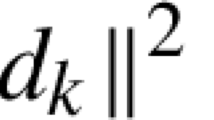Abstract
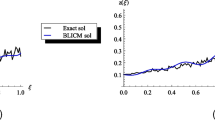
In this paper we design a class of general split-step balanced methods for solving Itô stochastic differential systems with m-dimensional multiplicative noise, in which the drift or deterministic increment function can be taken from any chosen one-step ODE solver. We then give an analysis of their order of strong convergence in a general setting, but for the mean-square stability analysis, we confine our investigation to a special case in which the drift increment function of the methods is replaced by the one from the well known Rosenbrock method. The resulting class of stochastic differential equation (SDE) solvers will have more appropriate and useful mean-square stability properties for SDEs with stiffness in their drift and diffusion parts, compared to some other already reported split-step balanced methods. Finally, numerical results show the effectiveness of these methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcock, J., Burrage, K.: A note on the Balanced Method. BIT 46(4), 689–710 (2006)
Burrage, K., Burrage, P.M., Tian, T.: Numerical methods for strong solutions of stochastic differential equations: an overview. Roy. Soc. London Proc. Ser. A 460(2041), 373–402 (2004)
Burrage, K., Tian, T.: The composite Euler method for stiff stochastic differential equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 131, 407–426 (2001)
Dekker, K., Verwer, J.: Stability of Runge-Kutta Methods for Stiff Nonlinear Differential equations. Elsiver-North Holand, Amesterdam (1984)
Devroye, L., Karasözen, B., Kohler, M., Korn, R. (eds.): Recent Developments in Applied Probability and Statistics: Dedicated to the Memory of Jürgen Lehn. Berlin, Heidelberg, Springer (2010)
Fisher, P., Platen, E.: Application of balanced method to stochastic differential equations in filtering. Monte Carlo Methods Appl. 5, 19–38 (1999)
Haghighi, A., Hosseini, S.M.: On the stability of some second order numerical methods for weak approximation of Itô SDEs. Numer. Algorithms 57, 101–124 (2011)
Hairer, E., Wanner, G.: Solving Ordinary Differential Equations. II, Stiff and Differential-Algebraic Problems. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1996)
Higham, D.J.: Mean-square and asymptotic stability of the stochastic theta method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 38(3), 753–769 (2000)
Higham, D.J.: An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations. SIAM Rev. Edu. Sect. 43, 525–546 (2001)
Kahl, C., Schurz, H.: Balanced Milstein methods for ordinary SDEs. Monte Carlo Methods Appl. 12(2), 143–170 (2006)
Kloeden, P.E., Platen, E.: A survey of numerical methods for stochastic differential equations. Stoch. Hydrol. Hydraul. 3, 155–178 (1989)
Kloeden, P.E., Platen, E., Wright, W.: The approximation of multiple stochastic integrals. Stoch. Anal. Appl. 10, 431–441 (1992)
Kloeden, P.E., Platen, E.: Numerical Solution of Stochastic Differential Equations. Applications of Mathematics, vol. 23. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1999)
Milstein, G.N.: A theorem on the order of convergence of mean square approximations of solutions of systems of stochastic differential equations. Theory Probab. Appl. 32, 738–741 (1988)
Milstein, G.N.: Numerical Integration of Stochastic Differential Equations. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1995)
Milstein, G.N., Platen, E., Schurz, H.: Balanced implicit methods for stiff stochastic systems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 35, 1010–1019 (1998)
Petersen, W.P.: A general implicit splitting for stabilizing numerical simulations of Itô stochastic differential equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 35, 1439–1451 (1998)
Stoer, J., Bulirsch, R.: Introduction to Numerical Analysis, Second Edition. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1991)
Tian, T.H., Burrage, K.: Implicit Taylor methods for stiff stochastic differential equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 38, 167–185 (2001)
Wang, P., Liu, Z.: Split-step backward balanced Milstein methods for stiff stochastic systems. Appl. Numer. Math. 59, 1198–1213 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haghighi, A., Hosseini, S.M. A class of split-step balanced methods for stiff stochastic differential equations. Numer Algor 61, 141–162 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-012-9534-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-012-9534-5