Abstract
Purpose
The invention and application of new immunotherapeutic methods can compensate for the inefficiency of conventional cancer treatment approaches, partly due to the inhibitory microenvironment of the tumor. In this study, we tried to inhibit the growth of cancer cells and induce anti-tumor immune responses by silencing the expression of the β-catenin in the tumor microenvironment and transmitting interleukin (IL)-15 cytokine to provide optimal conditions for the dendritic cell (DC) vaccine.
Methods
For this purpose, we used folic acid (FA)-conjugated SPION-carboxymethyl dextran (CMD) chitosan (C) nanoparticles (NPs) to deliver anti-β-catenin siRNA and IL-15 to cancer cells.
Results
The results showed that the codelivery of β-catenin siRNA and IL-15 significantly reduced the growth of cancer cells and increased the immune response. The treatment also considerably stimulated the performance of the DC vaccine in triggering anti-tumor immunity, which inhibited tumor development and increased survival in mice in two different cancer models.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that the use of new nanocarriers such as SPION-C-CMD-FA could be an effective way to use as a novel combination therapy consisting of β-catenin siRNA, IL-15, and DC vaccine to treat cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Change history
07 December 2022
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03456-y
References
Takebe N, Miele L, Harris PJ, Jeong W, Bando H, Kahn M, Yang SX, Ivy SP. Targeting notch, hedgehog, and Wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: clinical update. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015;12(8):445–64.
Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2012;490(7418):61–70.
Hajizadeh F, Okoye I, Esmaily M, Ghasemi Chaleshtari M, Masjedi A, Azizi G, Irandoust M, Ghalamfarsa G, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Hypoxia inducible factors in the tumor microenvironment as therapeutic targets of cancer stem cells. Life Sci. 2019;237:116952.
Ganesh S, Shui X, Craig KP, Park J, Wang W, Brown BD, Abrams MT. RNAi-mediated β-catenin inhibition promotes T cell infiltration and antitumor activity in combination with immune checkpoint blockade. Mol Ther. 2018;26(11):2567–79.
Verma UN, Surabhi RM, Schmaltieg A, Becerra C, Gaynor RB. Small interfering RNAs directed against β-catenin inhibit the in vitro and in vivo growth of colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(4):1291–300.
Lyou Y, Habowski AN, Chen GT, Waterman ML. Inhibition of nuclear Wnt signalling: challenges of an elusive target for cancer therapy. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(24):4589–99.
Vasir JK, Labhasetwar V. Targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2005;4(4):363–74.
Baudino TA. Targeted cancer therapy: the next generation of cancer treatment. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2015;12(1):3–20.
K.C. RB, Thapa B, Valencia-Serna J, Aliabadi HM, Uludağ H. Nucleic acid combinations: a new frontier for cancer treatment. J Control Release. 2017;256:153–69.
Li J, Wang Y, Zhu Y, Oupický D. Recent advances in delivery of drug–nucleic acid combinations for cancer treatment. J Control Release. 2013;172(2):589–600.
Xu C-F, Wang J. Delivery systems for siRNA drug development in cancer therapy. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2015;10(1):1–12.
Joshi N, Hajizadeh F, Ansari Dezfouli E, Zekiy AO, Nabi Afjadi M, Mousavi SM, Hojjat-Farsangi M, Karpisheh V, Mahmoodpoor A, Hassannia H, Dolati S, Mohammadi H, Yousefi M, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Silencing STAT3 enhances sensitivity of cancer cells to doxorubicin and inhibits tumor progression. Life Sci. 2021;275:119369.
Allahyari SE, Hajizadeh F, Zekiy AO, Mansouri N, Gilan PS, Mousavi SM, Masjedi A, Hassannia H, Ahmadi M, Mohammadi H, Yousefi M, Izadi S, Zolbanin NM, Jafari R, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Simultaneous inhibition of CD73 and IL-6 molecules by siRNA-loaded nanoparticles prevents the growth and spread of cancer. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine. 2021;34:102384.
