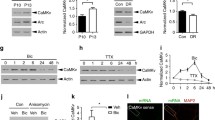
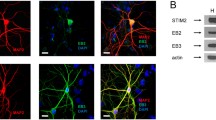
Abstract
A majority of excitatory synapses in the brain are localized on the dendritic spines. Alterations of spine density and morphology are associated with many neurological diseases. Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying spine formation is important for understanding these diseases. Kalirin7 (Kal-7) is localized to the postsynaptic side of excitatory synapses in the neurons. Overexpression of Kal-7 causes an increase in spine density whereas knockdown expression of endogenous Kal-7 results in a decrease in spine density in primary cultured cortical neurons. However, the mechanisms underlying Kal-7-mediated spine formation are not entirely clear. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) plays a vital role in the formation of spines and synaptic plasticity. Kal-7 is phosphorylated by CDK5 at Thr1590, the unique Cdk5 phosphorylation site in the Kal-7 protein. This study was to explore the role of CDK5-mediated phosphorylation of Kal-7 in spine formation and the underlying mechanisms. Our results showed expression of Kal-7T/D (mimicked phosphorylation), Kal-7T/A mutants (blocked phosphorylation) or wild-type (Wt) Kal-7 caused in a similar increase in spine density, while spine size of Wt Kal-7-expressing cortical neurons was bigger than that in Kal-7 T\A-expressing neurons, but smaller than that in Kal-7T/D-expressing neurons. The fluorescence intensity of NMDA receptor subunit NR2B (GluN2B) staining was stronger along the MAP2 positive dendrites of Kal-7T/D-expressing neurons than that in Kal-7T/A- or Wt Kal-7-expressing neurons. The fluorescence intensity of AMPA receptor subunit GluR1 (GluA1) staining showed the same trend as GluN2B staining. These findings suggest that Cdk5 affects the function of Kal-7 on spine morphology and function via GluN2B and GluA1 receptors during dendritic spine formation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yuste R, Bonhoeffer T (2001) Morphological changes in dendritic spines associated with long-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1071–1089. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.1071
Ehlers MD (2002) Molecular morphogens for dendritic spines. Trends Neurosci 25:64–67
Engert F, Bonhoeffer T (1999) Dendritic spine changes associated with hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity. Nature 399:66–70
Yang Y, Zhou Q (2009) Spine modifications associated with long-term potentiation. Neuroscientist 15:464–476
McKinney RA (2010) Excitatory amino acid involvement in dendritic spine formation, maintenance and remodelling. J Physiol 588:107–116
Akashi K et al (2009) NMDA receptor GluN2B (GluR epsilon 2/NR2B) subunit is crucial for channel function, postsynaptic macromolecular organization, and actin cytoskeleton at hippocampal CA3 synapses. J Neurosci 29:10869–10882
Tang YP et al (1999) Genetic enhancement of learning and memory in mice. Nature 401:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1038/43432
Kasai H, Matsuzaki M, Noguchi J, Yasumatsu N, Nakahara H (2003) Structure-stability-function relationships of dendritic spines. Trends Neurosci 26:360–368
Matsuzaki M et al (2001) Dendritic spine geometry is critical for AMPA receptor expression in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Nat Neurosci 4:1086–1092
Kopec CD, Real E, Kessels HW, Malinow R (2007) GluR1 links structural and functional plasticity at excitatory synapses. J Neurosci 27:13706–13718
van Spronsen M, Hoogenraad CC (2010) Synapse pathology in psychiatric and neurologic disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 10:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-010-0104-8
Qiao H et al (2016) Dendritic spines in depression: what we learned from animal models. Neural Plast 2016:8056370. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8056370
Waites CL, Garner CC (2011) Presynaptic function in health and disease. Trends Neurosci 34:326–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2011.03.004
Gipson CD, Olive MF (2017) Structural and functional plasticity of dendritic spines—root or result of behavior? Genes Brain Behav 16:101–117. https://doi.org/10.1111/gbb.12324
Mandela P, Ma XM (2012) Kalirin, a key player in synapse formation, is implicated in human diseases. Neural Plast 2012:728161
Lai KO, Ip NY (2013) Structural plasticity of dendritic spines: the underlying mechanisms and its dysregulation in brain disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832:2257–2263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.08.012
Forrest MP, Parnell E, Penzes P (2018) Dendritic structural plasticity and neuropsychiatric disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 19:215–234. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2018.16
Ma XM, Huang J, Wang Y, Eipper BA, Mains RE (2003) Kalirin, a multifunctional Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor, is necessary for maintenance of hippocampal pyramidal neuron dendrites and dendritic spines. J Neurosci 23:10593–10603
