleman AF (1996) The vegetation N:P ratio: a new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. J Appl Ecol:1441–1450
Kozovits AR, Bustamante MMC, Garofalo CR, Bucci S, Franco AC, Goldstein G, Meinzer FC (2007) Nutrient resorption and patterns of litter production and decomposition in a Neotropical Savanna. Funct Ecol 21:1034–1043
Liu X, Zhang Y, Han W, Tang A, Shen J, Cui Z, Vitousek P, Erisman JW, Goulding K, Christie P, Fangmeier A, Zhang F (2013) Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 494:459–462
Lü X-T, Han X-G (2010) Nutrient resorption responses to water and nitrogen amendment in semi-arid grassland of Inner Mongolia, China. Plant Soil 327:481–491
Lü XT, Kong DL, Pan QM, Simmons ME, Han XG (2012) Nitrogen and water availability interact to affect leaf stoichiometry in a semi-arid grassland. Oecologia 168:301–310
Lü XT, Reed S, Yu Q, He NP, Wang ZW, Han XG (2013) Convergent responses of nitrogen and phosphorus resorption to nitrogen inputs in a semiarid grassland. Glob Chang Biol 19:2775–2784
Menge DNL, Field CB (2007) Simulated global changes alter phosphorus demand in annual grassland. Glob Chang Biol 13:2582–2591
Mikola J, Setälä H, Virkajärvi P, Saarijärvi K, Ilmarinen K, Voigt W, Vestberg M (2009) Defoliation and patchy nutrient return drive grazing effects on plant and soil properties in a dairy cow pasture. Ecol Monogr 79:221–244
Müller I, Schmid B, Weiner J (2000) The effect of nutrient availability on biomass allocation patterns in 27 species of herbaceous plants. Perspect Plant Ecol 3:115–127
Novotny AM, Schade JD, Hobbie SE, Kay AD, Kyle M, Reich PB, Elser JJ (2007) Stoichiometric response of nitrogen-fxing and non-fxing dicots to manipulations of CO2, nitrogen, and diversity. Oecologia 151:687–696
Parton W, Silver WL, Burke IC, Grassens L, Harmon ME, Currie WS, King JY, Adair EC, Brandt LA, Hart SC, Fasth B (2007) Global-scale similarities in nitrogen release patterns during long-term decomposition. Science 315:361–364
Perring MP, Hedin LO, Levin SA, McGroddy M, de Mazancourt C (2008) Increased plant growth from nitrogen addition should conserve phosphorus in terrestrial ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:1971–1976
Phoenix GK, Booth RE, Leake JR, Read DJ, Grime JP, Lee JA (2004) Simulated pollutant nitrogen deposition increases P demand and enhances root-surface phosphatase activities of three plant functional types in a calcareous grassland. New Phytol 161:279–289
Rowe EC, Smart SM, Kennedy VH, Emmett BA, Evans CD (2008) Nitrogen deposition increases the acquisition of phosphorus and potassium by heather Calluna vulgaris. Environ Pollut 155:201–207
Sardans J, Penuelas J (2012) The role of plants in the effects of global change on nutrient availability and stoichiometry in the plant–soil system. Plant Physiol 160:1741–1761
Semmartin M, Aguiar MR, Distel RA, Moretto AS, Ghersa CM (2004) Litter quality and nutrient cycling affected by grazing-induced species replacements along precipitation gradient. Oikos 107:148–160
Turner CL, Seastedt TR, Dyer MI (1993) Maximization of aboveground grassland production: the role of defoliation frequency, intensity, and history. Ecol Appl 3:175–186
Vitousek PM, Aber JD, Howarth RW, Likens GE, Matson PA, Schindler DW, Schlesinger WH, Tilman DG (1997) Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: sources and consequences. Ecol Appl 7:737–750
Wang X-G, Lü X-T, Han X-G (2014) Responses of nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry of senesced leaves in dominant plants to nitrogen addition and prescribed burning in a temperate steppe. Ecol Eng 70:154–161
Waring BG (2013) Exploring relationships between enzyme activities and leaf litter decomposition in a wet tropical forest. Soil Biol Biochem 64:89–95
Wedin DA, Tilman D (1996) Influence of nitrogen loading and species composition on the carbon balance of grasslands. Science 274:1720–1723
Wright IJ, Westoby M (2003) Nutrient concentration, resorption and life span: leaf traits of Australian sclerophyll species. Funct Ecol 17:10–19
Xia J, Wan S (2008) Global response patterns of terrestrial plant species to nitrogen addition. New Phytol 179:428–439
Zhang Y, Lu X, Isbell F, Stevens C, Han X, He N, Zhang G, Yu Q, Huang J, Han X (2014) Rapid plant species loss at high rates and at low frequency of N addition in temperate steppe. Glob Chang Biol 20:3520–3529
Zhang Y, Feng J, Isbell F, Lu X, Han X (2015) Productivity depends more on the rate than the frequency of N addition in a temperate grassland. Sci Rep 5:12558
Zhang Y, Loreau M, Lu X, He N, Zhang G, Han X (2016) Nitrogen enrichment weakens ecosystem stability through decreased species asynchrony and population stability in a temperate grassland. Glob Chang Biol 22:1445–1455
Ziter C, MacDougall AS (2013) Nutrients and defoliation increase soil carbon inputs in grassland. Ecology 94:106–116
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the staff of the Inner Mongolia Grassland Ecosystem Research Station (IMGERS) for supporting this work and Chenxi Tian, Sihan Liu, Yi Wu, and Yue Sun for their assistance with laboratory work. This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2016YFC0500601 and 2015CB150802), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770503, 31470505, and 31430016), Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB15010403), Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (2014174), and the Key Research Program from CAS (QYZDB-SSW-DQC006 and KFZD-SW-305-002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Alfonso Escudero
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, SL., Yin, JX., Yang, JJ. et al. Consistent responses of litter stoichiometry to N addition across different biological organization levels in a semi-arid grassland. Plant Soil 421, 191–202 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3446-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3446-z