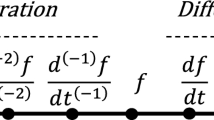Abstract
A novel observer-based control policy based on an interval type-3 fuzzy logic system is developed to tackle the main limitations of fuzzy-based controllers in sense of approximation of uncertainties and analyzing nonlinear complex systems without detailed dynamics model information. For this purpose, a novel scheme is proposed that includes online optimized tuning rules, a simple type reduction method, and adaptive mechanisms. Also, an adaptive compensator is implemented to enhance the robust performance of the closed-loop system and reduce the effect of approximation errors. For the stability analysis, appropriate Lyapunov functions and Barbalat’s lemma are employed. By both simulations and experimentally implementation, it is shown that the suggested approach results in a more accurate approximation of unknown models and complicated nonlinearities, and good resistance against uncertainties and parameter variations.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
There are no data associated with this paper.
Abbreviations
- IT3FLS:
-
Interval type-3 fuzzy logic system
- SM:
-
Sliding mode
- TS:
-
Takagi-Sugeno
- IT2FLS:
-
Interval type-2 fuzzy logic system
- T1FLS:
-
Type-1 fuzzy logic system
- T2F:
-
Type-2 fuzzy
- PI:
-
Proportional–Integral
- FS:
-
Fuzzy set
- MPU6050:
-
Angle acceleration sensor
- PCB:
-
Printed circuit board
- GFSK:
-
Gaussian frequency shift keying
- MF:
-
Membership function
References
Liu, X., Yu, H.: Continuous adaptive integral-type sliding mode control based on disturbance observer for pmsm drives. Nonlinear Dyn. 104(2), 1429–1441 (2021)
Li, T., Liu, X.: Non-cascade fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on disturbance observers. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 17(2), 1061–1075 (2022)
Fridman, L., Shtessel, Y., Edwards, C., Yan, X.-G.: Higher-order sliding-mode observer for state estimation and input reconstruction in nonlinear systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 18(4–5), 399–412 (2008)
Efimov, D., Fridman, L., Raïssi, T., Zolghadri, A., Seydou, R.: Interval estimation for lpv systems applying high order sliding mode techniques. Automatica 48(9), 2365–2371 (2012)
Edwards, C., Shtessel, Y.B.: Adaptive continuous higher order sliding mode control. Automatica 65, 183–190 (2016)
Yang, J., Li, S., Su, J., Yu, X.: Continuous nonsingular terminal sliding mode control for systems with mismatched disturbances. Automatica 49(7), 2287–2291 (2013)
da Silva, C., Campos, V., Nguyen, A.-T., Martínez Palhares, R.: Adaptive gain-scheduling control for continuous-time systems with polytopic uncertainties: an lmi-based approach. Automatica 133, 109856 (2021)
Taghieh, A., Shafiei, M.H.: Static output feedback control of switched nonlinear systems with time-varying delay and parametric uncertainties under asynchronous switching. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control. 43(5), 1156–1167 (2021)
Li, D., Ge, S.S., Lee, T.H.: Simultaneous arrival to origin convergence: sliding-mode control through the norm-normalized sign function. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 67(4), 1966–1972 (2021)
Su, H., Zhang, W.: Observer-based adaptive neural quantized control for nonlinear systems with asymmetric fuzzy dead zones and unknown control directions. Nonlinear Dyn. 1–14 (2022)
Meng, Q., Ma, Q., Zhou, G.: Adaptive output feedback control for stochastic uncertain nonlinear time-delay systems. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs
Zhang, X., Huang, W.: Robust \({H_\infty }\) adaptive output feedback sliding mode control for interval type-2 fuzzy fractional-order systems with actuator faults. Nonlinear Dyn. 104(1), 537–550 (2021)
Zhang, X., Jin, K.: State and output feedback controller design of takagi-sugeno fuzzy singular fractional order systems. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 19(6), 2260–2268 (2021)
