Abstract
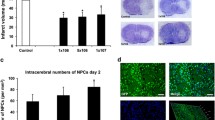
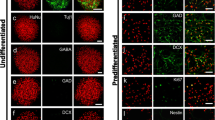
Effective transplant-mediated repair of ischemic brain lesions entails extensive tissue remodeling, especially in the ischemic core. Neural stem cells (NSCs) are promising reparative candidates for stroke induced lesions, however, their survival and integration with the host-tissue post-transplantation is poor. In this study, we address this challenge by testing whether co-grafting of NSCs with olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs), a special type of glia with proven neuroprotective, immunomodulatory, and angiogenic effects, can promote graft survival and host tissue remodelling. Transient focal cerebral ischemia was induced in adult rats by a 60-min middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo) followed by reperfusion. Ischemic lesions were verified by neurological testing and magnetic resonance imaging. Transplantation into the globus pallidus of NSCs alone or in combination with OECs was performed at two weeks post-MCAo, followed by histological analyses at three weeks post-transplantation. We found evidence of extensive vascular remodelling in the ischemic core as well as evidence of NSC motility away from the graft and into the infarct border in severely lesioned animals co-grafted with OECs. These findings support a possible role of OECs as part of an in situ tissue engineering paradigm for transplant mediated repair of ischemic brain lesions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doyle KP, Simon RP, Stenzel-Poore MP (2008) Mechanisms of ischemic brain damage. Neuropharmacology 55:310–318
Eltzschig HK, Eckle T (2011) Ischemia and reperfusion–from mechanism to translation. Nat Med 17:1391–1401
Fisher M (2004) The ischemic penumbra: identification, evolution and treatment concepts. Cerebrovasc Dis 17(Suppl 1):1–6
Robinson T, Zaheer Z, Mistri AK (2011) Thrombolysis in acute ischaemic stroke: an update. Ther Adv Chronic Dis 2:119–131
Chen L, Qiu R, Li L, He D, Lv H, Wu X, Gu N (2014) The role of exogenous neural stem cells transplantation in cerebral ischemic stroke. J Biomed Nanotechnol 10:3219–3230
Jendelova P, Kubinova S, Sandvig I, Erceg S, Sandvig A, Sykova E (2016) Current developments in cell- and biomaterial-based approaches for stroke repair. Expert Opin Biol Ther 16:43–56
Bible E, Qutachi O, Chau DY, Alexander MR, Shakesheff KM, Modo M (2012) Neo-vascularization of the stroke cavity by implantation of human neural stem cells on VEGF-releasing PLGA microparticles. Biomaterials 33:7435–7446
Patkar S, Tate R, Modo M, Plevin R, Carswell HV (2012) Conditionally immortalised neural stem cells promote functional recovery and brain plasticity after transient focal cerebral ischaemia in mice. Stem Cell Res 8:14–25
Smith EJ, Stroemer RP, Gorenkova N, Nakajima M, Crum WR, Tang E, Stevanato L, Sinden JD, Modo M (2012) Implantation site and lesion topology determine efficacy of a human neural stem cell line in a rat model of chronic stroke. Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio) 30:785–796
De Feo D, Merlini A, Laterza C, Martino G (2012) Neural stem cell transplantation in central nervous system disorders: from cell replacement to neuroprotection. Curr Opin Neurol 25:322–333
Kokaia Z, Martino G, Schwartz M, Lindvall O (2012) Cross-talk between neural stem cells and immune cells: the key to better brain repair? Nat Neurosci 15:1078–1087
Andres RH, Choi R, Steinberg GK, Guzman R (2008) Potential of adult neural stem cells in stroke therapy. Regen Med 3:893–905
Franklin RJ, Barnett SC (2000) Olfactory ensheathing cells and CNS regeneration: the sweet smell of success? Neuron 28:15–18
Dai C, Khaw PT, Yin ZQ, Li D, Raisman G, Li Y (2012) Olfactory ensheathing cells rescue optic nerve fibers in a rat glaucoma model. Transl Vis Sci Technol 1:3
Li J, Chen W, Li Y, Chen Y, Ding Z, Yang D, Zhang X (2015) Transplantation of olfactory ensheathing cells promotes partial recovery in rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:11149–11156
Li Y, Li D, Raisman G (2016) Functional repair of rat corticospinal tract lesions does not require permanent survival of an immunoincompatible transplant. Cell Transplant 25:293–299
Toft A, Scott DT, Barnett SC, Riddell JS (2007) Electrophysiological evidence that olfactory cell transplants improve function after spinal cord injury. Brain 130:970–984
Toft A, Tome M, Lindsay SL, Barnett SC, Riddell JS (2012) Transplant-mediated repair properties of rat olfactory mucosal OM-I and OM-II sphere-forming cells. J Neurosci Res 90:619–631
