Abstract
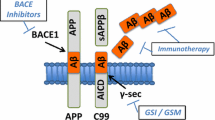
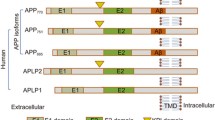
The accumulation of amyloid beta (Aβ) in the brain is believed to play a central role in the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Revisions to the amyloid cascade hypothesis now acknowledge the dynamic equilibrium in which Aβ exists and the importance of enzymes involved in the production and breakdown of Aβ in maintaining healthy Aβ levels. However, while a wealth of pharmacological and immunological therapies are being generated to inhibit the Aβ-producing enzymes, β-site APP cleavage enzyme 1 and γ-secretase, the therapeutic potential of stimulating Aβ-degrading enzymes such as neprilysin, endothelin-converting enzyme-1 and insulin-degrading enzyme remains relatively unexplored. Recent evidence indicates that increasing Aβ degradation as opposed to inhibiting synthesis is a more effective strategy to prevent Aβ build-up. Therefore Aβ degrading enzymes have become valuable targets of therapy. In this review, we discuss the pathway of Aβ synthesis and clearance along with the opportunities they present for therapeutic intervention, the benefits of increasing the expression/activity of Aβ-degrading enzymes, and the untapped therapeutic potential of enzyme activation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Serrano-Pozo A, Frosch MP, Masliah E, Hyman BT (2011) Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 1:a006189
Zempel H, Thies E, Mandelkow E, Mandelkow EM (2010) Abeta oligomers cause localized Ca(2+) elevation, missorting of endogenous Tau into dendrites, Tau phosphorylation, and destruction of microtubules and spines. J Neurosci 30:11938–11950
Shankar GM, Walsh DM (2009) Alzheimer’s disease: synaptic dysfunction and Abeta. Mol Neurodegener 4:48
Tsai J, Grutzendler J, Duff K, Gan WB (2004) Fibrillar amyloid deposition leads to local synaptic abnormalities and breakage of neuronal branches. Nat Neurosci 7:1181–1183
Muller U, Winter P, Graeber MB (2013) A presenilin 1 mutation in the first case of Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol 12:129–130
Selkoe DJ (2001) Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev 81:741–766
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297:353–356
Hardy JA, Higgins GA (1992) Alzheimer’s disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 256:184–185
Nalivaeva NN, Belyaev ND, Zhuravin IA, Turner AJ (2012) The Alzheimer’s amyloid-degrading peptidase, neprilysin: can we control it? Int J Alzheimers Dis 2012:383796
Mawuenyega KG, Sigurdson W, Ovod V, Munsell L, Kasten T, Morris JC, Yarasheski KE, Bateman RJ (2010) Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 330:1774
Chow VW, Mattson MP, Wong PC, Gleichmann M (2010) An overview of APP processing enzymes and products. Neuromol Med 12:1–12
Haass C, Kaether C, Thinakaran G, Sisodia S (2012) Trafficking and proteolytic processing of APP. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a006270
Puzzo D, Privitera L, Leznik E, Fa M, Staniszewski A, Palmeri A, Arancio O (2008) Picomolar amyloid-beta positively modulates synaptic plasticity and memory in hippocampus. J Neurosci 28:14537–14545
Baruch-Suchodolsky R, Fischer B (2009) Abeta40, either soluble or aggregated, is a remarkably potent antioxidant in cell-free oxidative systems. Biochemistry 48:4354–4370
Guglielmotto M, Aragno M, Autelli R, Giliberto L, Novo E, Colombatto S, Danni O, Parola M, Smith MA, Perry G, Tamagno E, Tabaton M (2009) The up-regulation of BACE1 mediated by hypoxia and ischemic injury: role of oxidative stress and HIF1alpha. J Neurochem 108:1045–1056
Igbavboa U, Sun GY, Weisman GA, He Y, Wood WG (2009) Amyloid beta-protein stimulates trafficking of cholesterol and caveolin-1 from the plasma membrane to the Golgi complex in mouse primary astrocytes. Neuroscience 162:328–338
Yao ZX, Papadopoulos V (2002) Function of beta-amyloid in cholesterol transport: a lead to neurotoxicity. FASEB J 16:1677–1679
