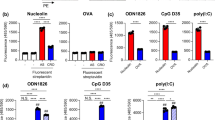
Abstract
Purpose
Cationized gelatin nanoparticles (GNPs) were used as carrier to improve delivery of immunostimulatory CpG oligonucleotides (CpG ODN) both in vitro and in vivo.
Methods
Uptake of CpG ODN-loaded cationized gelatin nanoparticles (CpG-GNPs) into murine myeloid dendritic cells (DCs) and their respective immunostimulatory activity was monitored. In vivo, induction of cytokine secretion by CpG-GNPs was measured. For experiments on primary human cells, prototypes of the three CpG ODN classes were adsorbed onto GNPs. Uptake and induction of proinflammatory cytokines were assessed in human plasmacytoid DCs and B cells, the only existing human target cells for CpG ODN.
Results
In the murine system, gelatin nanoparticle formulations enhanced the uptake and immunostimulatory activity of CpG ODN both in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, delivery by cationized gelatin nanoparticles of CpG ODN of the classes B and C to primary human plasmacytoid DCs increased production of IFN-α, a key cytokine in the driving of both the innate and adaptive immune responses.
Conclusion
GNPs can be used as a biodegradable and well tolerated carrier to deliver CpG ODN to their target cells and strongly increase activation of the immune system. This concept may be applied as novel adjuvant for antiviral and antitumoral vaccines.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. M. Krieg. Therapeutic potential of Toll-like receptor 9 activation. Nat. Rev., Drug Discov. 5(6):471–484 (2006).
M. Diwan, M. Tafaghodi, and J. Samuel. Enhancement of immune responses by co-delivery of a CpG oligodeoxynucleotide and tetanus toxoid in biodegradable nanospheres. J. Control. Release 85(1–3):247–262 (2002).
M. Diwan, P. Elamanchili, M. Cao, and J. Samuel. Dose sparing of CpG oligodeoxynucleotide vaccine adjuvants by nanoparticle delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 1(4):405–412 (2004).
S. Jain, W. T. Yap, and D. J. Irvine. Synthesis of protein-loaded hydrogel particles in an aqueous two-phase system for coincident antigen and CpG oligonucleotide delivery to antigen-presenting cells. Biomacromolecules 6(5):2590–2600 (2005).
Y. J. Kwon, S. M. Standley, S. L. Goh, and J. M. J. Frechet. Enhanced antigen presentation and immunostimulation of dendritic cells using acid-degradable cationic nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 105(3):199–212(2005).
M. Singh, G. Ott, J. Kazzaz, M. Ugozzoli, M. Briones, J. Donnelly, and D. T. O’Hagan. Cationic microparticles are an effective delivery system for immune stimulatory CpG DNA. Pharm. Res. 18(10):1476–1479 (2001).
Y. Suzuki, D. Wakita, K. Chamoto, Y. Narita, T. Tsuji, T. Takeshima, H. Gyobu, Y. Kawarada, S. Kondo, S. Akira, H. Katoh, H. Ikeda, and T. Nishimura. Liposome-encapsulated CpG oligodeoxynucleotides as a potent adjuvant for inducing type 1 innate immunity. Cancer Res. 64(23):8754–8760 (2004).
A. Joseph, I. Louria-Hayon, A. Plis-Finarov, E. Zeira, Z. Zakay-Rones, E. Raz, T. Hayashi, K. Takabayashi, Y. Barenholz, and E. Kedar. Liposomal immunostimulatory DNA sequence (ISS-ODN): an efficient parenteral and mucosal adjuvant for influenza and hepatitis B vaccines. Vaccine 20(27–28):3342–3354 (2002).
R. Rankin, R. Pontarollo, X. Ioannou, A. M. Krieg, R. Hecker, L. A. Babiuk, and Littel-van den Hurk van Drunen, S. CpG motif identification for veterinary and laboratory species demonstrates that sequence recognition is highly conserved. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 11(5):333–340 (2001).
G. Hartmann, and A. M. Krieg. Mechanism and function of a newly identified CpG DNA motif in human primary B cells. J. Immunol. 164(2):944–953 (2000).
S. Rothenfusser, E. Tuma, S. Endres, and G. Hartmann. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells: the key to CpG. Hum. Immunol. 63(12):1111–1119 (2002).
