Abstract
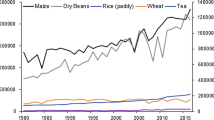
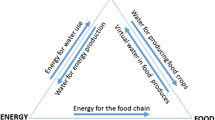
Agricultural water use plays an important role in maintaining food security. The present paper utilizes an agent-based model of the complex adaptive systems (CAS) theory for the dynamic simulation of four water resource utilization plans and was able to forecast the per capita food share, per capita income and water security rate under three climatic conditions in Heilongjiang Province, China, in 2020. The forecasts were performed under the broad principle of coordinated regional development and based on Heilongjiang’s food production, water resources and population data 2003–2010. The measured data for Heilongjiang Province in 2011 were used to perform joint risk analyses of the forecast results. The results showed that the comprehensive plan combining technological innovation and policy control provides the best method of achieving food security under the three climatic conditions. However, compared to maintaining the status quo, this combination plan decreases by approximately 8 % under the three climatic conditions, but the per capita share of food and the rate of water security increase to over 10 and 20 %, respectively. Therefore, to further reduce the pressure on water resources in Heilongjiang Province and to lessen the impact of climate on food production, advanced technology and policy regulations should be increasingly integrated into various industries to ensure the sustainable supply of regional water resources for food production.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S, Siwar C, Talib BA, Chamhuri N, Islam R (2014) Tackling food price volatility: the challenge of the days to come. UMK Proc 1:103–113
Bessembinder JJE, Leffelaar PA, Dhindwal AS, Ponsioen TC (2005) Which crop and which drop, and the scope for improvement of water productivity. Agric Water Manag 73(2):113–130
Breisinger C, Ecker O (2014) Simulating economic growth effects on food and nutrition security in Yemen: a new macro–micro modeling approach. Econ Model 43:100–113
Brooks J (2014) Policy coherence and food security: the effects of OECD countries’ agricultural policies. Food Policy 44:88–94
Brown LR, Halweil B (2009) China’s water shortage could shake world food security. World Water 11(4):6–10
Cao X, Wu P, Wang Y, Zhao X, Zhang B (2012) Spatial and temporal variation of crop water productivity in China. J Drain Irrig Mach Eng 30(3):356–361 (in Chinese)
de Fraiture C, Molden D, Wichelns D (2010) Investing in water for food, ecosystems, and livelihoods: an overview of the comprehensive assessment of water management in agriculture. Agric Water Manag 97(4):495–501
Fu Q, Wang K, Ren S (2012) Real coded multi-objective nested accelerating genetic algorithm based on complex system evolutionary optimization. Syst Eng Theory Pract 32:2718–2723 (in Chinese)
Fu Q, Gong F, Jiang Q, Cheng K, Dong H, Ma X (2013) Risk assessment of the city water resources system based on Pansystems Observation-Control Model of Periphery. Nat Hazards 71(3):1899–1912
Gies L, Agusdinata DB, Merwade V (2014) Drought adaptation policy development and assessment in East Africa using hydrologic and system dynamics modeling. Nat Hazards 74(2):789–813
Guo E, Zhang J, Ren X, Zhang Q, Sun Z (2014) Integrated risk assessment of flood disaster based on improved set pair analysis and the variable fuzzy set theory in central Liaoning Province, China. Nat Hazards 74(2):947–965
Holland JH (1995) Hidden order: how adaptation builds complexity. Canada: The Perseus Books Group
Holland JH (1998) Emergence: from chaos to order. America: The Perseus Books Group
Ji X, Liu L, Qi X (2014) Risk assessment method of grain production guarantees the capacity of regional cultivated land. Trans CSAE 30:219–226 (in Chinese)
Magombeyi MS, Taigbenu AE (2014) Sensitivity and uncertainty propagation in coupled models for assessing smallholder farmer food security in the Olifants River Basin, South Africa. Environ Model Softw 60:228–240
Mariano MJM, Giesecke JA (2014) The macroeconomic and food security implications of price interventions in the Philippine rice market. Econ Model 37:350–361
Molden D, Oweis T, Steduto P, Bindraban P, Hanjra MA, Kijne J (2010) Improving agricultural water productivity: between optimism and caution. Agric Water Manag 97(4):528–535
National Development and Reform Commission of PRC (2008) Opinions on the implementation of the most stringent water management system. http://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2013-01/06/content_2305762.htm (in Chinese)
Nyakudya IW, Stroosnijder L, Nyagumbo I (2014) Infiltration and planting pits for improved water management and maize yield in semi-arid Zimbabwe. Agric Water Manag 141:30–46
Popova Z, Ivanova M, Martins D, Pereira LS, Doneva K, Alexandrov V, Kercheva M (2014) Vulnerability of Bulgarian agriculture to drought and climate variability with focus on rainfed maize systems. Nat Hazards 74(2):865–886
Qadir M, Wichelns D, Raschid-Sally L, McCornick PG, Drechsel P, Bahri A, Minhas PS (2010) The challenges of wastewater irrigation in developing countries. Agric Water Manag 97(4):561–568