Sandvig I, Thuen M, Hoang L, Olsen O, Sardella TC, Brekken C, Tvedt KE, Barnett SC, Haraldseth O, Berry M, Sandvig A (2012) In vivo MRI of olfactory ensheathing cell grafts and regenerating axons in transplant mediated repair of the adult rat optic nerve. NMR Biomed 25:620–631
Lakatos A, Franklin RJ, Barnett SC (2000) Olfactory ensheathing cells and Schwann cells differ in their in vitro interactions with astrocytes. Glia 32:214–225
Lakatos A, Barnett SC, Franklin RJ (2003) Olfactory ensheathing cells induce less host astrocyte response and chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan expression than Schwann cells following transplantation into adult CNS white matter. Exp Neurol 184:237–246
Tabakow P, Raisman G, Fortuna W, Czyz M, Huber J, Li D, Szewczyk P, Okurowski S, Miedzybrodzki R, Czapiga B, Salomon B, Halon A, Li Y, Lipiec J, Kulczyk A, Jarmundowicz W (2014) Functional regeneration of supraspinal connections in a patient with transected spinal cord following transplantation of bulbar olfactory ensheathing cells with peripheral nerve bridging. Cell Transplant 23:1631–1655
Li Y, Carlstedt T, Berthold CH, Raisman G (2004) Interaction of transplanted olfactory-ensheathing cells and host astrocytic processes provides a bridge for axons to regenerate across the dorsal root entry zone. Exp Neurol 188:300–308
Chuah MI, Hale DM, West AK (2011) Interaction of olfactory ensheathing cells with other cell types in vitro and after transplantation: glial scars and inflammation. Exp Neurol 229:46–53
Memezawa H, Smith ML, Siesjo BK (1992) Penumbral tissues salvaged by reperfusion following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke 23:552–559
Haberg A, Qu H, Haraldseth O, Unsgard G, Sonnewald U (1998) In vivo injection of [1-13C]glucose and [1,2-13C]acetate combined with ex vivo 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a novel approach to the study of middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 18:1223–1232
Modo M, Rezaie P, Heuschling P, Patel S, Male DK, Hodges H (2002) Transplantation of neural stem cells in a rat model of stroke: assessment of short-term graft survival and acute host immunological response. Brain Res 958:70–82
Schallert T, Fleming SM, Leasure JL, Tillerson JL, Bland ST (2000) CNS plasticity and assessment of forelimb sensorimotor outcome in unilateral rat models of stroke, cortical ablation, parkinsonism and spinal cord injury. Neuropharmacology 39:777–787
Massensini AR, Ghuman H, Saldin LT, Medberry CJ, Keane TJ, Nicholls FJ, Velankar SS, Badylak SF, Modo M (2015) Concentration-dependent rheological properties of ECM hydrogel for intracerebral delivery to a stroke cavity. Acta Biomaterialia 27:116–130
Feigin VL, Barker-Collo S, Krishnamurthi R, Theadom A, Starkey N (2010) Epidemiology of ischaemic stroke and traumatic brain injury. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol 24:485–494
Liu SJ, Zou Y, Belegu V, Lv LY, Lin N, Wang TY, McDonald JW, Zhou X, Xia QJ, Wang TH (2014) Co-grafting of neural stem cells with olfactory en sheathing cells promotes neuronal restoration in traumatic brain injury with an anti-inflammatory mechanism. J Neuroinflammation 11:66
Shukla S, Chaturvedi RK, Seth K, Roy NS, Agrawal AK (2009) Enhanced survival and function of neural stem cells-derived dopaminergic neurons under influence of olfactory ensheathing cells in parkinsonian rats. J Neurochem 109:436–451
Li Y, Li D, Raisman G (2005) Interaction of olfactory ensheathing cells with astrocytes may be the key to repair of tract injuries in the spinal cord: the ‘pathway hypothesis’. J Neurocytol 34:343–351
Ao Q, Wang AJ, Chen GQ, Wang SJ, Zuo HC, Zhang XF (2007) Combined transplantation of neural stem cells and olfactory ensheathing cells for the repair of spinal cord injuries. Med Hypotheses 69:1234–1237
Wang G, Ao Q, Gong K, Zuo H, Gong Y, Zhang X (2010) Synergistic effect of neural stem cells and olfactory ensheathing cells on repair of adult rat spinal cord injury. Cell Transplant 19:1325–1337
Coralli C, Cemazar M, Kanthou C, Tozer GM, Dachs GU (2001) Limitations of the reporter green fluorescent protein under simulated tumor conditions. Cancer Res 61:4784–4790
Heim R, Prasher DC, Tsien RY (1994) Wavelength mutations and posttranslational autoxidation of green fluorescent protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:12501–12504
Modo M, Cash D, Mellodew K, Williams SC, Fraser SE, Meade TJ, Price J, Hodges H (2002) Tracking transplanted stem cell migration using bifunctional, contrast agent-enhanced, magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 17:803–811
Modo M, Mellodew K, Cash D, Fraser SE, Meade TJ, Price J, Williams SC (2004) Mapping transplanted stem cell migration after a stroke: a serial, in vivo magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuroimage 21:311–317