Zhao, T., Zou, X., Dian, S.: Fixed-time observer-based adaptive fuzzy tracking control for mecanum-wheel mobile robots with guaranteed transient performance. Nonlinear Dyn. 107(1), 921–937 (2022)
Guo, B., Dian, S., Zhao, T.: Event-driven-observer-based fuzzy fault-tolerant control for nonlinear system with actuator fault. Nonlinear Dyn. 1–15 (2022)
Yan, S., Gu, Z., Park, J.H., Xie, X.: Adaptive memory-event-triggered static output control of TS fuzzy wind turbine systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst
Yan, S., Shen, M., Nguang, S.K., Zhang, G., Zhang, L.: A distributed delay method for event-triggered control of T-S fuzzy networked systems with transmission delay. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 27(10), 1963–1973 (2019)
Hao, R.-B., Lu, Z.-Q., Ding, H., Chen, L.-Q.: A nonlinear vibration isolator supported on a flexible plate: analysis and experiment. Nonlinear Dyn. 108(2), 941–958 (2022)
Zhang, Z., Niu, Y.: Sliding mode control of interval type-2 ts fuzzy systems with redundant channels. Nonlinear Dyn. 1–15 (2022)
Mohammadzadeh, A., Kaynak, O., Teshnehlab, M.: Two-mode indirect adaptive control approach for the synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems by the use of a hierarchical interval type-2 fuzzy neural network. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22(5), 1301–1312 (2014)
Castillo, O., Melin, P.: A review on the design and optimization of interval type-2 fuzzy controllers. Appl. Soft Comput. 12(4), 1267–1278 (2012)
Castillo, O., Amador-Angulo, L.: A generalized type-2 fuzzy logic approach for dynamic parameter adaptation in bee colony optimization applied to fuzzy controller design. Inf. Sci. 460–461, 476–496 (2018)
Khooban, M.H., Vafamand, N., Liaghat, A., Dragicevic, T.: An optimal general type-2 fuzzy controller for urban traffic network. ISA Trans. 66, 335–343 (2017)
Mohammadzadeh, A., Ghaemi, S., Kaynak, O., Khanmohammadi, S.: Robust \({H_\infty }\)-based synchronization of the fractional-order chaotic systems by using new self-evolving nonsingleton type-2 fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 24(6), 1544–1554 (2016)
Kumbasar, T., Hagras, H.: A self-tuning zslices-based general type-2 fuzzy pi controller. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23(4), 991–1013 (2015)
Yang, Y., Niu, Y., Reza Karimi, H.: Dynamic learning control design for interval type-2 fuzzy singularly perturbed systems: a component-based event-triggering protocol. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 32(5), 2518–2535 (2022)
Yang, Y., Niu, Y., Li, J.: Local-boundary-information-dependent control design for interval type-2 fuzzy systems under self-triggered scheme. Inf. Sci. 596, 137–152 (2022)
Mohammadzadeh, A., Kumbasar, T.: A new fractional-order general type-2 fuzzy predictive control system and its application for glucose level regulation. Appl. Soft Comput. 91, 106241 (2020)
Amirkhani, A., Shirzadeh, M., Kumbasar, T., Mashadi, B.: A framework for designing cognitive trajectory controllers using genetically evolved interval type-2 fuzzy cognitive maps. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 37(1), 305–335 (2022)
Li, H., Wu, C., Wu, L., Lam, H.-K., Gao, Y.: Filtering of interval type-2 fuzzy systems with intermittent measurements. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 46(3), 668–678 (2016)
Sabzalian, M.H., Mohammadzadeh, A., Rathinasamy, S., Zhang, W.: A developed observer-based type-2 fuzzy control for chaotic systems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 1–20 (2021)
Mohammadzadeh, A., Sabzalian, M.H., Ahmadian, A., Nabipour, N.: A dynamic general type-2 fuzzy system with optimized secondary membership for online frequency regulation. ISA Trans. 112, 150–160 (2021)
