Abstract
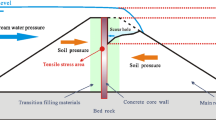
The standard procedure in Quebec, Canada, for evaluating the failure of an embankment dam, per the Loi sur la sécurité des barrages, specifies a 30-min-long failure scenario with a breach width equal to four times the maximal height of the dam. We demonstrate a new method for evaluating the flood overtopping failure scenario for embankment dams with concrete upstream slope protection, using Toulnustouc dam for example computations. Our new methodology computes safety factors for a range of potential failure mechanisms taking into account geotechnical, hydraulic, and structural factors. We compile the results of our investigations of the various dam failure mechanisms and compare the corresponding dam failure hydrographs to the current hydrograph specified in the standard analysis procedures. Our investigations tend to invalidate the current standard procedures for evaluating the failure of rock-fill dams with concrete upstream faces, by indicating that the current standard procedures underestimate the peak failure discharge and overestimate the time to the peak discharge.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bazergui A, Thang BQ, Biron A (2002) Résistance des matériaux, 3rd edn. Presses internationales Polytechnique, Montreal, Canada
Beauséjour N, Bouzaïene H, Hammamji Y, Bigras A, Bergeron A (2006) Conception du barrage et de la digue sud de l’aménagement hydroélectrique de la Toulnustouc. Paper presented at the Annual Conference of the Canadian Dam Association
Bennis S (2007) Hydraulique et hydrologie, 2nd edn. Presses de l'Université du Québec, Montreal, Canada, p 452
Ergun S (1952) Flow of water through packed columns. Chem Eng Prog 48(2):89–94
Fand RM, Thinakaran R (1990) The influence of the wall on flow through pipes packed with spheres. J Fluids Eng 112(1):84–88
Franca MJ, Almeida AB (2002) Experimental Tests on Rockfill Dam breaching Process. IAHR—International Symposium on Hydraulic and Hydrological Aspects and Safety assessment of Hydraulic Structures, St. Petersburg, May
Guyon E, Hulin H-P, Petit L (2001) Hydrodynamique physique. EDP Sciences, Paris, France, 674 p
Hansen D, Garga VK, Townsend DR (1995) Selection and application of a one-dimensional non-Darcy flow equation for two-dimensional flow through rockfill embankments. Can Geotech J 32:223–232
Holtz RD, Kovacs WD (1991) Introduction à la géotechnique (trans: Lafleur J). Presses International Polytechnique Press, Montreal, Canada, 817 p
Lancellota R (2009) Geotechnical engineering, 2nd edn. Taylor and Francis Group, New York, USA, 499 p
Marche C (2008) Barrages, crues de rupture et protection civile. Presses Internationales Polytechnique, Montreal
Martins R (1990) Turbulent seepage flow through rockfill structures. Water Power and Dam Construction, March, 90 41–45
Masson L (2009) Évaluation du gain de sécurité relié au réhaussement d’une digue munie d’un élément d’Étanchéité rigide. École Polytechnique de Montréal, Montréal
McCorquodale JA, Hannoura A, Nasser MS (1978) Hydraulic conductivity of rockfill. J Hydraul Res 16(2):123–137
Mehta D, Hawley MC (1969) Wall effect in packed columns. Ind Eng Chem Process Des Dev 8(2):280–282
Morris MW (2000) CADAM: Concerted Action on Dambreach Modelling, Final report, Environment and Climate Programme, Report SR 571. H. R. Wallingford Ltd., Wallingford, UK
Singh VP, Scarlatos PD (1988) Analysis of gradual earth-dam failure. J Hydraul Eng 114(1):21–42
Stephenson D (ed) (1979) Rockfill in hydraulic engineering. Amsterdam, Netherlands
US Army Corps of Engineers (1995) Gravity dam design (vol EM 1110-2-2200). University Press of Pacific, Honolulu
Wilkins JK (1956) Flow of water through rockfill and its application to the design of dams. Paper presented at the New-Zealand Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering
Acknowledgments
This work was possible through the support of the National Science and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) Discovery Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiganne, F., Marche, C. & Mahdi, TF. Evaluation of the overflow failure scenario and hydrograph of an embankment dam with a concrete upstream slope protection. Nat Hazards 71, 21–39 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0897-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0897-2