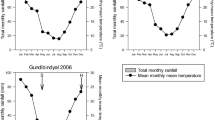
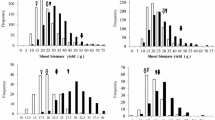
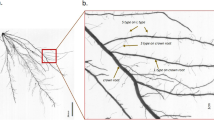
Abstract
Aims
In rice, seminal root elongation plays an important role in acquisition of nutrients such as N and P, but the extent to which different N forms and P concentrations affect root growth is poorly understood. This study aimed to examine N- and P-mediated seminal root elongation response and to identify putative QTLs associated with seminal root elongation.
Methods
Seminal root elongation was evaluated in 15 diverse wild and cultivated accessions of rice, along with 48 chromosome segment substitution lines (CSSLs) derived from a cross between the rice variety ‘Curinga’ and Oryza rufipogon (IRGC 105491). Root elongation in response to different forms of N (NH4 +, NO3 − and NH4NO3) and concentrations of P was evaluated under hydroponic conditions, and associated putative QTL regions were identified.
Results
The CSSL parents had contrasting root responses to N and P. Root elongation in O. rufipogon was insensitive to N source and concentration, whereas Curinga was responsive. In contrast to N, seminal root elongation and P concentration was positively correlated. Three putative QTLs for seminal root elongation in response to N were detected on chromosome 1, and one QTL on chromosome 3 was associated with low P concentration.
Conclusions
Genetic variation in seminal root elongation and plasticity of nutrient response may be appropriate targets for marker-assisted selection to improve rice nutrient acquisition efficiency.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CSSL:
-
Chromosome segment substitution line
- N:
-
Nitrogen
- NAE:
-
Nitrogen acquisition efficiency
- P:
-
Phosphorus
- PNN:
-
Partial nitrate nutrition
- PAE:
-
Phosphorus acquisition efficiency
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
References
Abdul Rahman Z, Musa MH (2009) Upland rice root characteristics and their relationship to nitrogen uptake. Pertanika J Trop Agric Sci 32:261–266
Balkos KD, Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ (2010) Optimization of ammonium acquisition and metabolism by potassium in rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. IR-72). Plant Cell Environ 33:23–34
Bates TR, Lynch JP (1996) Stimulation of root hair elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana by low phosphorus availability. Plant Cell Environ 19:529–538
Bloom AJ, Frensch J, Taylor AR (2006) Influence of inorganic nitrogen and pH on the elongation of maize seminal roots. Ann Bot 97:867–873
Brar DS, Khush GS (1997) Alien introgression in rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:35–47
Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ (2002) NH4 + toxicity in higher plants: a critical review. J Plant Physiol 159:567–584
Champoux MC, Wang G, Sarkarung S, Mackill DJ, O’Toole JC, Huang N, McCouch SR (1995) Locating genes associated with root morphology and drought avoidance in rice via linkage to molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 90:969–981
Chen G, Guo S, Kronzucker HJ, Shi W (2013) Nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) in rice links to NH4 + toxicity and futile NH4 + cycling in roots. Plant Soil 369:351–363
Chin JH, Lu X, Haefele SM, Gamuyao R, Ismail A, Wissuwa M, Heuer S (2010) Development and application of gene-based markers for the major rice QTL Phosphorus uptake 1. Theor Appl Genet 120:1073–1086
Da Silva AA, Delatorre CA (2009) Alterações na arquitetura de raiz em resposta à disponibilidade de fósforo e nitrogênio. Rev Ciênc Agrov 8:152–163
De la Torre F, De Santis L, Suárez MF, Crespillo R, Canovás FM (2006) Identification and functional analysis of a prokaryotic-type aspartate aminotransferase: implications for plant amino acid metabolism. Plant J 46:414–425
Duan YH, Zhang YL, Shen QR, Wang SW (2006) Nitrate effect on rice growth and nitrogen absorption and assimilation at different growth stages. Pedosphere 16:707–717
Falkengren-Grerup U (1995) Interspecies differences in the preference of ammonium and nitrate in vascular plants. Oecologia 102:305–311
Famoso AN, Clark RT, Shaff JE, Craft E, McCouch SR, Kochian LV (2010) Development of a novel aluminum tolerance phenotyping platform used for comparisons of cereal aluminum tolerance and investigations into rice aluminum tolerance mechanisms. Plant Physiol 153:1678–1691
Fu Q, Zhang P, Tan L, Zhu Z, Ma D, Fu Y, Zhan X, Cai H, Sun C (2010) Analysis of QTLs for yield-related traits in Yuanjiang common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). J Genet Genome 37:147–157