G. Hartmann, J. Battiany, H. Poeck, M. Wagner, M. Kerkmann, N. Lubenow, S. Rothenfusser, and S. Endres. Rational design of new CpG oligonucleotides that combine B cell activation with high IFN-α induction in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 33(6):1633–1641 (2003).
A. G. Ward, and A. Courts. The Science and Technology of Gelatin. Academic Press, New York, 1977.
H. G. Schwick, and K. Heide. Immunochemistry and immunology of collagen and gelatin. Bibl. Haematol. 33:111–125 (1969).
C. Coester, H. von Briesen, K. Langer, and J. Kreuter. Gelatin nanoparticles by two step desolvation—a new preparation method, surface modifications and cell uptake. J. Microencapsul 17:187–194 (2000).
K. Zwiorek, J. Kloeckner, E. Wagner, and C. Coester. Gelatin nanoparticles as a new and simple gene delivery system. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 7(4):22–28 (2004).
M. B. Lutz, N. Kukutsch, A. L. Ogilvie, S. Rossner, F. Koch, N. Romani, and G. Schuler. An advanced culture method for generating large quantities of highly pure dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow. J. Immunol. Methods 223(1):77–92 (1999).
C. Coester, P. Nayyar, and J. Samuel. In vitro uptake of gelatin nanoparticles by murine dendritic cells and their intracellular localisation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 62(3):306–314 (2006).
A. M. Krieg, A. K. Yi, S. Matson, T. J. Waldschmidt, G. A. Bishop, R. Teasdale, G. A. Koretzky, and D. M. Klinman. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA trigger direct B-cell activation. Nature 374(6522):546–549 (1995).
A. M. Krieg. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA and their immune effects. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20:709–760 (2002).
T. Jakob, P. S. Walker, A. M. Krieg, E. Von Stebut, M. C. Udey, and J. C. Vogel. Bacterial DNA and CpG-containing oligodeoxynucleotides activate cutaneous dendritic cells and induce IL-12 production: implications for the augmentation of Th1 responses. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 118(2–4):457–461 (1999).
J. F. Arrighi, M. Rebsamen, F. Rousset, V. Kindler, and C. Hauser. A critical role for p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in the maturation of human blood-derived dendritic cells induced by lipopolysaccharide, TNF-a, and contact sensitizers. J. Immunol. 166(6):3837–3845 (2001).
N. Iijima, Y. Yanagawa, and K. Onoe. Role of early- or late-phase activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase induced by tumour necrosis factor-a or 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene during maturation of murine dendritic cells. Immunology 110(3):322–328 (2003).
A. Krug, S. Rothenfusser, V. Hornung, B. Jahrsdorter, S. Blackwell, Z. K. Ballas, S. Endres, A. M. Krieg, and G. Hartmann. Identification of CpG oligonucleotide sequences with high induction of IFN-a/b in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 31:2154–2163 (2001).
J. D. Marshall, K. Fearon, C. Abbate, S. Subramanian, P. Yee, J. Gregorio, R. L. Coffman, and G. Van Nest. Identification of a novel CpG DNA class and motif that optimally stimulate B cell and plasmacytoid dendritic cell functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 73(6):781–792 (2003).
L. T. Costa, M. Kerkmann, G. Hartmann, S. Endres, P. M. Bisch, W. M. Heckl, and S. Thalhammer. Structural studies of oligonucleotides containing G-quadruplex motifs using AFM. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 313(4):1065–1072 (2004).
M. Kerkmann, L. T. Costa, C. Richter, S. Rothenfusser, J. Battiany, V. Hornung, J. Johnson, S. Englert, T. Ketterer, W. Heckl, S. Thalhammer, S. Endres, and G. Hartmann. Spontaneous formation of nucleic acid-based nanoparticles is responsible for high interferon-a induction by CpG-A in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 280(9):8086–8093 (2005).
S. Raychaudhuri, and K. L. Rock. Fully mobilizing host defense: building better vaccines. Nat. Biotechnol. 16(11):1025–1031 (1998).
M. Singh, and D. T. O’Hagan. Recent advances in vaccine adjuvants. Pharm. Res. 19(6):715–728 (2002).
L. Thiele, B. Rothen-Rutishauser, S. Jilek, H. Wunderli-Allenspach, H. P. Merkle, and E. Walter. Evaluation of particle uptake in human blood monocyte-derived cells in vitro. Does phagocytosis activity of dendritic cells measure up with macrophages? J. Control. Release 76(1–2):59–71 (2001).