Qi X, Liu L, Liu Y et al (2013) Risk assessment for sustainable food security in China according to integrated food security: taking Dongting Lake area for example. Environ Monit Assess 185(6):4855–4867
Qiu W, Fan Q, Zhao Q, Yuan Y (2010) Calculation on ecological carrying capacity of water resources in Heilongjiang Province. J Harbin Inst Technol 42(6):1000–1003 (in Chinese)
Rutten M, van Dijk M, van Rooij W, Hilderink H (2014) Land use dynamics, climate change, and food security in Vietnam: a global-to-local modeling approach. World Dev 59:29–46
Santos F, Fletschner D, Savath V, Peterman A (2014) Can government-allocated land contribute to food security ? Intrahousehold analysis of West Bengal’s Microplot Allocation Program. World Dev 64:860–872
Sharma BR, Rao KV, Vittal KPR, Ramakrishna YS, Amarasinghe U (2010) Estimating the potential of rainfed agriculture in India: prospects for water productivity improvements. Agric Water Manag 97(1):23–30
Shi W, Tao F (2014) Spatio-temporal distributions of climate disasters and the response of wheat yields in China from 1983 to 2008. Nat Hazards 74(2):569–583
Singh A (2014) Conjunctive use of water resources for sustainable irrigated agriculture. J Hydrol 519:1688–1697
Smyth SJ, Phillips PWB, Kerr WA (2015) Food security and the evaluation of risk. Glob Food Secur 4:16–23
Storm H, Heckelei T, Heidecke C (2011) Estimating irrigation water demand in the Moroccan Draa Valley using contingent valuation. J Environ Manag 92(10):2803–2809
Turral H, Svendsen M, Faures JM (2010) Investing in irrigation: reviewing the past and looking to the future. Agric Water Manag 97(4):551–560
van Grieken ME, Thomas CR, Roebeling PC, Thorburn PJ (2013) Integrating economic drivers of social change into agricultural water quality improvement strategies. Agric Ecosyst Environ 180(1):166–175
van Wijk MT (2014) From global economic modeling to household level analyses of food security and sustainability: how big is the gap and can we bridge it? Food Policy 49:378–388
van Wijk MT, Rufino MC, Enahoro D, Parsons D, Silvestri S, Valdivia RO, Herrero M (2014) Farm household models to analyse food security in a changing climate: a review. Glob Food Secur 3(2):77–84
Vervoort JM, Thornton PK, Kristjanson P, Förch W, Ericksen PJ, Kok K, Ingram John SI, Herrero M, Palazzo A, Helfgott Ariella ES, Wilkinson A, Havlík P, Mason-D’Croz D, Jost C (2014) Challenges to scenario-guided adaptive action on food security under climate change. Glob Environ Change 28:383–394
Wang Q, Wang F, Jiang D, Xuan D (2014a) A model based on Song Jian discrete population evolution equations applied in population forecast and analysis of Heilongjiang Province. Math Pract Theory 44:203–207 (in Chinese)
Wang X, Wang Z, Yang W, Xi X, Shi L, Dong W, Zhang Q, Zhou Y (2014b) Shortage of water resources in China and countermeasures. Water Pollut Control 7:1–5 (in Chinese)
World Bank (2006) Reengaging in agricultural water management: challenges and options. The Office of the Publisher, Washington D C
Xu D, Liu Y, Li Y, Gong S (2008) Overview on concepts and strategies studies of modern irrigation water management development. Shuili Xuebao 39(10):1204–1212 (in Chinese)
Xu D, Gong S, Li Y, Liu Y (2010) Problem and strategies for the development of agricultural water management. Trans CSAE 26(11):1–7 (in Chinese)
Yin S, Wu L, Zhang Y (2009) Empirical analysis of the factors influencing grain yield. Syst Eng Theory Pract 29(10):28–34 (in Chinese)
Zhang M, Wang F, Zhang G (2005) Problems of agricultural water use in China and the strategies for saving water. Trans CSAE 21(S1):1–6 (in Chinese)
Zhao J (2003) Study on the holistic model for the optimization of water resources allocation based on complex adaptive system theory. Tsinghua University Department of Hydraulic Engineering, BeiJing (in Chinese)
Zhong L, Liu L, Liu Y (2010) Natural disaster risk assessment of grain production in Dongting Lake Area, China. Agric Agric Sci Proc 1:24–32
Acknowledgments
National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 51179032, 51279031, 51209038); funding was provided by the Ministry of Water Resources special funds for nonprofit industry research projects(No: 201301096); Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (No: E201241); Ministry of Education New Century Excellent Talents; Heilongjiang Province University Changjiang Scholars backup support projects; Colleges and Universities in Heilongjiang Province New Century Excellent Talents Training Program (No: 1155-NCET-004); Heilongjiang Provincial Water Conservancy Science and Technology Project (No: 201318); and Excellent Youth Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (No: JC201402); Scientific Research Fund of Heilongjiang Provincial Education Department (No: 12531009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, K., Fu, Q., Li, T. et al. Regional food security risk assessment under the coordinated development of water resources. Nat Hazards 78, 603–619 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1735-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1735-5