Abstract
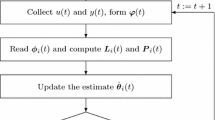
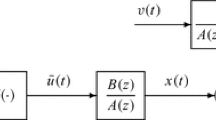
This paper considers iterative identification problems for a Hammerstein nonlinear system which consists of a memoryless nonlinear block followed by a linear dynamical block. The difficulty of identification is that the Hammerstein nonlinear system contains the products of the parameters of the nonlinear part and the linear part, which leads to the unidentifiability of the parameters. In order to obtain unique parameter estimates, we express the output of the system as a linear combination of all the system parameters by means of the key-term separation principle and derive a gradient based iterative identification algorithm by replacing the unknown variables in the information vectors with their estimates. The simulation results indicate that the proposed algorithm can work well.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ding, F.: System Identification—New Theory and Methods. Science Press, Beijing (2013)
Farjoud, A., Ahmadian, M.: Nonlinear modeling and experimental characterization of hydraulic dampers: effects of shim stack and orifice parameters on damper performance. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(2), 1437–1456 (2012)
Gaite, J.: Nonlinear analysis of spacecraft thermal models. Nonlinear Dyn. 65(3), 283–300 (2011)
Shams, S., Sadr, M.H., Haddadpour, H.: An efficient method for nonlinear aeroelasticy of slender wings. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(1), 659–681 (2012)
Li, J.H., Ding, F., Yang, G.W.: Maximum likelihood least squares identification method for input nonlinear finite impulse response moving average systems. Math. Comput. Model. 55(3–4), 442–450 (2012)
Wang, W., Ding, F., Dai, J.Y.: Maximum likelihood least squares identification for systems with autoregressive moving average noise. Appl. Math. Model. 36(5), 1842–1853 (2012)
Wang, S.J., Ding, R.: Three-stage recursive least squares parameter estimation for controlled autoregressive autoregressive systems. Appl. Math. Model. 37(12–13), 7489–7497 (2013)
Liu, Y.J., Sheng, J., Ding, R.F.: Convergence of stochastic gradient estimation algorithm for multivariable ARX-like systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 59(8), 2615–2627 (2010)
Ding, F., Yang, H.Z., Liu, F.: Performance analysis of stochastic gradient algorithms under weak conditions. Sci. China, Ser. F 51(9), 1269–1280 (2008)
Ding, F., Liu, X.P., Liu, G.: Gradient based and least-squares based iterative identification methods for OE and OEMA systems. Digit. Signal Process. 20(3), 664–677 (2010)
Liu, Y.J., Xiao, Y.S., Zhao, X.L.: Multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for multiple-input single-output systems using the auxiliary model. Appl. Math. Comput. 215(4), 1477–1483 (2009)
Liu, M.M., Xiao, Y.S., Ding, R.F.: Iterative identification algorithm for Wiener nonlinear systems using the Newton method. Appl. Math. Model. 37(9), 6584–6591 (2013)
Ding, F., Ma, J.X., Xiao, Y.S.: Newton iterative identification for a class of output nonlinear systems with moving average noises. Nonlinear Dyn. 74(1–2), 21–30 (2013)
Li, J.H., Ding, R.: Parameter estimation methods for nonlinear systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 219(9), 4278–4287 (2013)
Rashid, M.T., Frasca, M.: Nonlinear model identification for artemia population motion. Nonlinear Dyn. 69(4), 2237–2243 (2012)
Ding, F.: Hierarchical multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for Hammerstein nonlinear system modeling. Appl. Math. Model. 37(4), 1694–1704 (2013)
Ding, F., Duan, H.H.: Two-stage parameter estimation algorithms for Box-Jenkins systems. IET Signal Process. 7(8), 646–654 (2013)
Ding, F., Liu, G., Liu, X.P.: Partially coupled stochastic gradient identification methods for non-uniformly sampled systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 55(8), 1976–1981 (2010)
Ding, F.: Coupled-least-squares identification for multivariable systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 7(1), 68–79 (2013)
Ding, J., Fan, C.X., Lin, J.X.: Auxiliary model based parameter estimation for dual-rate output error systems with colored noise. Appl. Math. Model. 37(6), 4051–4058 (2013)
Ding, F.: Combined state and least squares parameter estimation algorithms for dynamic systems. Appl. Math. Model. 37 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.apm.2013.06.007
Li, J.H.: Parameter estimation for Hammerstein CARARMA systems based on the Newton iteration. Appl. Math. Lett. 26(1), 91–96 (2013)
