Abstract
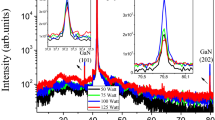
GaN thin film was successfully produced on \(n{\text{-}}Si\left({100} \right)\) substrate by RF magnetron sputter under different RF power. Experimental measurement techniques such as UV/Vis spectroscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and Micro-Raman Spectroscopy were used to research effects of Radio Frequency power on physical properties of produced thin film. It has been found that produced thin film was polycrystalline structure with (100) and (110) planes of hexagonal \(GaN\) from X-ray diffraction measurement result. It also proved that increasing RF power gives rise to deterioration in crystal quality of \(GaN\) thin film. Reason of this deterioration was discussed. It has been achieved that increasing RF power has resulted in decreasing optical band gap energy of \(GaN\) thin film. Reasons for these changes in optical band gap energy were explained. It was seen that some thin films were grown as layer-plus-island mode (Stranski–Krastanov growth mode) and others were grown as layer-by-layer growth mode (Frank van der Merwe mode) from AFM analysis. It has been found that increasing RF power has resulted in improvement of surface morphology of thin film from field emission scanning electron microscopy analysis. However, reaching RF power to 125 W leads to start to deteriorate of surface of \(GaN\) thin film. The reasons for this have been discussed. \(E_{1} \left( {TO} \right)\) transverse optical phonon mode of hexagonal \(GaN\) with different intensity was detected from Micro-Raman Spectroscopy measurement. The reasons for this difference have been discussed. It was concluded that RF power has played a significant role in growing high quality \(GaN\) thin film. Morphological, structural, and optical properties of \(GaN\) thin film were enhanced by controlling RF power, making them a potential candidate for LED, solar cell, diode application.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abud, S.H., Selman, A.M., Hassan, Z.: Investigation of structural and optical properties of GaN on flat and porous silicon. Superlattices Microstruct. 97, 586–590 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2016.07.017
Aggarwal, N., Krishna, S.T.C., Goswami, L., Mishra, M., Gupta, G., Maurya, K.K., Singh, S., Dilawar, N., Kaur, M.: Extenuation of stress and defects in GaN films grown on a metal-organic chemical vapor deposition-GaN/c-sapphire substrate by plasma-assisted molecular beam epitaxy. Cryst. Growth Des. 15(5), 2144–2150 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.5b00125
Bragg, W.H., Bragg W.L.: The reflection of X-rays by crystals. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 88(605), 428 (1913)
Braniste, T., Ciers, J., Monaico, E., Martin, D., Carlin, J.F., Ursaki, V.V., Sergentu, V.V., Tiginyanu, I.M., Grandjean, N.: Multilayer porous structures of HVPE and MOCVD grown GaN for photonic applications. Superlattices Microstruct. 102, 221–234 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2016.12.041
Cui, Z., Ke, X., Li, E., Liu, T.: Electronic and optical properties of titanium-doped GaN nanowires. Mater. Des. 96, 409–415 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.02.050
Cui, Z., Ke, X., Li, E., Zhao, T., Qi, Q., Yan, J., Ding, Y., Liu, T.: GaN nanowire field emitters with the adsorption of Pt nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 7(36), 22441–22446 (2017a). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA02568H
Cui, Z., Li, E., Ke, X., Zhao, T., Yang, Y., Ding, Y., Liu, T., Qu, Y., Xu, S.: Adsorption of alkali-metal atoms on GaN nanowires photocathode. Appl. Surf. Sci. 423, 829–835 (2017b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.06.233
Cui, Z., Li, M., Li, E., Ma, D., Zhao, B.: Optical and field emission performances of bamboo shoot-shaped GaN nanowires. Superlattices Microstruct. 120, 257–261 (2018a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2018.05.050