Penzes P et al (2001) The neuronal Rho-GEF Kalirin-7 interacts with PDZ domain-containing proteins and regulates dendritic morphogenesis. Neuron 29:229–242
Ma XM et al (2008) Kalirin-7 is required for synaptic structure and function. J Neurosci 28:12368–12382. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4269-08.2008
Ma XM, Wang Y, Ferraro F, Mains RE, Eipper BA (2008) Kalirin-7 is an essential component of both shaft and spine excitatory synapses in hippocampal interneurons. J Neurosci 28:711–724. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5283-07.2008
Ichikawa M, Muramoto K, Kobayashi K, Kawahara M, Kuroda Y (1993) Formation and maturation of synapses in primary cultures of rat cerebral cortical cells: an electron microscopic study. Neurosci Res 16:95–103
Lai KO, Ip NY (2015) Cdk5: a key player at neuronal synapse with diverse functions. Mini Rev Med Chem 15:390–395
Hawasli AH et al (2007) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 governs learning and synaptic plasticity via control of NMDAR degradation. Nat Neurosci 10:880–886. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1914
Mita N, He X, Sasamoto K, Mishiba T, Ohshima T (2016) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 regulates dendritic spine formation and maintenance of cortical neuron in the mouse brain. Cereb Cortex 26:967–976. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhu264
Mishiba T et al (2014) Cdk5/p35 functions as a crucial regulator of spatial learning and memory. Mol Brain 7:82. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-014-0082-x
Shah K, Rossie S (2018) Tale of the good and the Bad Cdk5: remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton in the brain. Mol Neurobiol 55:3426–3438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0525-3
Su SC, Tsai LH (2011) Cyclin-dependent kinases in brain development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27:465–491. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154023
Xin X et al (2008) Regulation of Kalirin by Cdk5. J Cell Sci 121:2601–2611
Johnson RC, Penzes P, Eipper BA, Mains RE (2000) Isoforms of kalirin, a neuronal Dbl family member, generated through use of different 5′- and 3′-ends along with an internal translational initiation site. J Biol Chem 275:19324–19333. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M000676200
Penzes P et al (2000) An isoform of kalirin, a brain-specific GDP/GTP exchange factor, is enriched in the postsynaptic density fraction. J Biol Chem 275:6395–6403
Ma XM et al (2011) Kalirin-7, an important component of excitatory synapses, is regulated by estradiol in hippocampal neurons. Hippocampus 21:661–677. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20780
Blanpied TA, Ehlers MD (2004) Microanatomy of dendritic spines: emerging principles of synaptic pathology in psychiatric and neurological disease. Biol Psychiatry 55:1121–1127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2003.10.006
Yuste R, Bonhoeffer T (2001) Morphological changes in dendritic spines associated with long-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1071–1089
Matsuzaki M, Honkura N, Ellis-Davies GC, Kasai H (2004) Structural basis of long-term potentiation in single dendritic spines. Nature 429:761–766. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02617
De Roo M, Klauser P, Garcia PM, Poglia L, Muller D (2008) Spine dynamics and synapse remodeling during LTP and memory processes. Prog Brain Res 169:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(07)00011-8
Segal M (2017) Dendritic spines: morphological building blocks of memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 138:3–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2016.06.007
Bourne JN, Harris KM (2008) Balancing structure and function at hippocampal dendritic spines. Annu Rev Neurosci 31:47–67. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125646
Nimchinsky EA, Sabatini BL, Svoboda K (2002) Structure and function of dendritic spines. Annu Rev Physiol 64:313–353. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.64.081501.160008
Segal M (1995) Dendritic spines for neuroprotection: a hypothesis. Trends Neurosci 18:468–471
El-Husseini AE, Schnell E, Chetkovich DM, Nicoll RA, Bredt D (2000) S. PSD-95 involvement in maturation of excitatory synapses. Science 290:1364–1368
Ebrahimi S, Okabe S (2014) Structural dynamics of dendritic spines: molecular composition, geometry and functional regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1838:2391–2398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.06.002
Noguchi J, Matsuzaki M, Ellis-Davies GC, Kasai H (2005) Spine-neck geometry determines NMDA receptor-dependent Ca2+ signaling in dendrites. Neuron 46:609–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2005.03.015
Xie Z et al (2007) Kalirin-7 controls activity-dependent structural and functional plasticity of dendritic spines. Neuron 56:640–656