Mohammadzadeh, A., Kaynak, O.: A novel general type-2 fuzzy controller for fractional-order multi-agent systems under unknown time-varying topology. J. Franklin Inst. 356(10), 5151–5171 (2019)
Moghadam, H.M., Mohammadzadeh, A., Vafaie, R.H., Tavoosi, J., Khooban, M.-H.: A type-2 fuzzy control for active/reactive power control and energy storage management. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control. 44(5), 1014–1028 (2022)
Mohammadzadeh, A., Kaynak, O.: A novel fractional-order fuzzy control method based on immersion and invariance approach. Appl. Soft Comput. 88, 106043 (2020)
Mohammadzadeh, A., Sabzalian, M.H., Zhang, W.: An interval type-3 fuzzy system and a new online fractional-order learning algorithm: theory and practice. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 28(9), 1940–1950 (2020)
Mohammadzadeh, A., Vafaie, R.H.: A deep learned fuzzy control for inertial sensing: micro electro mechanical systems. Appl. Soft Comput. 109, 107597 (2021)
Gheisarnejad, M., Mohammadzadeh, A., Farsizadeh, H., Khooban, M.-H.: Stabilization of 5g telecom converter-based deep type-3 fuzzy machine learning control for telecom applications. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 1–1 (2021)
Qasem, S.N., Ahmadian, A., Mohammadzadeh, A., Rathinasamy, S., Pahlevanzadeh, B.: A type-3 logic fuzzy system: optimized by a correntropy based kalman filter with adaptive fuzzy kernel size. Inf. Sci. 572, 424–443 (2021)
Boulkroune, A., M’saad, M.: On the design of observer-based fuzzy adaptive controller for nonlinear systems with unknown control gain sign. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 201, 71–85 (2012)
Lin, T.-C., Wang, C.-H., Liu, H.-L.: Observer-based indirect adaptive fuzzy-neural tracking control for nonlinear siso systems using vss and h-infinity approaches. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 143(2), 211–232 (2004)
Rovithakis, G.A., Christodoulou, M.A.: Direct adaptive regulation of unknown nonlinear dynamical systems via dynamic neural networks. Syst. Man Cybern. IEEE Trans. 25(12), 1578–1594 (1995)
Qasem, S.N., Ahmadian, A., Mohammadzadeh, A., Rathinasamy, S., Pahlevanzadeh, B.: A type-3 logic fuzzy system: optimized by a correntropy based kalman filter with adaptive fuzzy kernel size. Inf. Sci. 572, 424–443 (2021)
Krikochoritis, T., Tzafestas, S.: Control of flexible joint robots using neural networks. IMA J. Math. Control. Inf. 18(2), 269–280 (2001)
Meng, Q., Lai, X., Yan, Z., Su, C.-Y., Wu, M.: Motion planning and adaptive neural tracking control of an uncertain two-link rigid-flexible manipulator with vibration amplitude constraint. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst
Hung, L.-C., Chung, H.-Y., Chung-Li, T.-Y.: Hybrid neural sliding mode controller design for a robotic manipulator. J. Grey Syst. 17(2), 183–200 (2005)
Liu, Y.-J., Wang, W., Tong, S.-C., Liu, Y.-S.: Robust adaptive tracking control for nonlinear systems based on bounds of fuzzy approximation parameters. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. IEEE Trans. 40(1), 170–184 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This research is financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2019YFE0112400) and the Department of Science and Technology of Shandong Province (Grant No. 2021CXGC011204).
Funding
This research is financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No.2019YFE0112400) and the Department of Science and Technology of Shandong Province (Grant No. 2021CXGC011204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Taghieh, A., Mohammadzadeh, A., Zhang, C. et al. A novel adaptive interval type-3 neuro-fuzzy robust controller for nonlinear complex dynamical systems with inherent uncertainties. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 411–425 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07867-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07867-9