Bailey JA, Maloney B, Ge YW, Lahiri DK (2011) Functional activity of the novel Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide interacting domain (AbetaID) in the APP and BACE1 promoter sequences and implications in activating apoptotic genes and in amyloidogenesis. Gene 488:13–22
Maloney B, Lahiri DK (2011) The Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide (Abeta) binds a specific DNA Abeta-interacting domain (AbetaID) in the APP, BACE1, and APOE promoters in a sequence-specific manner: characterizing a new regulatory motif. Gene 488:1–12
Nalivaeva NN, Beckett C, Belyaev ND, Turner AJ (2012) Are amyloid-degrading enzymes viable therapeutic targets in Alzheimer’s disease? J Neurochem 120(Suppl 1):167–185
Bates KA, Verdile G, Li QX, Ames D, Hudson P, Masters CL, Martins RN (2009) Clearance mechanisms of Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta peptide: implications for therapeutic design and diagnostic tests. Mol Psychiatry 14:469–486
Deane R, Wu Z, Sagare A, Davis J, Du Yan S, Hamm K, Xu F, Parisi M, LaRue B, Hu HW, Spijkers P, Guo H, Song X, Lenting PJ, Van Nostrand WE, Zlokovic BV (2004) LRP/amyloid beta-peptide interaction mediates differential brain efflux of Abeta isoforms. Neuron 43:333–344
Shibata M, Yamada S, Kumar SR, Calero M, Bading J, Frangione B, Holtzman DM, Miller CA, Strickland DK, Ghiso J, Zlokovic BV (2000) Clearance of Alzheimer’s amyloid-ss(1–40) peptide from brain by LDL receptor-related protein-1 at the blood-brain barrier. J Clin Investig 106:1489–1499
Atwal JK, Chen Y, Chiu C, Mortensen DL, Meilandt WJ, Liu Y, Heise CE, Hoyte K, Luk W, Lu Y, Peng K, Wu P, Rouge L, Zhang Y, Lazarus RA, Scearce-Levie K, Wang W, Wu Y, Tessier-Lavigne M, Watts RJ (2011) A therapeutic antibody targeting BACE1 inhibits amyloid-beta production in vivo. Sci Transl Med 3:84ra43
Yan R (2016) Stepping closer to treating Alzheimer’s disease patients with BACE1 inhibitor drugs. Transl Neurodegener 5:13
Doody RS, Raman R, Farlow M, Iwatsubo T, Vellas B, Joffe S, Kieburtz K, He F, Sun X, Thomas RG, Aisen PS, Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study Steering C, Siemers E, Sethuraman G, Mohs R, Semagacestat Study G (2013) A phase 3 trial of semagacestat for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 369:341–350
Vlad SC, Miller DR, Kowall NW, Felson DT (2008) Protective effects of NSAIDs on the development of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 70:1672–1677
Eriksen JL, Sagi SA, Smith TE, Weggen S, Das P, McLendon DC, Ozols VV, Jessing KW, Zavitz KH, Koo EH, Golde TE (2003) NSAIDs and enantiomers of flurbiprofen target gamma-secretase and lower Abeta 42 in vivo. J Clin Investig 112:440–449
Green RC, Schneider LS, Amato DA, Beelen AP, Wilcock G, Swabb EA, Zavitz KH, Tarenflurbil Phase 3 Study G (2009) Effect of tarenflurbil on cognitive decline and activities of daily living in patients with mild Alzheimer disease: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 302:2557–2564
Szekely CA, Green RC, Breitner JC, Ostbye T, Beiser AS, Corrada MM, Dodge HH, Ganguli M, Kawas CH, Kuller LH, Psaty BM, Resnick SM, Wolf PA, Zonderman AB, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Zandi PP (2008) No advantage of A beta 42-lowering NSAIDs for prevention of Alzheimer dementia in six pooled cohort studies. Neurology 70:2291–2298
Garcia-Alloza M, Subramanian M, Thyssen D, Borrelli LA, Fauq A, Das P, Golde TE, Hyman BT, Bacskai BJ (2009) Existing plaques and neuritic abnormalities in APP:PS1 mice are not affected by administration of the gamma-secretase inhibitor LY-411575. Mol Neurodegener 4:19
Orgogozo JM, Gilman S, Dartigues JF, Laurent B, Puel M, Kirby LC, Jouanny P, Dubois B, Eisner L, Flitman S, Michel BF, Boada M, Frank A, Hock C (2003) Subacute meningoencephalitis in a subset of patients with AD after Abeta42 immunization. Neurology 61:46–54
Eckman EA, Reed DK, Eckman CB (2001) Degradation of the Alzheimer’s amyloid beta peptide by endothelin-converting enzyme. J Biol Chem 276:24540–24548
