Abstract
Aim
The objective of this study was to develop a remediation strategy for soil co-contaminated with decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) and heavy metals (Cd, Pb and Zn) using co-plantation of the hyperaccumulator plant (Sedum alfredii) with tall fescue (Festuca arundinaceae) associated with a BDE degrader (Bacillus cereus strain JP12).
Methods
A 120-day remediation experiment was conducted under greenhouse conditions. S. alfredii and tall fescue were grown in monoculture and intercropped in artificially contaminated soil. Plant biomass, concentration of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, density of soil bacteria, soil enzyme activity, and the physiological profile of the soil microbial community were determined.
Results and discussion
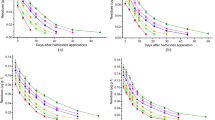
Inoculation with JP12 significantly increased BDE-209 dissipation in soil. Phytoextraction of metals was also enhanced by JP12 inoculation due to the improved plant growth. Planting of tall fescue significantly enhanced BDE-209 dissipation as compared to that in the bare soil because of the increased soil microbial activity. Tall fescue showed higher Pb phytoextraction efficiency than S. alfredii, but Pb was principally retained in the roots of tall fescue. BDE-209 dissipation and metal phytoextraction were highest when co-planting S. alfredii with tall fescue inoculated with strain JP12. Pyrosequencing analysis revealed that the inoculated JP12 could functionally adapt to the introduced soil, against competition with indigenous microorganisms in soil.
Conclusions
Co-planting of S. alfredii with tall fescue combined with BDE-degrading bacterial strain JP12 is promising for remediation of soil co-contaminated with BDE-209 and metals.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becerra-Castro C, Kidd PS, Rodríguez-Garrido B, Monterroso C, Santos-Ucha P, Prieto-Fernández Á (2013) Phytoremediation of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH)-contaminated soils using Cytisus striatus and bacterial inoculants in soils with distinct organic matter content. Environ Pollut 178:202–210
Begonia MT, Begonia GB, Ighoavodha M, Gilliard D (2005) Lead accumulation by tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.) grown on a lead-contaminated soil. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2:228–233
Cheema SA, Khan MI, ShenCF TXJ, Farooq M, Chen L, ZhangCK CYX (2010) Degradation of phenanthrene and pyrene in spiked soils by single and combined plants cultivation. J Hazard Mater 177:384–389
Chen YC, Banks MK, Schwab AP (2003) Pyrene degradation in the rhizosphere of tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea) and switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.). Environ Sci Technol 37:5778–5782
Cheng KY, Wong JW (2008) Fate of 14C–Pyrene in soil–plant system amended with pig manure compost and Tween 80: a growth chamber study. Bioresour Technol 99:8406–8412
Chigbo CO (2013) Phytoremediation potential for co-contaminated soils. Ph. D thesis, division of environmental health and risk management, College of life and environmental sciences, University of Birmingham, Edgbaston, United Kingdom
Claesson M, O’Sullivan O, Wang Q, Nikkila J, Marchesi J, Smidt H, de Vos W, Ross R, O’Toole P (2009) Comparative analysis of pyrosequencing and a phylogenetic microarray for exploring microbial community structures in the human distal intestine. PLoS One 4:e6669
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The ribosomal database project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D141–D145
Davis LMG, Martínez I, Walter J, Goin C, Hutkins RW (2011) Barcoded pyrosequencing reveals that consumption of galactooligosaccharides results in a highly specific bifidogenic response in humans. PLoS One 6:e25200
Deng DM, Deng JC, Li JT, Zhang J, Hu M, Lin Z, Liao B (2008) Accumulation of zinc, cadmium, and lead in four populations of Sedum alfredii growing on lead/zinc mine spoils. J Integr Plant Biol 50:691–698
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Gandhi N, Bhavsar SP, Gewurtz SB, Tomy GT (2011) Can biotransformation of BDE-209 in lake trout cause bioaccumulation of more toxic, lower-brominated PBDEs (BDE-47,-99) over the long term? Environ Int 37:170–177
Gerhardt KE, Huang XD, Glick BR, Greenberg BM (2009) Phytoremediation and rhizoremediation of organic soil contaminants: potential and challenges. Plant Sci 176:20–30
Huang K, Guo J, Xu Z (2009) Recycling of waste printed circuit boards: a review of current technologies and treatment status in China. J Hazard Mater 164:399–408