Cui, Z., Wang, X., Ding, Y., Li, M.: Exploration work function and optical properties of monolayer SnSe allotropes. Superlattices Microstruct. 114, 251–258 (2018b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2017.12.039
Cui, Z., Wang, X., Ding, Y., Zhang, C., Li, M.: Alkali-metal-embedded in monolayer MoS2: optical properties and work functions. Opt. Quant. Electron. 50(9), 348 (2018c). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-018-1612-z
Cui, Z., Wang, X., Li, E., Ding, Y., Sun, C., Sun, M.: Alkali-metal-adsorbed g-GaN monolayer: ultralow work functions and optical properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 13(1), 207 (2018d). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2625-z
Davydov, V.Y., Averkiev, N.S., Goncharuk, I.N., Nelson, D.K., Nikitina, I.P., Polkovnikov, A.S., Smirnov, A.N., Jacobson, M.A., Semchinova, O.K.: Raman and photoluminescence studies of biaxial strain in GaN epitaxial layers grown on 6H–SiC. J. Appl. Phys. 82(10), 5097–5102 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.366310
Demir, M., Yarar, Z., Ozdemir, M.: Effect of polarization and interface roughness on the transport properties of AlGaN/GaN heterostructure. Solid State Commun. 158, 29–33 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2013.01.004
Dyson, A.: Phonon-plasmon coupled modes in GaN. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 21(17), 174204 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/21/17/174204
Erdoğan, E., Kundakçı, M., Mantarcı, A.: InGaN thin film deposition on Si (100) and glass substrates by termionic vacuum arc. In: Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2016, vol. 1. IOP Publishing, Bristol
Fong, C.Y., Ng, S.S., Yam, F.K., Abu Hassan, H., Hassan, Z.: Growth of GaN on sputtered GaN buffer layer via low cost and simplified sol–gel spin coating method. Vacuum 119, 119–122 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2015.04.042
Gu, S., Chagarov, E.A., Min, J., Madisetti, S., Novak, S., Oktyabrsky, S., Kerr, A.J., Kaufman-Osborn, T., Kummel, A.C., Asbeck, P.M.: Characterization of interface and border traps in ALD Al2O3/GaN MOS capacitors with two-step surface pretreatments on Ga-polar GaN. Appl. Surf. Sci. 317, 1022–1027 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.09.028
Gueddim, A., Eloud, T., Messikine, N., Bouarissa, N.: Energy levels and optical properties of GaN spherical quantum dots. Superlattices Microstruct. 77, 124–133 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2014.11.003
He, X.G., Zhao, D.G., Jiang, D.S., Zhu, J.J., Chen, P., Liu, Z.S., Le, L.C., Yang, J., Li, X.J., Liu, J.P., Zhang, L.Q., Yang, H.: GaN high electron mobility transistors with AlInN back barriers. J. Alloys Compd. 662, 16–19 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.12.031
Hughes, W.C., Jr., W.H. Rowland, Jr., Johnson, M.A.L., Fujita, S., Jr., J.W. Cook, Jr., Schetzina, J.F., Ren, J., Edmond, J.A.: Molecular beam epitaxy growth and properties of GaN films on GaN/SiC substrates. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B: Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 13(4), 1571–1577 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1116/1.588189
Hwang, D.-K., Bang, K.-H., Jeong, M.-C., Myoung, J.-M.: Effects of RF power variation on properties of ZnO thin films and electrical properties of p–n homojunction. J. Cryst. Growth 254(3), 449–455 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0248(03)01205-3
Kaufmann, N.A.K., Lahourcade, L., Hourahine, B., Martin, D., Grandjean, N.: Critical impact of Ehrlich–Schwöbel barrier on GaN surface morphology during homoepitaxial growth. J. Cryst. Growth 433, 36–42 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2015.06.013
Kawwam, M., Lebbou, K.: The influence of deposition parameters on the structural quality of PLD-grown GaN/sapphire thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 292, 906–914 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.12.078