Budi HS, Izadi S, Timoshin A, Asl SH, Beyzai B, Ghaderpour A, Alian F, Eshaghi FS, Mousavi SM, Rafiee B, Nikkhoo A, Ahmadi A, Hassannia H, Ahmadi M, Sojoodi M, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Blockade of HIF-1α and STAT3 by hyaluronate-conjugated TAT-chitosan-SPION nanoparticles loaded with siRNA molecules prevents tumor growth. Nanomed: Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2021;34:102373.
Ma H, Liu Y, Shi M, Shao X, Zhong W, Liao W, Xing MMQ. Theranostic, pH-responsive, doxorubicin-loaded nanoparticles inducing active targeting and apoptosis for advanced gastric cancer. Biomacromolecules. 2015;16(12):4022–31.
Salimi M, Sarkar S, Hashemi M, Saber R. Treatment of Breast Cancer-Bearing BALB/c Mice with Magnetic Hyperthermia using Dendrimer Functionalized Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(11).
Luo X, Peng X, Hou J, Wu S, Shen J, Wang L. Folic acid-functionalized polyethylenimine superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as theranostic agents for magnetic resonance imaging and PD-L1 siRNA delivery for gastric cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:5331–43.
Kamalzare S, Noormohammadi Z, Rahimi P, Atyabi F, Irani S, Tekie FSM, Mottaghitalab F. Carboxymethyl dextran-trimethyl chitosan coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: an effective siRNA delivery system for HIV-1 Nef. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(11):20554–65.
Palucka K, Banchereau J. Cancer immunotherapy via dendritic cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(4):265–77.
Anguille S, Lion E, van den Bergh J, van Acker HH, Willemen Y, Smits EL, van Tendeloo VF, Berneman ZN. Interleukin-15 dendritic cells as vaccine candidates for cancer immunotherapy. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013;9(9):1956–61.
Waldmann TA. The shared and contrasting roles of IL2 and IL15 in the life and death of normal and neoplastic lymphocytes: implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015;3(3):219–27.
Ranson T, Vosshenrich CAJ, Corcuff E, Richard O, Müller W, di Santo JP. IL-15 is an essential mediator of peripheral NK-cell homeostasis. Blood. 2003;101(12):4887–93.
Islam MS, Haque P, Rashid TU, Khan MN, Mallik AK, Khan MNI, Khan M, Rahman MM. Core–shell drug carrier from folate conjugated chitosan obtained from prawn shell for targeted doxorubicin delivery. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28(4):55.
Alzamely KO, et al. Combined inhibition of CD73 and ZEB1 by Arg-Gly-asp (RGD)-targeted nanoparticles inhibits tumor growth. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2020;197:111421.
Karpisheh V, Fakkari Afjadi J, Nabi Afjadi M, Haeri MS, Abdpoor Sough TS, Heydarzadeh Asl S, Edalati M, Atyabi F, Masjedi A, Hajizadeh F, Izadi S, Mirzazadeh Tekie FS, Hajiramezanali M, Sojoodi M, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Inhibition of HIF-1α/EP4 axis by hyaluronate-trimethyl chitosan-SPION nanoparticles markedly suppresses the growth and development of cancer cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;167:1006–19.
Izadi S, Moslehi A, Kheiry H, Karoon Kiani F, Ahmadi A, Masjedi A, Ghani S, Rafiee B, Karpisheh V, Hajizadeh F, Atyabi F, Assali A, Mirzazadeh tekie FS, Namdar A, Ghalamfarsa G, Sojoodi M, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Codelivery of HIF-1α siRNA and dinaciclib by carboxylated graphene oxide-trimethyl chitosan-hyaluronate nanoparticles significantly suppresses cancer cell progression. Pharm Res. 2020;37(10):1–20.
Hallaj S, Heydarzadeh Asl S, Alian F, Farshid S, Eshaghi FS, Namdar A, Atyabi F, Masjedi A, Hallaj T, Ghorbani A, Ghalamfarsa G, Sojoodi M, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Inhibition of CD73 using folate targeted nanoparticles carrying anti-CD73 siRNA potentiates anticancer efficacy of Dinaciclib. Life Sci. 2020;259:118150.