Pacheco-Quinto J, Herdt A, Eckman CB, Eckman EA (2013) Endothelin-converting enzymes and related metalloproteases in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 33(Suppl 1):S101–S110
Nalivaeva NN, Turner AJ (2017) Role of ageing and oxidative stress in regulation of Amyloid-degrading enzymes and development of neurodegeneration. Curr Aging Sci 10:32–40
Turner AJ, Nalivaeva NN (2013) Peptide degradation (Neprilysin and other regulatory peptidases). In: Kastin AJ (ed) Handbook of biologically active peptides. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 1757–1764
Miners JS, Barua N, Kehoe PG, Gill S, Love S (2011) Abeta-degrading enzymes: potential for treatment of Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 70:944–959
Saido T, Leissring MA (2012) Proteolytic degradation of amyloid beta-protein. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a006379
Dolev I, Michaelson DM (2004) A nontransgenic mouse model shows inducible amyloid-beta (Abeta) peptide deposition and elucidates the role of apolipoprotein E in the amyloid cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13909–13914
Nisemblat Y, Belinson H, Dolev I, Michaelson DM (2008) Activation of the amyloid cascade by intracerebroventricular injection of the protease inhibitor phosphoramidon. Neuro-degener Dis 5:166–169
Marr RA, Rockenstein E, Mukherjee A, Kindy MS, Hersh LB, Gage FH, Verma IM, Masliah E (2003) Neprilysin gene transfer reduces human amyloid pathology in transgenic mice. J Neurosci 23:1992–1996
Marr RA, Spencer BJ (2010) NEP-like endopeptidases and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 7:223–229
Hafez D, Huang JY, Huynh AM, Valtierra S, Rockenstein E, Bruno AM, Lu B, DesGroseillers L, Masliah E, Marr RA (2011) Neprilysin-2 is an important beta-amyloid degrading enzyme. Am J Pathol 178:306–312
Eckman EA, Watson M, Marlow L, Sambamurti K, Eckman CB (2003) Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid peptide is increased in mice deficient in endothelin-converting enzyme. J Biol Chem 278:2081–2084
Kilger E, Buehler A, Woelfing H, Kumar S, Kaeser SA, Nagarathinam A, Walter J, Jucker M, Coomaraswamy J (2011) BRI2 protein regulates beta-amyloid degradation by increasing levels of secreted insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE). J Biol Chem 286:37446–37457
Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, Lindsley L, Eckman EA, Frosch MP, Eckman CB, Tanzi RE, Selkoe DJ, Guenette S (2003) Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4162–4167
Bernstein KE, Koronyo Y, Salumbides BC, Sheyn J, Pelissier L, Lopes DH, Shah KH, Bernstein EA, Fuchs DT, Yu JJ, Pham M, Black KL, Shen XZ, Fuchs S, Koronyo-Hamaoui M (2014) Angiotensin-converting enzyme overexpression in myelomonocytes prevents Alzheimer’s-like cognitive decline. J Clin Investig 124:1000–1012
Yin KJ, Cirrito JR, Yan P, Hu X, Xiao Q, Pan X, Bateman R, Song H, Hsu FF, Turk J, Xu J, Hsu CY, Mills JC, Holtzman DM, Lee JM (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases expressed by astrocytes mediate extracellular amyloid-beta peptide catabolism. J Neurosci 26:10939–10948
Liu RM, van Groen T, Katre A, Cao D, Kadisha I, Ballinger C, Wang L, Carroll SL, Li L (2011) Knockout of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 gene reduces amyloid beta peptide burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 32:1079–1089
Jacobsen JS, Comery TA, Martone RL, Elokdah H, Crandall DL, Oganesian A, Aschmies S, Kirksey Y, Gonzales C, Xu J, Zhou H, Atchison K, Wagner E, Zaleska MM, Das I, Arias RL, Bard J, Riddell D, Gardell SJ, Abou-Gharbia M, Robichaud A, Magolda R, Vlasuk GP, Bjornsson T, Reinhart PH, Pangalos MN (2008) Enhanced clearance of Abeta in brain by sustaining the plasmin proteolysis cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:8754–8759
Mueller-Steiner S, Zhou Y, Arai H, Roberson ED, Sun B, Chen J, Wang X, Yu G, Esposito L, Mucke L, Gan L (2006) Antiamyloidogenic and neuroprotective functions of cathepsin B: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 51:703–714
