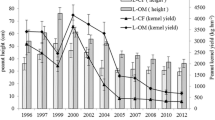
Abstract
Background and aims
Paenibacillus spp. are widely considered to impact the fertility and health of soil. The aim of this study was to evaluate how different fertilization regimes affect the population size and community structure of Paenibacillus spp. over a long period of time in red soil.
Methods
Soil samples were collected from a long-term experiment and were then analyzed using real-time PCR and PCR-DGGE. The correlation analysis, PCA and RDA were used to explore the relationships among Paenibacillus spp. population, community structure and soil properties in different treatments.
Results
The pH was seriously decreased only by the application of chemical fertilizer. The largest population of Paenibacillus spp. was found in the soil treated with organic fertilizer application, while the richest diversity was observed in the soil treated only with the chemical fertilizer. The Paenibacillus spp., Paenibacillus alkaliterrae, Paenibacillus campinasensis, and Paenibacillus xylanilyticus were found in all treatments. Paenibacillus castaneae was found in the soil treated with NPK, and Paenibacillus pabuli was specifically observed in the lime-amended treatment. Paenibacillus taichungensis and Paenibacillus prosopidis were detected in the soil treated with only chemical fertilizer. Except for the ammonium and pH, all the tested soil fertility parameters (total C, total N, nitrate, available K and available P) could significantly affect both the Paenibacillus spp. population number and diversity. The soil pH was significantly correlated with Paenibacillus spp. diversity only.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that the different long-term fertilization regimes have varied impact on both the Paenibacillus spp. population size and the diversity of the community associated with the soil properties tested. These results can help to enrich the information on the response of beneficial soil microbes to different long-term fertilization regimes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai C, Liang G, Sun J, Wang X, Zhou W (2012) Responses of extracellular enzyme activities and microbial community in both the rhizosphere and bulk soil to long-term fertilization practices in a fluvo-aquic soil. Geoderma 173–174:330–338
Anand R, Chanway CP (2013) nif gene sequence and arrangement in the endophytic diazotroph Paenibacillus polymyxa strain P2b-2R. Biol Fertil Soils 49:965–970
Anand R, Grayston S, Chanway C (2013) N-2-Fixation and seedling growth promotion of lodgepole pine by endophytic Paenibacillus polymyxa. Microb Ecol 66:369–374
Bååth E, Anderson TH (2003) Comparison of soil fungal/bacterial ratios in a pH gradient using physiological and PLFA-based techniques. Soil Biol Biochem 35:955–963
Bassam BJ, Caetano-Anolles G, Gresshoff PM (1991) Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 196:80–83
Blagodatskaya EV, Anderson T-H (1998) Interactive effects of pH and substrate quality on the fungal-to-bacterial ratio and qCO2 of microbial communities in forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1269–1274
Chen H-B, Kao P-M, Huang H-C, Shieh C-J, Chen C-I, Liu Y-C (2010) Effects of using various bioreactors on chitinolytic enzymes production by Paenibacillus taichungensis. Biochem Eng J 49:337–342
Coelho MR, Da Mota FF, Carneiro NP, Marriel IE, Paiva E, Rosado AS, Seldin L (2007) Diversity of Paenibacillus spp. in the rhizosphere of four sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) cultivars sown with two contrasting levels of nitrogen fertilizer assessed by rpoB-based PCR-DGGE and sequencing analysis. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:753–760
Coelho MR, Carneiro NP, Marriel IE, Seldin L (2009) Molecular detection of nifH gene-containing Paenibacillus in the rhizosphere of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) sown in Cerrado soil. Lett Appl Microbiol 48:611–617
da Mota FF, Gomes EA, Paiva E, Rosado AS, Seldin L (2004) Use of rpoB gene analysis for identification of nitrogen-fixing Paenibacillus species as an alternative to the 16S rRNA gene. Lett Appl Microbiol 39:34–40
da Mota FF, Gomes EA, Paiva E, Seldin L (2005) Assessment of the diversity of Paenibacillus species in environmental samples by a novel rpoB-based PCR-DGGE method. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 53:317–328
da Silva KR, Salles JF, Seldin L, van Elsas JD (2003) Application of a novel Paenibacillus-specific PCR-DGGE method and sequence analysis to assess the diversity of Paenibacillus spp. in the maize rhizosphere. J Microbiol Methods 54:213–231
Finnegan PM, Brumbley SM, O’Shea MG, Nevalainen KM, Bergquist PL (2004) Paenibacillus isolates possess diverse dextran-degrading enzymes. J Appl Microbiol 97:477–485
Guo T, Liao MD (2014) Suppression of Rhizoctonia solani and induction of host plant resistance by Paenibacillus kribbensis PS04 towards controlling of rice sheath blight. Biocontrol Sci Technol 24:116–121
Guo JH, Liu XJ, Zhang Y, Shen JL, Han WX, Zhang WF, Christie P, Goulding KW, Vitousek PM, Zhang FS (2010) Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 327:1008–1010
He J-Z, Zheng Y, Chen C-R, He Y-Q, Zhang L-M (2008) Microbial composition and diversity of an upland red soil under long-term fertilization treatments as revealed by culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches. J Soils Sediments 8:349–358
