Abstract
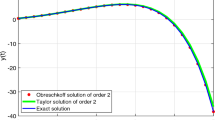
In this paper, we present two families of second-order and third-order explicit methods for numerical integration of initial-value problems of ordinary differential equations. Firstly, a family of second-order methods with two free parameters is derived by considering a suitable rational approximation to the theoretical solution of the problem at some grid points. Imposing that the principal term of the local truncation error of this family vanishes, we obtain an expression for one of the parameters in terms of the other. With this approach, a new one-parameter family of third-order methods is obtained. By selecting any 3(2) pair of second and third order methods, they can be implemented as an embedded type method, thus leading to a variable step-size formulation. We have considered one 3(2) pair of second and third order methods and made a comparison of numerical results with several ode solvers which are currently used in practice. The comparison of numerical results shows that the embedded 3(2) pair outperforms the methods considered for comparison.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deuflhard, P.: Newton Methods for Nonlinear Problems. Springer, Berlin (2004)
Brezinski, C.: Intégration des systèmes différentiels à l’aide du ρ-algorithme. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris. 278 A, 875–878 (1974)
Brezinski, C., Redivo-Zaglia, M.: Extrapolation Methods: Theory and Practice. Elsevier (1991)
Ramos, H.: A non-standard explicit integration scheme for initial-value problems. Appl. Math. Comp. 189, 710–718 (2007)
Ramos, H.: A nonlinear explicit one-step integration scheme for singular autonomous initial value problems. In: Simos, T. (ed.) AIP Conference Proceedings 936, New York, pp 448–451 (2007)
Lambert, J.D.: Nonlinear methods for stiff systems of ordinary differential equations. In: Proc. conference on numerical solution of ordinary differential equations 363, University of Dundee, pp 75–88 (1973)
Van Niekerk, F.D.: Rational one-step methods for initial value problems. Comput. Math. Appl. 16(12), 1035–1039 (1988)
Oliver, J.: A curiosity of low-order explicit Runge-Kutta methods. Math. of. Comp. 29(132), 1032–1036 (1975)
Negrut, D., Jay, L.O., Khude, N.: A discussion of low-order numerical integration formulas for rigid and flexible multi-body dynamics. J. of Comput. Nonlinear Dynam. 4, 210081–2100811 (2009)
Hilber, H.M., Hughes, T.J.R., Taylor, R.L.: Improved numerical dissipation for time integration algorithms in structural dynamics. Earthquake Eng. Struct. Dyn. 5, 283–292 (1977)
Newmark, N.M.: A method of computation for structural dynamics. J. Engrg. Mech. Div. 112, 67–94 (1959)
Sofroniou, M.: Order stars and linear stability theory. J. Symb. Comp. 21, 101–131 (1996)
Wanner, G., Hairer, E., Nörsett, S.P.: Order Stars and stability theorems. BIT 18, 475–489 (1978)
Iserles, A., Nörsett, S.P.: Order Stars. Chapman and Hall, London (1991)
Leveque, R.J.: Finite Difference Methods for Ordinary and Partial Differential Equations. Siam (2007)
Shampine, L.F., Witt, A.: Control of local error stabilizes integrations. J. Comp. Appl. Math. 62, 333–351 (1995)
Calvo, M., Montijano, J.I., Randez, L.: On the change of step size in multi-step codes. Numer. Alg. 4, 283–304 (1993)
Watts, H.A.: Starting step size for an ODE solver. J. Comp. Appl. Math. 9, 177–191 (1983)
Sedgwick, A.E.: An effective variable order variable step Adams method. Dept. of Computer Science Rept, vol. 53. University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada (1973)
Lambert, J.D.: Numerical Methods for Ordinary Differential Systems: The Initial Value Problem. John Wiley, New York (1991)
Lambert, J.D.: Computational Methods in Ordinary Differential Equations. Wiley, London (1973)
Jain, M.K.: Numerical Solution of Differential Equations. New Age Inter, (P) Ltd., New Delhi (2014)
Hairer, E., Nörsett, S.P., Wanner, G.: Solving Ordinary Differential Equations I. Springer, Berlin (1993)
Hairer, E., Wanner, G.: Solving Ordinary Differential Equations II. Springer, Berlin (1996)
Shampine, L.F., Gordon, M.K.: Computer Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations: The Initial Value Problem. Freeman, San Francisco CA (1975)
Calvo, M., Mar-Quemada, M.: On the stability of rational Runge-Kutta methods. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 8, 289–293 (1982)
Sottas, G.: Rational Runge-Kutta methods are not suitable for stiff systems of ODEs. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 10, 169–174 (1984)
Hairer, E.: Unconditionally stable explicit methods for parabolic equations. Numer. Math. 35, 57–68 (1980)
Rosenbrock, H.H.: Some general implicit processes for the numerical solution of differential equations. Comput. J. 5, 329–330 (1963)
Shampine, L.F., Reichelt, M.W.: The MATLAB ODE Suite. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 18, 1–22 (1997)
Dormand, J.R., Prince, P.J.: A family of embedded Runge-Kutta formulae. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 6, 19–26 (1980)
Ramos, H.: Contributions to the development of differential systems exactly solved by multi step finite-difference schemes. Appl. Math. Comp. 217, 639–649 (2010)
Alt, R.: A-stable one-step methods with step-size control for stiff systems of ordinary differential equations. J. Comp. Appl. Math 4(1) (1978)
Malley, R.E.O’.: Singular Perturbation Methods for Ordinary Differential Equations. Springer, New York (1991)
Ashino, R., Nagase, M., Vaillancourt, R.: Behind and beyond the Matlab ODE suite. Comput. Math. Appl. 40, 491–512 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramos, H., Singh, G., Kanwar, V. et al. An embedded 3(2) pair of nonlinear methods for solving first order initial-value ordinary differential systems. Numer Algor 75, 509–529 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-016-0209-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-016-0209-5