Yamin R, Zhao C, O’Connor PB, McKee AC, Abraham CR (2009) Acyl peptide hydrolase degrades monomeric and oligomeric amyloid-beta peptide. Mol Neurodegener 4:33
Hemming ML, Patterson M, Reske-Nielsen C, Lin L, Isacson O, Selkoe DJ (2007) Reducing amyloid plaque burden via ex vivo gene delivery of an Abeta-degrading protease: a novel therapeutic approach to Alzheimer disease. PLoS Med 4:e262
Jin X, Yang YD, Li YM (2008) Gene therapy: regulations, ethics and its practicalities in liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 14:2303–2307
Cabrol C, Huzarska MA, Dinolfo C, Rodriguez MC, Reinstatler L, Ni J, Yeh LA, Cuny GD, Stein RL, Selkoe DJ, Leissring MA (2009) Small-molecule activators of insulin-degrading enzyme discovered through high-throughput compound screening. PLoS ONE 4:e5274
Ayoub S, Melzig MF (2006) Induction of neutral endopeptidase (NEP) activity of SK-N-SH cells by natural compounds from green tea. J Pharm Pharmacol 58:495–501
Niikura T, Sidahmed E, Hirata-Fukae C, Aisen PS, Matsuoka Y (2011) A humanin derivative reduces amyloid beta accumulation and ameliorates memory deficit in triple transgenic mice. PLoS ONE 6:e16259
Klein C, Patte-Mensah C, Taleb O, Bourguignon JJ, Schmitt M, Bihel F, Maitre M, Mensah-Nyagan AG (2013) The neuroprotector kynurenic acid increases neuronal cell survival through neprilysin induction. Neuropharmacology 70:254–260
Smith AI, Rajapakse NW, Kleifeld O, Lomonte B, Sikanyika NL, Spicer AJ, Hodgson WC, Conroy PJ, Small DH, Kaye DM (2016) N-terminal domain of Bothrops asper myotoxin II enhances the activity of endothelin converting enzyme-1 and neprilysin. Sci Rep 6:22413
Camargo AC, Ianzer D, Guerreiro JR, Serrano SM (2012) Bradykinin-potentiating peptides: beyond captopril. Toxicon 59:516–523
Furman BL (2012) The development of Byetta (exenatide) from the venom of the Gila monster as an anti-diabetic agent. Toxicon 59:464–471
Hamad MK, He K, Abdulrazeq HF, Mustafa AM, Luceri R, Kamal N, Ali M, Nakhla J, Herzallah MM, Mammis A (2018) Potential uses of isolated toxin peptides in neuropathic pain relief: a literature review. World Neurosurg 113:333–347 e335
Dannhardt G, Kiefer W (2001) Cyclooxygenase inhibitors–current status and future prospects. Eur J Med Chem 36:109–126
McFarlane SI, Kumar A, Sowers JR (2003) Mechanisms by which angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors prevent diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol 91:30H–37H
Sweitzer NK (2003) What is an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor? Circulation 108:e16–e18
Istvan ES, Deisenhofer J (2001) Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science 292:1160–1164
van Spronsen FJ (2010) Phenylketonuria: a 21st century perspective. Nat Rev Endocrinol 6:509–514
Mehta D, Jackson R, Paul G, Shi J, Sabbagh M (2017) Why do trials for Alzheimer’s disease drugs keep failing? A discontinued drug perspective for 2010–2015. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 26:735–739
Nakamura A, Kaneko N, Villemagne VL, Kato T, Doecke J, Dore V, Fowler C, Li QX, Martins R, Rowe C, Tomita T, Matsuzaki K, Ishii K, Ishii K, Arahata Y, Iwamoto S, Ito K, Tanaka K, Masters CL, Yanagisawa K (2018) High performance plasma amyloid-beta biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 554:249–254
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Virginia Wilke and John Farrell Postgraduate Research Scholarship, the Yulgilbar Alzheimer’s Research Program and Monash University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Special Issue: In Honor of S.I. : Prof. Anthony J. Turner.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sikanyika, N.L., Parkington, H.C., Smith, A.I. et al. Powering Amyloid Beta Degrading Enzymes: A Possible Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res 44, 1289–1296 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02756-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02756-x