Bastaki S, Aravindhan S, Ahmadpour Saheb N, Afsari Kashani M, Evgenievich Dorofeev A, Karoon Kiani F, Jahandideh H, Beigi Dargani F, Aksoun M, Nikkhoo A, Masjedi A, Mahmoodpoor A, Ahmadi M, Dolati S, Namvar Aghdash S, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Codelivery of STAT3 and PD-L1 siRNA by hyaluronate-TAT trimethyl/thiolated chitosan nanoparticles suppresses cancer progression in tumor-bearing mice. Life Sci. 2020;266:118847.
Ghalamfarsa G, Rastegari A, Atyabi F, Hassannia H, Hojjat-Farsangi M, Ghanbari A, Anvari E, Mohammadi J, Azizi G, Masjedi A, Yousefi M, Yousefi B, Hadjati J, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Anti-angiogenic effects of CD73-specific siRNA-loaded nanoparticles in breast cancer-bearing mice. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(10):7165–77.
Masjedi A, Ahmadi A, Ghani S, Malakotikhah F, Nabi Afjadi M, Irandoust M, Karoon Kiani F, Heydarzadeh Asl S, Atyabi F, Hassannia H, Hojjat-Farsangi M, Namdar A, Ghalamfarsa G, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Silencing adenosine A2a receptor enhances dendritic cell-based cancer immunotherapy. Nanomed: Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2020;29:102240.
Jadidi-Niaragh F, Atyabi F, Rastegari A, Kheshtchin N, Arab S, Hassannia H, Ajami M, Mirsanei Z, Habibi S, Masoumi F, Noorbakhsh F, Shokri F, Hadjati J. CD73 specific siRNA loaded chitosan lactate nanoparticles potentiate the antitumor effect of a dendritic cell vaccine in 4T1 breast cancer bearing mice. J Control Release. 2017;246:46–59.
Juliá EP, Mordoh J, Levy EM. Cetuximab and IL-15 promote NK and dendritic cell activation in vitro in triple negative breast Cancer. Cells. 2020;9(7):1573.
Ochoa MC, Fioravanti J, Rodriguez I, Hervas-Stubbs S, Azpilikueta A, Mazzolini G, Gúrpide A, Prieto J, Pardo J, Berraondo P, Melero I. Antitumor immunotherapeutic and toxic properties of an HDL-conjugated chimeric IL-15 fusion protein. Cancer Res. 2013;73(1):139–49.
Kishida T, Asada H, Itokawa Y, Cui FD, Shin-Ya M, Gojo S, Yasutomi K, Ueda Y, Yamagishi H, Imanishi J, Mazda O. Interleukin (IL)-21 and IL-15 genetic transfer synergistically augments therapeutic antitumor immunity and promotes regression of metastatic lymphoma. Mol Ther. 2003;8(4):552–8.
Waldmann TA, Dubois S, Miljkovic MD, Conlon KC. IL-15 in the combination immunotherapy of Cancer. Front Immunol. 2020;11.
Jadidi-Niaragh F, Mirshafiey A. Regulatory T-cell as orchestra leader in immunosuppression process of multiple sclerosis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2011;33(3):545–67.
Hajizadeh F, Moghadaszadeh Ardebili S, Baghi Moornani M, Masjedi A, Atyabi F, Kiani M, Namdar A, Karpisheh V, Izadi S, Baradaran B, Azizi G, Ghalamfarsa G, Sabz G, Yousefi M, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Silencing of HIF-1α/CD73 axis by siRNA-loaded TAT-chitosan-spion nanoparticles robustly blocks cancer cell progression. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;882:173235.
Izadi S, Moslehi A, Kheiry H, Karoon Kiani F, Ahmadi A, Masjedi A, Ghani S, Rafiee B, Karpisheh V, Hajizadeh F, Atyabi F, Assali A, Mirzazadeh tekie FS, Namdar A, Ghalamfarsa G, Sojoodi M, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Codelivery of HIF-1α siRNA and Dinaciclib by Carboxylated graphene oxide-Trimethyl chitosan-hyaluronate nanoparticles significantly suppresses Cancer cell progression. Pharm Res. 2020;37(10):196.