Ding, F., Liu, G., Liu, X.P.: Parameter estimation with scarce measurements. Automatica 47(8), 1646–1655 (2011)
Ding, J., Ding, F., Liu, X.P., Liu, G.: Hierarchical least squares identification for linear SISO systems with dual-rate sampled-data. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 56(11), 2677–2683 (2011)
Wang, D.Q., Ding, R., Dong, X.Z.: Iterative parameter estimation for a class of multivariable systems based on the hierarchical identification principle and the gradient search. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 31(6), 2167–2177 (2012)
Ding, J., Ding, F.: Bias compensation based parameter estimation for output error moving average systems. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 25(12), 1100–1111 (2011)
Lopes dos Santos, P., Ramos, J.A., Martins de Carvalho, J.L.: Identification of a benchmark Wiener-Hammerstein: a bilinear and Hammerstein-bilinear model approach. Control Eng. Pract. 20(11), 1156–1164 (2012)
Wang, D.Q., Ding, F.: Hierarchical least squares estimation algorithm for Hammerstein-Wiener systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 19(12), 825–828 (2012)
Shi, Y., Fang, H.: Kalman filter based identification for systems with randomly missing measurements in a network environment. Int. J. Control 83(3), 538–551 (2010)
Shi, Y., Yu, B.: Robust mixed H-2/H-infinity control of networked control systems with random time delays in both forward and backward communication links. Automatica 47(4), 754–760 (2011)
Wang, D.Q., Chu, Y.Y., Yang, G.W., Ding, F.: Auxiliary model-based recursive generalized least squares parameter estimation for Hammerstein OEAR systems. Math. Comput. Model. 52(1–2), 309–317 (2010)
Yu, B., Fang, H., Lin, Y., Shi, Y.: Identification of Hammerstein output-error systems with two-segment nonlinearities: algorithm and applications. J. Control Intel. Syst. 38(4), 194–201 (2010)
Wills, A., Schön, T.B., Ljung, L., Ninness, B.: Identification of Hammerstein-Wiener models. Automatica 49(1), 70–81 (2013)
Ding, F., Liu, X.G., Chu, J.: Gradient-based and least-squares-based iterative algorithms for Hammerstein systems using the hierarchical identification principle. IET Control Theory Appl. 7(2), 176–184 (2013)
Ding, F.: Decomposition based fast least squares algorithm for output error systems. Signal Process. 93(5), 1235–1242 (2013)
Ding, F., Liu, Y.J., Bao, B.: Gradient based and least squares based iterative estimation algorithms for multi-input multi-output systems. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part I, J. Syst. Control Eng. 226(1), 43–55 (2012)
Dehghan, M., Hajarian, M.: An iterative method for solving the generalized coupled Sylvester matrix equations over generalized bisymmetric matrices. Appl. Math. Model. 34(3), 639–654 (2010)
Dehghan, M., Hajarian, M.: Analysis of an iterative algorithm to solve the generalized coupled Sylvester matrix equations. Appl. Math. Model. 35(7), 3285–3300 (2011)
Ding, F.: Two-stage least squares based iterative estimation algorithm for CARARMA system modeling. Appl. Math. Model. 37(7), 4798–4808 (2013)
Wang, D.Q., Yang, G.W., Ding, R.F.: Gradient-based iterative parameter estimation for Box-Jenkins systems. Comput. Math. Appl. 60(5), 1200–1208 (2010)
Vörös, J.: Parameter identification of Wiener systems with discontinuous nonlinearities. Syst. Control Lett. 44(5), 363–372 (2001)
Vörös, J.: Modeling and identification of systems with backlash. Automatica 46(2), 369–374 (2010)
Wang, D.Q., Ding, F., Chu, Y.Y.: Data filtering based recursive least squares algorithm for Hammerstein systems using the key-term separation principle. Inf. Sci. 222(10), 203–212 (2013)
Li, J.H., Ding, F.: Maximum likelihood stochastic gradient estimation for Hammerstein systems with colored noise based on the key term separation technique. Comput. Math. Appl. 62(11), 4170–4177 (2011)
Wang, Z.Y., Ji, Z.C.: Data filtering based iterative identification methods for nonlinear FIR-MA systems. J. Vib. Control (2013). doi:10.1177/1077546313484048
Ding, F., Liu, X.P., Liu, G.: Identification methods for Hammerstein nonlinear systems. Digit. Signal Process. 21(2), 215–238 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61273194), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (China, BK2012549), and the PAPD of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Q., Ding, F. Iterative estimation methods for Hammerstein controlled autoregressive moving average systems based on the key-term separation principle. Nonlinear Dyn 75, 709–716 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-013-1097-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-013-1097-z