Lesley CB, Colette D (2013) The potential use of phytoremediation for sites with mixed organic and inorganic contamination. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 43:217–259
Li Y, Liang F, Zhu Y, Wang F (2013) Phytoremediation of a PCB-contaminated soil by alfalfa and tall fescue single and mixed plants cultivation. J Soils Sediments 13:925–931
Lu M, Zhang ZZ, Wu XJ, Xu YX, Su XL, Zhang M, Wang JX (2013) Biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) by a metal resistant strain, Bacillus cereus JP12. Bioresour Technol 149:8–15
Lu M, Zhang ZZ, Wang JX, Zhang M, Xu YX, Wu XJ (2014) Interaction of heavy metals and pyrene on their fates in soil and tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea). Environ Sci Technol 48:1158–1165
Ma Y, Zhang JY, Wong MH (2003) Microbial activity during composting of anthracene-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 52:1505–1513
Ma Y, Prasad MNV, Rajkumar M, Freitas H (2011) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and endophytes accelerate phytoremediation of metalliferous soils. Biotechnol Adv 29:248–258
Maqbool F, Wang Z, Xu Y, Zhao J, Gao D, Zhao YG, Bhatti ZA, Xing B (2012) Rhizodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons by Sesbania cannabina in bioaugmented soil with free and immobilized consortium. J Hazard Mater 237–238:262–269
Murphy E, Cotter P, Healy S, Marques T, O’Sullivan O, Fouhy F, Clarke S, O’Toole P, Quigley E, Stanton C, Ross P, O’Doherty R, Shanahan F (2010) Composition and energy harvesting capacity of the gut microbiota: relationship to diet, obesity and time in mouse models. Gut 59:1635–1642
Secher C, Lollier M, Jézéquel K, Cornu JY, Amalric L, Lebeau T (2013) Decontamination of a polychlorinated biphenyls-contaminated soil by phytoremediation-assisted bioaugmentation. Biodegradation 24:549–562
Shan Q, Liu X, Zhang J, Chen G, Liu S, Zhang P, Wang Y (2011) Analysis on the tolerance of four ecotype plants against copper stress in soil. Procedia Environ Sci 10:1802–1810
Sheng XF, Gong JX (2006) Increased degradation of phenanthrene in soil by Pseudomonas sp. GF3 in the presence of wheat. Soil Biol Biochem 38:2587–2592
Sun M, Fu D, Teng Y, Shen Y, Luo Y, Li Z, Christie P (2011) In situ phytoremediation of PAH-contaminated soil by intercropping alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) with tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.) and associated soil microbial activity. J Soils Sediments 11:980–989
Wang Y, Luo C, Li J, Yin H, Li X, Zhang G (2011) Characterization of PBDEs in soils and vegetations near an e-waste recycling site in South China. Environ Pollut 159:2443–2448
Wang K, Zhu Z, Huang H, Li T, He Z, Yang X, Alva A (2012) Interactive effects of Cd and PAHs on contaminants removal from co-contaminated soil planted with hyperaccumulator plant Sedum alfredii. J Soils Sediments 12:556–564
Wang K, Huang H, Zhu Z, Li T, He Z, Yang X, Alva A (2013) Phytoextraction of metals and rhizoremediation of PAHs in co-contaminated soil by co-planting of Sedum alfredii with ryegrass (Lolium perenne) or castor (Ricinus communis). Int J Phytoremed 15:283–298
Wu QT, Wei ZB, Ouyang Y (2006) Phytoextraction of metal-contaminated soil by Sedum alfredii H: effects of chelator and co-planting. Water Air Soil Pollut 180:131–139
Xiao W, Wang H, Li T, Zhu Z, Zhang J, He Z, Yang X (2013) Bioremediation of Cd and carbendazim co-contaminated soil by Cd-hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii associated with carbendazim-degrading bacterial strains. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:380–389
Zhang WH, Wu YX, Simonnot MO (2012) Soil contamination due to e-waste disposal and recycling activities: a review with special focus on China. Pedosphere 22:434–455
Zurek G, Pogrzeba M, Rybka K, Prokopiuk K (2013) Suitability of grass species for phytoremediation of soils polluted with heavy-metals. In breeding strategies for sustainable forage and turf grass improvement. Springer, Netherlands, pp 245–248
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41102231, No. 41172333), and the Science & Technology Plan Projects of Education Department of Jiangxi Province (No. GJJ13631).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Juan Barcelo.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 47 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, M., Zhang, ZZ. Phytoremediation of soil co-contaminated with heavy metals and deca-BDE by co-planting of Sedum alfredii with tall fescue associated with Bacillus cereus JP12. Plant Soil 382, 89–102 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2147-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2147-0