Karpisheh V, Fakkari Afjadi J, Nabi Afjadi M, Haeri MS, Abdpoor Sough TS, Heydarzadeh Asl S, Edalati M, Atyabi F, Masjedi A, Hajizadeh F, Izadi S, Mirzazadeh Tekie FS, Hajiramezanali M, Sojoodi M, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Inhibition of HIF-1α/EP4 axis by hyaluronate-trimethyl chitosan-SPION nanoparticles markedly suppresses the growth and development of cancer cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;167:1006–19.
Yoo HS, Park TG. Folate receptor targeted biodegradable polymeric doxorubicin micelles. J Control Release. 2004;96(2):273–83.
Zhang D, Fei F, Li S, Zhao Y, Yang Z, Qu J, Zhang X, Yin Y, Zhang S. The role of β-catenin in the initiation and metastasis of TA2 mice spontaneous breast cancer. J Cancer. 2017;8(11):2114–23.
Singh N, Jenkins GJS, Asadi R, Doak SH. Potential toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION). Nano Rev. 2010;1(1):5358.
Lapham A, Adams JE, Paterson A, Lee M, Brimmell M, Packham G. The Bcl-w promoter is activated by β-catenin/TCF4 in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Gene. 2009;432(1–2):112–7.
Sinnberg T, Menzel M, Ewerth D, Sauer B, Schwarz M, Schaller M, Garbe C, Schittek B. β-Catenin signaling increases during melanoma progression and promotes tumor cell survival and chemoresistance. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23429.
Santana Carrero RM, Beceren-Braun F, Rivas SC, Hegde SM, Gangadharan A, Plote D, Pham G, Anthony SM, Schluns KS. IL-15 is a component of the inflammatory milieu in the tumor microenvironment promoting antitumor responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2019;116(2):599–608.
Hassannia H, Ghasemi Chaleshtari M, Atyabi F, Nosouhian M, Masjedi A, Hojjat-Farsangi M, Namdar A, Azizi G, Mohammadi H, Ghalamfarsa G, Sabz G, Hasanzadeh S, Yousefi M, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Blockage of immune checkpoint molecules increases T-cell priming potential of dendritic cell vaccine. Immunology. 2020;159(1):75–87.
Esmaily M, Masjedi A, Hallaj S, Nabi Afjadi M, Malakotikhah F, Ghani S, Ahmadi A, Sojoodi M, Hassannia H, Atyabi F, Namdar A, Azizi G, Ghalamfarsa G, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Blockade of CTLA-4 increases anti-tumor response inducing potential of dendritic cell vaccine. J Control Release. 2020;326:63–74.
Marrero B, Shirley S, Heller R. Delivery of interleukin-15 to B16 melanoma by electroporation leads to tumor regression and long-term survival. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2014;13(6):551–60.
Takahashi Y, Nishikawa M, Takakura Y. Suppression of tumor growth by intratumoral injection of short hairpin RNA-expressing plasmid DNA targeting β-catenin or hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. J Control Release. 2006;116(1):90–5.
Arozarena I, Bischof H, Gilby D, Belloni B, Dummer R, Wellbrock C. In melanoma, beta-catenin is a suppressor of invasion. Oncogene. 2011;30(45):4531–43.
Yaguchi T, Goto Y, Kido K, Mochimaru H, Sakurai T, Tsukamoto N, Kudo-Saito C, Fujita T, Sumimoto H, Kawakami Y. Immune suppression and resistance mediated by constitutive activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in human melanoma cells. J Immunol. 2012;189(5):2110–7.
Yazdani Y, Mohammadnia-Afrouzi M, Yousefi M, Anvari E, Ghalamfarsa G, Hasannia H, Sadreddini S, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in B cell malignancies. Tumor Biol. 2015;36(10):7339–53.