Kim, H.W., Kim, N.H.: Preparation of GaN films on ZnO buffer layers by rf magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 236(1–4), 192–197 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2004.04.029
Kudrawiec, R., Nyk, M., Syperek, M., Podhorodecki, A., Misiewicz, J., Strek, W.: Photoluminescence from GaN nanopowder: the size effect associated with the surface-to-volume ratio. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88(18), 181916 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2199489
Kunie, I., Keiko, K., Naoki, O., Hajime, H., Masahiro, K., Hrvoje, P.: The effect of n- and p-type doping on coherent phonons in GaN. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 25(20), 205404 (2013)
Kuo, D.-H., Tuan, T.T.A., Li, C.-C., Yen, W.-C.: Electrical and structural properties of Mg-doped InxGa1−xN (x ≤ 0.1) and p-InGaN/n-GaN junction diode made all by RF reactive sputtering. Mater. Sci. Eng., B 193, 13–19 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2014.11.005
Kusaka, K., Hanabusa, T., Tominaga, K.: Measurement of crystal orientation and residual stress in GaN film deposited by RF sputtering with powder target. Vacuum 74(3), 613–618 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2004.01.034
Lee, J.-M., Min, B.-G., Ju, C.-W., Ahn, H.-K., Lim, J.-W.: High temperature storage test and its effect on the thermal stability and electrical characteristics of AlGaN/GaN high electron mobility transistors. Curr. Appl. Phys. 17(2), 157–161 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2016.11.014
Li, S., Fang, G., Long, H., Wang, H., Huang, H., Mo, X., Zhao, X.: Low-threshold pure UV electroluminescence from n-ZnO:Al/i-layer/n-GaN heterojunction. J. Lumin. 132(7), 1642–1645 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2012.02.038
Li, L., Huang, J., Yang, W., Tang, K., Ren, B., Xu, H., Wang, L.: Fabrication and characterization of p-CuS/n-GaN thin film heterojunction diodes. Surf. Coat. Technol. 307, 1024–1028 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.08.005
Li, J.-S., Tang, Y., Li, Z.-T., Ding, X.-R., Li, Z.: Study on the optical performance of thin-film light-emitting diodes using fractal micro-roughness surface model. Appl. Surf. Sci. 410, 60–69 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.041
Li, E., Zhao, B., Lv, S., Cui, Z., Ma, D., Li, M.: Growth mechanism, field emission and photoluminescence property of Ge-doped hexagonal cone-shaped GaN nanorods. Superlattices Microstruct. 122, 404–409 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2018.07.002
Liao, J.-H., Huang, H.-W., Cheng, L.-C., Liu, H.-H., Chyi, J.-I., Cai, D.-P., Chen, C.-C., Lai, K.-Y.: Yellow-emitting Si-doped GaN: favorable characteristics for intermediate band solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 132, 544–548 (2015)
Lin, J.-H., Huang, S.-J., Su, Y.-K., Huang, K.-W.: The improvement of GaN-based LED grown on concave nano-pattern sapphire substrate with SiO2 blocking layer. Appl. Surf. Sci. 354, 168–172 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.02.151
Liu, L., Edgar, J.H.: Substrates for gallium nitride epitaxy. Mater. Sci. Eng., R Rep. 37(3), 61–127 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-796X(02)00008-6
Liu, Z., Chong, W.C., Wong, K.M., Lau, K.M.: GaN-based LED micro-displays for wearable applications. Microelectron. Eng. 148, 98–103 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2015.09.007
Liu, S., Wang, Q., Xiao, H., Wang, K., Wang, C., Wang, X., Ge, W., Wang, Z.: Optimization of growth and fabrication techniques to enhance the InGaN/GaN multiple quantum well solar cells performance. Superlattices Microstruct. 109, 194–200 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2017.05.014
Mantarcı, A., Gündüz, B.: A study on refractive index dispersion and optoelectronic parameters of the BCzVB OLED material by using solution method. Opt. Quant. Electron. 48(12), 547 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-016-0822-5