Gastal F, Lemaire G (2002) N uptake and distribution in crops: an agronomical and ecophysiological perspective. J Exp Bot 53:789–799
Gerendas J, Zhu Z, Bendixen R, Ratcliffe RG, Sattelmacher B (1997) Physiological and biochemical processes related to ammonium toxicity in higher plants. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 160:239–251
Hamada A, Nitta M, Nasuda S, Kato K, Fujita M, Matsunaka H, Okumoto Y (2011) Novel QTLs for growth angle of seminal roots in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Soil 354:395–405
Imai I, Kimball JA, Conway B, Yeater KM, McCouch S, McClung A (2013) Validation of yield-enhancing QTLs from a low-yielding wild ancestor of rice. Mol Breed 32:101120
Jones MP, Dingkuhn M, Aluko GK, Semon M (1997) Interspecific Oryza sativa L. × O. glaberrima Steud. progenies in upland rice improvement. Euphytica 92:237–246
Kirk GJD, Du LV (1997) Changes in rice root architecture, porosity, and oxygen and proton release under phosphorus deficiency. New Phytol 135:191–200
Kronzucker HJ, Siddiqi MY, Glass ADM, Kirk GJD (1999) Nitrate–ammonium synergism in rice: a subcellular flux analysis. Plant Physiol 119:1041–1045
Lian X, Xing Y, Yan H, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2005) QTLs for low nitrogen tolerance at seedling stage identified using a recombinant inbred line population derived from an elite rice hybrid. Theor Appl Genet 112:85–96
Linkohr BI, Williamson LC, Fitter AH, Leyser HMO (2002) Nitrate and phosphate availability and distribution have different effects on root system architecture of Arabidopsis. Plant J 29:751–760
Lorieux M (2005) CSSL finder: a free program for managing introgression lines. http://mapdisto.free.fr/
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic, London
Nguyen TV, Pham LN, Nguyen HT (2002) Identification and mapping of the QTL for aluminum tolerance introgressed from the new source, Oryza rufipogon Griff., into indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 106:583–593
Obara M, Tamura W, Ebitani T, Yano M, Sato T, Yamaya T (2010) Fine-mapping of qRL6.1, a major QTL for root length of rice seedlings grown under a wide range of NH4 + concentrations in hydroponic conditions. Theor Appl Genet 121:535–547
Obara M, Takeda T, Hayakawa T, Yamaya T (2011) Mapping quantitative trait loci controlling root length in rice seedlings grown with low or sufficient supply using backcross recombinant lines derived from a cross between Oryza sativa L. and Oryza glaberrima Steud. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 57:80–92
Price AH, Tomos AD (1997) Genetic dissection of root growth in rice (Oryza sativa L.) II: mapping quantitative trait loci using molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 95:143–152
Price AH, Tomos AD, Virk DS (1997) Genetic dissection of root growth in rice (Oryza sativa L.) I: a hydrophonic screen. Theor Appl Genet 95:132–142
Rauh BL, Basten C, Buckler ES IV (2002) Quantitative trait loci analysis of growth response to varying nitrogen sources in Arabidopsis thaliana. Theor Appl Genet 104:743–750
Redoña ED, Mackill DJ (1996) Mapping quantitative trait loci for seedling vigor in rice using RFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 92:395–402
Roosta HR, Schjoerring JK (2008) Root carbon enrichment alleviates ammonium toxicity in cucumber plants. J Plant Nutr 31:941–958
Rorison IH (1985) Nitrogen source and the tolerance of Deschampsia flexuosa, Holcus lanatus and Bromus erectus to aluminium during seedling growth. J Ecol 73:83–90
Rubio V, Linhares F, Solano R, Martin AC, Iglesias J, Leyva A, Paz-Ares J (2001) A conserved MYB transcription factor involved in phosphate starvation signaling both in vascular plants and unicellular algae. Genes Dev 15:2122–2133
Sakai T, Duque MC, Cabrera FA, Martínez PC, Ishitani M (2010) Establishment of drought screening protocols for rice under field conditions. Acta Agron 59:338–346
Shimizu A, Yanagihara S, Kawasaki S, Ikehashi H (2004) Phosphorus deficiency-induced root elongation and its QTL in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:1361–1368
Song J, Yamamoto K, Shomura A, Yano M, Minobe Y, Sasaki T (1996) Characterization and mapping of cDNA encoding aspartate aminotransferase in rice, Oryza sativa L. DNA Res 3:303–310
Song W, Makeen K, Wang D, Zhang C, Xu Y, Zhao H, Tu E, Zhang Y, Shen Q, Xu G (2011) Nitrate supply affects root growth differentially in two rice cultivars differing in nitrogen use efficiency. Plant Soil 343:357–368
Subbarao GV, Ishikawa T, Ito OA, Nakahara K, Wang HY, Berry WL (2006) A bioluminescence assay to detect nitrification inhibitors released from plant roots: a case study with Brachiaria humidicola. Plant Soil 288:101–112