Zhu WZ, Li X, Qi JP, Tang ZP, Wang W, Wei L, Lei H (2008) Experimental study of cell migration and functional differentiation of transplanted neural stem cells co-labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide and BrdU in an ischemic rat model. Biomed Environ Sci 21:420–424
Lu P, Jones LL, Snyder EY, Tuszynski MH (2003) Neural stem cells constitutively secrete neurotrophic factors and promote extensive host axonal growth after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 181:115–129
Barnett SC, Riddell JS (2007) Olfactory ensheathing cell transplantation as a strategy for spinal cord repair–what can it achieve? Nature clinical practice. Neurology 3:152–161
Barnett SC, Riddell JS (2004) Olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs) and the treatment of CNS injury: advantages and possible caveats. J Anat 204:57–67
Ding DC, Lin CH, Shyu WC, Lin SZ (2013) Neural stem cells and stroke. Cell Transplant 22:619–630
Jackson JS, Golding JP, Chapon C, Jones WA, Bhakoo KK (2010) Homing of stem cells to sites of inflammatory brain injury after intracerebral and intravenous administration: a longitudinal imaging study. Stem Cell Res Ther 1:17
Guzman R, Uchida N, Bliss TM, He D, Christopherson KK, Stellwagen D, Capela A, Greve J, Malenka RC, Moseley ME, Palmer TD, Steinberg GK (2007) Long-term monitoring of transplanted human neural stem cells in developmental and pathological contexts with MRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:10211–10216
Nudo RJ (2007) Postinfarct cortical plasticity and behavioral recovery. Stroke 38:840–845
Reglodi D, Tamas A, Lengvari I (2003) Examination of sensorimotor performance following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Brain Res Bull 59:459–466
Schaar KL, Brenneman MM, Savitz SI (2010) Functional assessments in the rodent stroke model. Exp Transl Stroke Med 2:13
Doeppner TR, Kaltwasser B, Teli MK, Sanchez-Mendoza EH, Kilic E, Bahr M, Hermann DM (2015) Post-stroke transplantation of adult subventricular zone derived neural progenitor cells—a comprehensive analysis of cell delivery routes and their underlying mechanisms. Exp Neurol 273:45–56
Mine Y, Tatarishvili J, Oki K, Monni E, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2013) Grafted human neural stem cells enhance several steps of endogenous neurogenesis and improve behavioral recovery after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Neurobiol Dis 52:191–203
Fluri F, Schuhmann MK, Kleinschnitz C (2015) Animal models of ischemic stroke and their application in clinical research. Drug Des Dev Ther 9:3445–3454
Howells DW, Porritt MJ, Rewell SS, O’Collins V, Sena ES, van der Worp HB, Traystman RJ, Macleod MR (2010) Different strokes for different folks: the rich diversity of animal models of focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:1412–1431
Kazanis I, Gorenkova N, Zhao JW, Franklin RJ, Modo M, Ffrench-Constant C (2013) The late response of rat subependymal zone stem and progenitor cells to stroke is restricted to directly affected areas of their niche. Exp Neurol 248:387–397
Sandvig I, Karstensen K, Rokstad AM, Aachmann FL, Formo K, Sandvig A, Skjak-Braek G, Strand BL (2014) RGD-peptide modified alginate by a chemoenzymatic strategy for tissue engineering applications. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 103:896–906
Janowski M, Wagner DC, Boltze J (2015) Stem cell-based tissue replacement after stroke: factual necessity or notorious fiction? Stroke 46:2354–2363
Acknowledgements
ILA, AKH, AS, and IS would like to acknowledge funding by the Liaison Committee between the Central Norway Regional Health Authority and the Norwegian University of Science and Technology—Samarbeidsorganet HMN-NTNU. Additionally, IS and AS acknowledge funding by the Norwegian Financial Mechanism 2009–2014 and the Czech Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports under Project Contract No. MSMT-28477/2014, Project 7F14057. The authors would like to thank Dr. Marius Widerøe for technical assistance with setting up the MR scanning parameters. Many thanks to Professors Berit Strand and Michel Modo for useful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Ingrid Lovise Augestad and Axel Karl Gottfrid Nyman have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Augestad, I.L., Nyman, A.K.G., Costa, A.I. et al. Effects of Neural Stem Cell and Olfactory Ensheathing Cell Co-transplants on Tissue Remodelling After Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia in the Adult Rat. Neurochem Res 42, 1599–1609 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2098-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2098-3