Jemli S, Ben Messaoud E, Ben Mabrouk S, Bejar S (2008) The cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase of Paenibacillus pabuli US132 strain: molecular characterization and overproduction of the recombinant enzyme. J Biomed Biotechnol 2008:692573
Juarez-Jimenez B, Rodelas B, Martinez-Toledo MV, Gonzalez-Lopez J, Crognale S, Gallo AM, Pesciaroli C, Fenice M (2008) Production of chitinolytic enzymes by a strain (BM17) of Paenibacillus pabuli isolated from crab shells samples collected in the east sector of central Tyrrhenian Sea. Int J Biol Macromol 43:27–31
Lauber CL, Hamady M, Knight R, Fierer N (2009) Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:5111–5120
Lee FL, Tien CJ, Tai CJ, Wang LT, Liu YC, Chern LL (2008) Paenibacillus taichungensis sp. nov., from soil in Taiwan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2640–2645
Ling N, Huang Q, Guo S, Shen Q (2011) Paenibacillus polymyxa SQR-21 systemically affects root exudates of watermelon to decrease the conidial germination of Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. niveum. Plant Soil 341:485–493
Ling N, Deng K, Song Y, Wu Y, Zhao J, Raza W, Huang Q, Shen Q (2013) Variation of rhizosphere bacterial community in watermelon continuous mono-cropping soil by long-term application of a novel bioorganic fertilizer. Microbiol Res. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2013.10.004
McSpadden Gardener BB (2004) Ecology of Bacillus and Paenibacillus spp. in agricultural systems. Phytopathology 94:1252–1258
Muyzer G, de Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nakhro N, Dkhar MS (2010) Impact of organic and inorganic fertilizers on microbial populations and biomass carbon in paddy field soil. J Agron 9:102–110
Park DJ, Lee YS, Choi YL (2013) Characterization of a cold-active beta-glucosidase from Paenibacillus xylanilyticus KJ-03 capable of hydrolyzing isoflavones daidzin and genistin. Protein J 32:579–584
Ranieri ML, Ivy RA, Mitchell WR, Call E, Masiello SN, Wiedmann M, Boor KJ (2012) Real-time PCR detection of Paenibacillus spp. in raw milk to predict shelf life performance of pasteurized fluid milk products. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:5855–5863
Rivas R, Mateos PF, Martinez-Molina E, Velazquez E (2005) Paenibacillus xylanilyticus sp. nov., an airborne xylanolytic bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:405–408
Rousk J, Baath E, Brookes PC, Lauber CL, Lozupone C, Caporaso JG, Knight R, Fierer N (2010) Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J 4:1340–1351
Shida O, Takagi H, Kadowaki K, Nakamura LK, Komagata K (1997) Transfer of Bacillus alginolyticus, Bacillus chondroitinus, Bacillus curdlanolyticus, Bacillus glucanolyticus, Bacillus kobensis, and Bacillus thiaminolyticus to the genus Paenibacillus and emended description of the genus Paenibacillus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:289–298
Valverde A, Peix A, Rivas R, Velazquez E, Salazar S, Santa-Regina I, Rodriguez-Barrueco C, Igual JM (2008) Paenibacillus castaneae sp. nov., isolated from the phyllosphere of Castanea sativa Miller. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2560–2564
Valverde A, Fterich A, Mahdhi M, Ramirez-Bahena MH, Caviedes MA, Mars M, Velazquez E, Rodriguez-Llorente ID (2010) Paenibacillus prosopidis sp. nov., isolated from the nodules of Prosopis farcta. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2182–2186
Ying J-Y, Zhang L-M, He J-Z (2010) Putative ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in an acidic red soil with different land utilization patterns. Environ Microbiol Rep 2:304–312
Yoon JH, Kang SJ, Yeo SH, Oh TK (2005) Paenibacillus alkaliterrae sp. nov., isolated from an alkaline soil in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2339–2344
Yu L, Nicolaisen M, Larsen J, Ravnskov S (2013) Organic fertilization alters the community composition of root associated fungi in Pisum sativum. Soil Biol Biochem 58:36–41
Zhang H, Wang B, Xu M (2008) Effects of inorganic fertilizer inputs on grain yields and soil properties in a long-term wheat-corn cropping system in south China. Commun Soil Sci Plan 39:1583–1599
Zhang W, Xu M, Wang B, Wang X (2009) Soil organic carbon, total nitrogen and grain yields under long-term fertilizations in the upland red soil of southern China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 84:59–69
Zhang Q, Tian M, Tang L, Li H, Li W, Zhang J, Zhang H, Mao Z (2013) Exploration of the key microbes involved in the cellulolytic activity of a microbial consortium by serial dilution. Bioresour Technol 132:395–400
Zhong WH, Cai ZC (2007) Long-term effects of inorganic fertilizers on microbial biomass and community functional diversity in a paddy soil derived from quaternary red clay. Appl Soil Ecol 36:84–91
Zhong W, Gu T, Wang W, Zhang B, Lin X, Huang Q, Shen W (2010) The effects of mineral fertilizer and organic manure on soil microbial community and diversity. Plant Soil 326:511–522
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (2013CB127403), by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (KYZ201307), by Agricultural Ministry of China (201103004) and by Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Jesus Mercado-Blanco.
Ning Ling and Dongsheng Wang contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, N., Wang, D., Zhu, C. et al. Response of the population size and community structure of Paenibacillus spp. to different fertilization regimes in a long-term experiment of red soil. Plant Soil 383, 87–98 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2146-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2146-1