Mantarcı, A., Kundakçı, M.: Some of structural and morphological optimization of GaN thin film on Si(100) substrate grown by RF sputter. AIP Conf. Proc. 1833(1), 020119 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4981767
Martinez-Guerrero, E., Adelmann, C., Chabuel, F., Simon, J., Pelekanos, N.T., Mula, G., Daudin, B., Feuillet, G., Mariette, H.: Self-assembled zinc blende GaN quantum dots grown by molecular-beam epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77(6), 809–811 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1306633
Miyoshi, M., Tsutsumi, T., Kabata, T., Mori, T., Egawa, T.: Effect of well layer thickness on quantum and energy conversion efficiencies for InGaN/GaN multiple quantum well solar cells. Solid-State Electron. 129, 29–34 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sse.2016.12.009
Moon, W.H., Kim, H.J., Choi, C.H.: Molecular dynamics simulation of melting behavior of GaN nanowires. Scripta Mater. 56(5), 345–348 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2006.11.013
Moultif, N., Divay, A., Joubert, E., Latry, O.: Localizing and analyzing defects in AlGaN/GaN HEMT using photon emission spectral signatures. Eng. Fail. Anal. 81, 69–78 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.07.014
Mutlu, K., Asim, M., Erman, E.: Growth and characterization of GaN thin film on Si substrate by thermionic vacuum arc (TVA). Mater. Res. Express 4(1), 016410 (2017)
Neumayer, D.A., Ekerdt, J.G.: Growth of group III nitrides. A review of precursors and techniques. Chem. Mater. 8(1), 9–25 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm950108r
Orak, I., Kocyigit, A., Turut, A.: The surface morphology properties and respond illumination impact of ZnO/n-Si photodiode by prepared atomic layer deposition technique. J. Alloys Compd. 691, 873–879 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.08.295
Patterson, A.: The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 56(10), 978–982 (1939)
Qian, H., Lee, K.B., Vajargah, S.H., Novikov, S.V., Guiney, I., Zaidi, Z.H., Jiang, S., Wallis, D.J., Foxon, C.T., Humphreys, C.J., Houston, P.A.: Novel GaN-based vertical heterostructure field effect transistor structures using crystallographic KOH etching and overgrowth. J. Cryst. Growth 459, 185–188 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2016.12.025
Said, A., Debbichi, M., Said, M.: Theoretical study of electronic and optical properties of BN, GaN and BxGa1−xN in zinc blende and wurtzite structures. Optik 127(20), 9212–9221 (2016)
Saito, W., Suwa, T., Uchihara, T., Naka, T., Kobayashi, T.: Breakdown behaviour of high-voltage GaN-HEMTs. Microelectron. Reliab. 55(9), 1682–1686 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2015.06.126
Sekine, T., Komatsu, Y., Iwaya, R., Kuroe, H., Kikuchi, A., Kishino, K.: Surface phonons studied by raman scattering in GaN nanostructures. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 86(7), 074602 (2017). https://doi.org/10.7566/JPSJ.86.074602
Selman, A.M., Hassan, Z., Husham, M.: Structural and photoluminescence studies of rutile TiO2 nanorods prepared by chemical bath deposition method on Si substrates at different pH values. Measurement 56, 155–162 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2014.06.027
Shet, S., Yan, Y., Ravindra, N., Turner, J., Al-Jassim, M.: Photoelectrochemical behavior of mixed ZnO and GaN (ZnO:GaN) thin films prepared by sputtering technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 270, 718–721 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.01.134
Sheu, J.-K., Chen, P.-C., Shin, C.-L., Lee, M.-L., Liao, P.-H., Lai, W.-C.: Manganese-doped AlGaN/GaN heterojunction solar cells with intermediate band absorption. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 157, 727–732 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2016.07.047