Herring BE, Nicoll RA (2016) Kalirin and Trio proteins serve critical roles in excitatory synaptic transmission and LTP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:2264–2269. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1600179113
Long LH et al (2009) Age-related synaptic changes in the CA1 stratum radiatum and spatial learning impairment in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 36:675–681. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.05132.x
Moser MB, Trommald M, Andersen P (1994) An increase in dendritic spine density on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells following spatial learning in adult rats suggests the formation of new synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:12673–12675
Berman RF, Hannigan JH, Sperry MA, Zajac CS (1996) Prenatal alcohol exposure and the effects of environmental enrichment on hippocampal dendritic spine density. Alcohol 13:209–216
Fiala JC, Spacek J, Harris KM (2002) Dendritic spine pathology: cause or consequence of neurological disorders? Brain Res Brain Res Rev 39:29–54
Irwin SA, Galvez R, Greenough WT (2000) Dendritic spine structural anomalies in fragile-X mental retardation syndrome. Cereb Cortex 10:1038–1044
Kaufmann WE, Moser HW (2000) Dendritic anomalies in disorders associated with mental retardation. Cereb Cortex 10:981–991
Kiraly DD et al (2010) Behavioral and morphological responses to cocaine require kalirin7. Biol Psychiatry 68:249–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.03.024
Xu C et al (2016) Orbitofrontal cortex 5-HT2A receptor mediates chronic stress-induced depressive-like behaviors and alterations of spine density and Kalirin7. Neuropharmacology 109:7–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.02.020
Roberts RC, Conley R, Kung L, Peretti FJ, Chute DJ (1996) Reduced striatal spine size in schizophrenia: a postmortem ultrastructural study. Neuroreport 7:1214–1218
Konopaske GT, Lange N, Coyle JT, Benes FM (2014) Prefrontal cortical dendritic spine pathology in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. JAMA Psychiatry 71:1323–1331. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.1582
Hill JJ, Hashimoto T, Lewis DA (2006) Molecular mechanisms contributing to dendritic spine alterations in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 11:557–566
Yan Y, Eipper BA, Mains RE (2015) Kalirin-9 and Kalirin-12 play essential roles in dendritic outgrowth and branching. Cereb Cortex 25:3487–3501. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhu182
May V, Schiller MR, Eipper BA, Mains RE (2002) Kalirin Dbl-homology guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1 domain initiates new axon outgrowths via RhoG-mediated mechanisms. J Neurosci 22:6980–6990
Kiraly DD, Lemtiri-Chlieh F, Levine ES, Mains RE, Eipper BA (2011) Kalirin binds the NR2B subunit of the NMDA receptor, altering its synaptic localization and function. J Neurosci 31:12554–12565. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3143-11.2011
Lemtiri-Chlieh F et al (2011) Kalirin-7 is necessary for normal NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity. BMC Neurosci 12:126. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-12-126
Brigman JL et al (2010) Loss of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors in CA1 hippocampus and cortex impairs long-term depression, reduces dendritic spine density, and disrupts learning. J Neurosci 30:4590–4600. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0640-10.2010
Paoletti P, Bellone C, Zhou Q (2013) NMDA receptor subunit diversity: impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:383–400. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3504
Shinohara Y, Hirase H (2009) Size and receptor density of glutamatergic synapses: a viewpoint from left-right asymmetry of CA3-CA1 connections. Front Neuroanat 3:10. https://doi.org/10.3389/neuro.05.010.2009
Kessels HW, Malinow R (2009) Synaptic AMPA receptor plasticity and behavior. Neuron 61:340–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2009.01.015
Mitsushima D, Ishihara K, Sano A, Kessels HW, Takahashi T (2011) Contextual learning requires synaptic AMPA receptor delivery in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:12503–12508. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1104558108
Rumpel S, LeDoux J, Zador A, Malinow R (2005) Postsynaptic receptor trafficking underlying a form of associative learning. Science 308:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1103944
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China [81671338 and 81371552], Connecticut Innovation [14SCBUCHC11], and Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education [T32524]. Thanks to Drs. Dick Mains and Betty Eipper for providing pEAK-myc-Kal-7, Kal-7 mutant vectors and Kal-7 antibody.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, MX., Qiao, H., Zhang, M. et al. Role of Cdk5 in Kalirin7-Mediated Formation of Dendritic Spines. Neurochem Res 44, 1243–1251 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02771-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02771-y