M. Roser, and T. Kissel. Surface-modified biodegradable albumin nano- and microspheres. Part 1. Preparation and characterization. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 39(1):8–12 (1993).
C. Foged, B. Brodin, S. Frokjaer, and A. Sundblad. Particle size and surface charge affect particle uptake by human dendritic cells in an in vitro model. Int. J. Pharm. 298(2):315–322 (2005).
A. T. Davis, R. Estensen, and P. G. Quie. Cytochalasin B. 3. Inhibition of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte phagocytosis. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 137(1):161–164 (1971).
J. M. Brewer, K. G. Pollock, L. Tetley, and D. G. Russell. Vesicle size influences the trafficking, processing, and presentation of antigens in lipid vesicles. J. Immunol. 173(10):6143–6150 (2004).
K. Honda, Y. Ohba, H. Yanai, H. Negishi, T. Mizutani, A. Takaoka, C. Taya, and T. Taniguchi. Spatiotemporal regulation of MyD88-IRF-7 signalling for robust type-I interferon induction. Nature 434:1035–1040 (2005).
K. Fearon, J. D. Marshall, C. Abbate, S. Subramanian, P. Yee, J. Gregorio, G. Teshima, G. Ott, S. Tuck, G. Van Nest, and R. L. Coffman. A minimal human immunostimulatory CpG motif that potently induces IFN-g and IFN-a production. Eur. J. Immunol. 33(8):2114–2122 (2003).
J. D. Marshall, D. Higgins, C. Abbate, P. Yee, G. Teshima, G. Ott, T. dela Cruz, D. Passmore, K. L. Fearon, S. Tuck, and G. Van Nest. Polymyxin B enhances ISS-mediated immune responses across multiple species. Cell. Immunol. 229(2):93–105 (2004).
C. C. N. Wu, J. Lee, E. Raz, M. Corr, and D. A. Carson. Necessity of oligonucleotide aggregation for toll-like receptor 9 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 279(32):33071–33078 (2004).
V. Hornung, J. Ellegast, S. Kim, K. Brzózka, A. Jung, H. Kato, H. Poeck, S. Akira, K.-K. Conzelmann, M. Schlee, S. Endres, and G. Hartmann. 5′-Triphosphate RNA Is the Ligand for RIG-I. Science 314(5801):994–997 (2006).
S. S. Diebold, T. Kaisho, H. Hemmi, S. Akira, and C. Reis e Sousa. Innate antiviral responses by means of TLR7-mediated recognition of single-stranded RNA. Science 303(5663):1529–1531 (2004).
V. Hornung, M. Guenthner-Biller, C. Bourquin, A. Ablasser, M. Schlee, S. Uematsu, A. Noronha, M. Manoharan, S. Akira, A. de Fougerolles, S. Endres, and G. Hartmann. Sequence-specific potent induction of IFN-alpha by short interfering RNA in plasmacytoid dendritic cells through TLR7. Nat. Med. 11(3):263-270 (2005).
C. Bourquin, L. Schmidt, V. Hornung, C. Wurzenberger, D. Anz, N. Sandholzer, S. Schreiber, A. Voelkl, G. Hartmann, and S. Endres. Immunostimulatory RNA oligonucleotides trigger an antigen-specific cytotoxic T cell and IgG2a response. Blood 109:2953–2960 (2007).
Acknowledgments
The author would like to dedicate this article to Prof. Dr. John Samuel, who passed away far too soon. We thank him and Praveen Elamanchili from the Faculty of Pharmacy at the University of Alberta for their awesome support during the first experiments with CpG ODNs. We thank Nadja Sandholzer for expert technical assistance. This study was supported by grants BMBF Biofuture 0311896 to G.H, and from the Else-Kröner Fresenius Foundation and the German Research Foundation (DFG En 169/7-2 and GK 1202) to C.B. and S.E.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zwiorek, K., Bourquin, C., Battiany, J. et al. Delivery by Cationic Gelatin Nanoparticles Strongly Increases the Immunostimulatory Effects of CpG Oligonucleotides. Pharm Res 25, 551–562 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9410-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9410-5