Shinoda, H., Mutsukura, N.: Structural properties of GaN layers grown on Al2O3 (0001) and GaN/Al2O3 template by reactive radio-frequency magnetron sputter epitaxy. Vacuum 125, 133–140 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2015.12.008
Stenzel, O.: The Physics of Thin Film Optical Spectra. Springer, New York (2005)
Strite, S., Morkoc, H.J.: GaN, AlN, and InN: A review. Vac. Sci. Technol. B B10, 1237–1266 (1992)
Sun, M., Chou, J.-P., Ren, Q., Zhao, Y., Yu, J., Tang, W.: Tunable Schottky barrier in van der Waals heterostructures of graphene and g-GaN. Appl. Phys. Lett. 110(17), 173105 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4982690
Tang, J., Liang, T., Shi, W., Zhang, Q., Wang, Y., Liu, J., Xiong, J.: The testing of stress-sensitivity in heteroepitaxy GaN/Si by Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257(21), 8846–8849 (2011)
Tauc, J., Menth, A.: States in the gap. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 8, 569–585 (1972)
Van de Walle, C.G.: Effects of impurities on the lattice parameters of GaN. Phys. Rev. B 68(16), 165209 (2003)
Wang, M., Bian, J., Sun, H., Liu, W., Zhang, Y., Luo, Y.: n-VO2/p-GaN based nitride–oxide heterostructure with various thickness of VO2 layer grown by MBE. Appl. Surf. Sci. 389, 199–204 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.07.109
Wu, Y., Xue, C., Zhuang, H., Tian, D., Liu, Y.A., He, J., Sun, L., Wang, F., Ai, Y., Cao, Y.: Synthesis of GaN nanorods through ammoniating Ga2O3/BN thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. J. Cryst. Growth 292(2), 294–297 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2006.04.012
Xie, M.H., Seutter, S.M., Zhu, W.K., Zheng, L.X., Wu, H., Tong, S.Y.: Anisotropic step-flow growth and island growth of GaN(0001) by molecular beam epitaxy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82(13), 2749–2752 (1999)
Xing, Z., Wang, R.X., Fan, Y.M., Wang, J.F., Zhang, B.S., Xu, K.: The effect of transparent conductive nanocrystalline oxide thin layer on performance of UV detectors fabricated on Fe-doped GaN. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 57, 132–136 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2016.10.017
Yang, M., Chang, B., Hao, G., Wang, H., Wang, M.: Optoelectronic properties of GaN, AlN, and GaAlN alloys. Optik 126(22), 3357–3361 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.07.096
Yin, M.L., Zou, C.W., Li, M., Liu, C.S., Guo, L.P., Fu, D.J.: Middle-frequency magnetron sputtering for GaN growth. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 262(2), 189–193 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2007.05.034
You, Y.-S., Feng, S.-W., Wang, H.-C., Song, J., Han, J.: The effects of indium aggregation in InGaN/GaN single and multiple quantum wells grown on nitrogen-polar GaN templates by a pulsed metalorganic chemical vapor deposition. J. Lumin. 182, 196–199 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2016.10.039
Yudate, S., Fujii, T., Shirakata, S.: Structural properties of Eu-doped GaN films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 517(4), 1453–1456 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2008.09.022
Zhang, Y., Cui, Z., Ding, Y., Liu, T.: Density functional theories study on optoelectronic properties of arsenic-doped GaN nanowires. Opt. Quant. Electron. 48(12), 548 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-016-0824-3
Zhang, H., Zhang, D., Wang, W.: Improved emission of GaN-LED based on the optimized multilayered lamellar micro-gratings. J. Lumin. 192, 470–477 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2017.07.022
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Muş Alparslan University Scientific Research Coordination Unit. Project Number: BAP-18FEF-4901-03.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mantarcı, A., Kundakçi, M. Physical properties of RF magnetron sputtered GaN/n-Si thin film: impacts of RF power. Opt Quant Electron 51, 81 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-1795-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-1795-y