Abstract
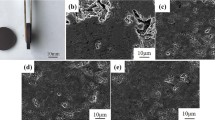
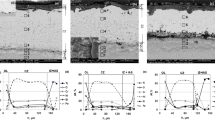
To understand the role of composition in the oxidation behavior of Ti–Mo system and to evaluate the extent of oxygen ingress into the metal substrate during high temperature exposure, a compositionally graded Ti–xMo specimen (0 ≤ x ≤ 12 wt% Mo) was prepared using an additive manufacturing technique, solutionized and then subjected to oxidation tests at 650 °C for different exposure times. The depth of oxygen diffusion, across the composition range, was assessed via change in the local hardness and the results were coupled with quantitative measurement of the oxygen concentration. The concentration of O in the α phase was reduced by 90 % after a short distance of 16 μm from the metal/oxide interface while it remained more or less the same in β phase. The solubility of Mo in α phase also approached zero near the surface as O changed the partition coefficient of this element between α and β phases. It was shown that the addition of Mo reduces the solubility of O in the metal substrate which in turn retards the transition point from parabolic to the linear oxidation stage.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Unless otherwise specified, all compositions are in wt%.
References
P. Kofstad, Nonstoichiometry, Diffusion, and Electrical Conductivity in Binary Metal Oxides, (Wiley, New York, 1972).
I. Menzies and K. Strafford, J. Less Common Met. 12, 85 (1967).
P. Samimi, Y. Liu, I. Ghamarian and P. C. Collins, Corrosion Science 89, 295 (2014).
C. Shamblen and T. Redden, Air Contamination and Embrittlement of Titanium Alloys, (General Electric Co., Cincinnati, 1970).
J. Williams, A. Sommer and P. Tung, Metall. Trans. 3, 2979 (1972).
M. Imam, Microst. Prop. Relatsh. Titan. Alloys 107, 107 (1994).
P. Kofstad, High-Temperature Oxidation of Metals, (Wiley, New York, 1966).
H. Conrad, Progress in Materials Science 26, 123 (1981).
P. Samimi, Y. Liu, I. Ghamarian, D. A. Brice and P. C. Collins, Corrosion Science 97, 150 (2015).
J. Unnam, R. Shenoy and R. Clark, Oxidation of Metals 26, 231 (1986).
P. Kofstad, K. Hauffe and H. Kjollesdal, Acta Chemica Scandinavica 12, 239 (1958).
R. T. Bryant, J. Less Common Met. 4, 62 (1962).
R. I. Jaffee and N. E. Promisel, The science, technology, and application of titanium: Proceedings, Pergamon, 1970.
H. Dong and X. Li, Materials Science and Engineering A 280, 303 (2000).
A. M. Chaze and C. Coddet, Journal Materials Science 22, 1206 (1987).
Y. Shida and H. Anada, Corrosion Science 35, 945 (1993).
J. Fanning, Min. Met. Mater. Soc. (USA) 397, 397 (1993).
P. C. Collins, A Combinatorial Approach to the Development of Composition-Microstructure-Property Relationships in Titanium Alloys Using Directed Laser Deposition, (The Ohio State University, Columbus, 2004).
B. H. Collins, A Combinatorial Approach to the Development of a Creep Resistant Beta Titanium Alloy, (The Ohio State University, Columbus, 2008).
R. Banerjee, P. C. Collins, D. Bhattacharyya, S. Banerjee and H. L. Fraser, Acta Materialia 51, 3277 (2003).
P. Samimi, Y. Liu, I. Ghamarian, J. Song and P. C. Collins, Acta Materialia 69, 92 (2014).
M. K. Miller, Atom Probe Tomography: Analysis at the Atomic Level, (Springer, New York, 2012).
H. Kuhn, D. Medlin and A. I. H. Committee, Mechanical Testing and Evaluation, (ASM International, Materials Park, 2000).
Y. J. Kim, B. J. Choi, Y. M. Ryu, B. S. Han, S. Y. Sung, S. H. Noh and C. S. Hahn, Advanced Materials Research 26, 519 (2007).
H. Guleryuz and H. Cimenoglu, J. Alloys Compd. 472, 241 (2009).
W. P. Roe, H. R. Palmer and W. R. Opie, Trans. ASM 52, 191 (1960).
R. Jaffee, H. Ogden and D. Maykuth, Trans. Am. Inst. Mining Metall. Eng. 188, 1261 (1950).
E. Bumps, H. Kessler and M. Hansen, Trans. ASM 45, 1008 (1953).
A. Jenkins, J. Inst. Metals 82, 213 (1954).
L. Glikman, V. Deryabina, N. Kolgatin, I. Bytenskii, V. Teodorovich and N. Teplov, Titan. Alloys Isr. Prog. Sci. Transl. Jerus. 122, 122 (1966).
J. Reynolds, H. Ogden and R. Jaffee, Trans. Am. Soc. Met. 49, 280 (1957).
M. Hansen, R. P. Elliott and F. A. Shunk, Constitution of binary alloys. First-supplement, (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1965).
T. Hurlen, J. Inst. Met. 89, 128 (1960).
P. Kofstad, P. Anderson and O. Krudtaa, J. Less Common Met. 3, 89 (1961).
C. J. Rosa. Report for the Naval Air Systems Command Department of the Navy University of Cinannati, 1972.
N. Birks, G. H. Meier and F. S. Pettit, Introduction to the High Temperature Oxidation of Metals, (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2006).
S. Andersson, B. Collen, U. Kuylenstierna and A. Magneli, Acta Chemica Scandinavica 11, 1641 (1957).
G. Viswanathan, E. Lee, D. M. Maher, S. Banerjee and H. L. Fraser, Acta Materialia 53, 5101 (2005).
S. R. Kalidindi and S. J. Vachhani, Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science 18, 196 (2014).
Acknowledgments
This work was conducted within the NSF I/UCRC Center for Advanced Non-Ferrous Structural Alloys (CANFSA) which is a joint industry-university center between the Colorado School of Mines and the University of North Texas. The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of NSF (Award Number 1134873) and the support and active mentorship of the industrial partners. The authors also gratefully acknowledge the facilities available at the University of North Texas’ Center for Advanced Research and Technology (CART).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samimi, P., Brice, D.A., Ghamarian, I. et al. Systematic Assessment of the Influence of Mo Concentration on the Oxygen Ingress in Ti–Mo System During High Temperature Oxidation. Oxid Met 85, 357–368 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-015-9600-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-015-9600-1