Spranger S, Bao R, Gajewski TF. Melanoma-intrinsic β-catenin signalling prevents anti-tumour immunity. Nature. 2015;523(7559):231–5.
Tang F, Zhao L, Jiang Y, Ba D, Cui L, He W. Activity of recombinant human interleukin-15 against tumor recurrence and metastasis in mice. Cell Mol Immunol. 2008;5(3):189–96.
Dubsky P, Saito H, Leogier M, Dantin C, Connolly J E, Banchereau J, Palucka A K. IL-15-induced human DC efficiently prime melanoma-specific naive CD8+ T cells to differentiate into CTL. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37(6):1678–90.
Ji L, Qian W, Gui L, Ji Z, Yin P, Lin GN, Wang Y, Ma B, Gao WQ. Blockade of β-catenin–induced CCL28 suppresses gastric Cancer progression via inhibition of Treg cell infiltration. Cancer Res. 2020;80(10):2004–16.
Feng M, Jin JQ, Xia L, Xiao T, Mei S, Wang X, Huang X, Chen J, Liu M, Chen C, Rafi S, Zhu AX, Feng YX, Zhu D. Pharmacological inhibition of β-catenin/BCL9 interaction overcomes resistance to immune checkpoint blockades by modulating Treg cells. Sci Adv. 2019;5(5):eaau5240.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Armin Mahmoud Salehi Kheshti: Conceptualization; Methodology; Data curation; Writing – review & editing. Farnaz Hajizadeh:Writing Original draft, Conceptualization; Methodology. Asal Barshidi: Methodology. Bentolhoda Rashidi: Methodology; Data curation. Farbod Ebrahimi: Methodology. Simin Bahmanpour: review & editing. Vahid Karpisheh: Methodology; Formal analysis. Fatemeh Karimian Noukabadi: review & editing. Fariba Karoon Kiani: review & editing. Hadi Hassannia: Methodology. Fatemeh Atyabi: Methodology. Seyed Hossein Kiaie: Methodology; Data curation. Fatah Kashanchi: review & editing. Jamshid Gholizadeh Navashenaq: review & editing. Hamed Mohammadi: review & editing. Rafieh Bagherifar: review & editing. Reza Jafari: Methodology; Data curation. Naime Majidi Zolbanin: Conceptualization; Supervision; Writing–review &; editing; Correspondence. Farhad Jadidi-Niaragh: Conceptualization; Supervision; Writing–review & editing; Correspondence; Project administration.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Figure S1
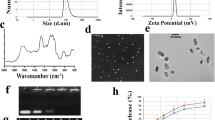
Validation of FA-C-CMD-SPION NPs. While the NPs were about 161 nm in size with a PDI of about 0.37 (a), they showed a zeta potential of about 9.2 mV (b). FTIR spectra demonstrate the proper formation of NPs (c). NPs had a regular spherical shape as investigated by SEM microscopy (d). TEM(e). NPs (1 ml at a concentration of 5 mg /ml) showed a high capacity to contain siRNA molecules so that they could load up to 20 μg of siRNA (Lane 1: naked siRNA, Lane 2: 5 μg, Lane 3: 10 μg, Lane 4: 15 μg, Lane 5: 20 μg of siRNA) (f). Evaluation of the stability of NPs in the serum environment showed their high ability to preserve the loaded contents (g). The release pattern of siRNA and IL-15 cytokine from NPs at two different pH values was investigated by spectroscopy and BCA protein measurement kit, respectively (h). (Folate–chitosan conjugate and carboxymethyl dextran (CMD) coated the SPIONs core). (JPG 2114 kb)
ESM 1
(JPG 8169 kb)
ESM 2
(JPG 924 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kheshti, A.M.S., Hajizadeh, F., Barshidi, A. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Combination Cancer Immunotherapy with Dendritic Cell Vaccine and Nanoparticles Loaded with Interleukin-15 and Anti-beta-catenin siRNA Significantly Inhibits Cancer Growth and Induces Anti-Tumor Immune Response. Pharm Res 39, 353–367 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03169-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-022-03169-2