Suenaga A, Moriya K, Sonoda Y, Ikeda A, Von Wiren N, Hayakawa T, Yamaguchi J, Yamaya T (2003) Constitutive expression of a novel-type ammonium transporter OsAMT2 in rice plants. Plant Cell Physiol 44:206–211
Tanaka S, Yamauchi A, Kono Y (1993) Response of the seminal root elongation to NH4 + nitrogen in several rice (Oryza sativa) cultivars. Jpn J Crop Sci 62:288–293
Thomson MJ, Tai TH, McClung AM, Lai XH, Hinga ME, Lobos KB, Xu Y, Martinez CP, McCouch SR (2003) Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield, yield components and morphological traits in an advanced backcross population between Oryza rufipogon and the Oryza sativa cultivar Jefferson. Theor Appl Genet 107:479–493
Thomson MJ, Zhao K, Wright M, McNally KL, Rey J, Tung CW, Reynolds A, Scheffler B, Eizeng G, McClung A, Kim H, Ismail AM, Ocampo M, Mojica C, Reveche MY, Dilla-Ermita JC, Mauleon R, Leung H, Bustamante C, McCouch S (2012) High-throughput single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping for breeding applications in rice using the BeadXpress platform. Mol Breed 29:875–886
Tuberosa R, Sanguineti MC, Landi P, Giuliani MM, Salvi S, Conti S (2002) Identification of QTLs for root characteristics in maize grown in hydroponics and analysis of their overlap with QTLs for grain yield in the field at two water regimes. Plant Mol Biol 48:697–712
Vinod KK, Heuer S (2012) Approaches towards nitrogen- and phosphorus-efficient rice. AoB Plants. doi:10.1093/aobpla/pls028
Wang MY, Siddeqi MY, Ruth TJ, Glass ADM (1993) Ammonium uptake by rice roots. I. Kinetics of 13NH4 + influx across the plasmalemma. Plant Physiol 103:1259–1267
Williamson LC, Ribrioux SP, Fitter AH, Leyser HM (2001) Phosphate availability regulates root system architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126:875–882
Wissuwa M, Yano M, Ae N (1998) Mapping of QTLs for phosphorus-deficiency tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 97:777–783
Wojciechowski T, Gooding MJ, Ramsay L, Gregory PJ (2009) The effects of dwarfing genes on seedling root growth of wheat. J Exp Bot 60:2565–2573
Wu P, Liao CY, Hu B, Yi KK, Jin WZ, Ni JJ, He C (2000) QTLs and epistasis for aluminum tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) at different seedling stages. Theor Appl Genet 100:1295–1303
Xu CG, Li XQ, Xue Y, Huang YW, Gao J, Xing YZ (2004) Comparison of quantitative trait loci controlling seedling characteristics at two seedling stages using rice recombinant inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 109:640–647
Yadav R, Courtois B, Huang N, McLaren G (1997) Mapping genes controlling root morphology and root distribution in a doubled-haploid population of rice. Theor Appl Genet 94:619–632
Yeo ME, Yeo AR, Flowers TJ (1994) Photosynthesis and photorespiration in the genus Oryza. J Exp Bot 45:553–560
Zhang H, Rong H, Pilbeam D (2007) Signalling mechanisms underlying the morphological responses of the root system to nitrogen in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 58:2329–2338
Zhao XQ, Guo SW, Shinmachi F, Sunairi M, Noguchi A, Hasegawa I, Shen RF (2012) Aluminium tolerance in rice is antagonistic with nitrate preference and synergistic with ammonium preference. Ann Bot 111:69–77
Zhu J, Mickelson SM, Kaeppler SM, Lynch JP (2006) Detection of quantitative trait loci for seminal root traits in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings grown under differential phosphorus levels. Theor Appl Genet 113:1–10
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Edgar Torres (CIAT, Colombia) and Dr. Uga Y (National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, Japan) for providing the seed materials used this study, and Dr. Joe Tohme, CIAT Agrobiodiversity Research Area Director, for his continuous support. We also thank Dr. T. Ramasubramanian (Sugarcane Breeding Institute, Indian Council of Agricultural Research, Tamil Nadu, India) for his critical evaluation of the manuscript, and are grateful for the assistance of Lucia Chavez and Milton Valencia.
This work was supported by Ministry of foreign Affairs of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Herbert J. Kronzucker.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 375 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogawa, S., Selvaraj, M.G., Fernando, A.J. et al. N- and P-mediated seminal root elongation response in rice seedlings. Plant Soil 375, 303–315 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1955-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1955-y