Abstract
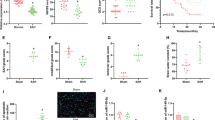
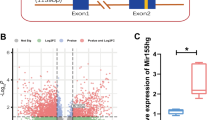
The present study was designed to evaluate the potential role of miR-93 in cerebral ischemic/reperfusion (I/R) injury in mice. The stroke model was produced in C57BL/6 J mice via middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) for 1 h followed by reperfusion. And miR-93 antagomir was transfected to down-regulate the miR-93 level. Our results showed that miR-93 levels in the cerebral cortex of mice increased at 24 and 48 h after reperfusion. Importantly, in vivo study demonstrated that treatment with miR-93 antagomir reduced cerebral infarction volume, neural apoptosis and restored the neurological scores. In vitro study demonstrated that miR-93 antagomir attenuated hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced injury. Moreover, miR-93 antagomir suppressed oxidative stress in I/R brain and H2O2 treated cortical neurons. Furthermore, we founded that down-regulation of miR-93 increased the expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and the luciferase reporter assay confirmed that miR-93 directly binds to the predicted 3′-UTR target sites of the nrf2 gene. Finally, we found that knockdown of Nrf2 or HO-1 abolished miR-93 antagomir-induced neuroprotection against oxidative stress in H2O2 treated neuronal cultures. These results suggested that miR-93 antagomir alleviates ischemic injury through the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH, Iadecola C (2010) The science of stroke: mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 67:181–198
Jung JE, Kim GS, Chen H, Maier CM, Narasimhan P, Song YS, Niizuma K, Katsu M, Okami N, Yoshioka H, Sakata H, Goeders CE, Chan PH (2010) Reperfusion and neurovascular dysfunction in stroke: from basic mechanisms to potential strategies for neuroprotection. Mol Neurobiol 41:172–179
Nguyen T, Nioi P, Pickett CB (2009) The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 284:13291–13295
Keum YS, Choi BY (2014) Molecular and chemical regulation of the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Molecules 19:10074–10089
Shah ZA, Li RC, Ahmad AS, Kensler TW, Yamamoto M, Biswal S, Dore S (2010) The flavanol (−)-epicatechin prevents stroke damage through the Nrf2/HO1 pathway. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:1951–1961
Ding Y, Chen M, Wang M, Wang M, Zhang T, Park J, Zhu Y, Guo C, Jia Y, Li Y, Wen A (2014) Neuroprotection by acetyl-11-keto-beta-Boswellic acid, in ischemic brain injury involves the Nrf2/HO-1 defense pathway. Sci Rep 4:7002
Alfieri A, Srivastava S, Siow RC, Cash D, Modo M, Duchen MR, Fraser PA, Williams SC, Mann GE (2013) Sulforaphane preconditioning of the Nrf2/HO-1 defense pathway protects the cerebral vasculature against blood–brain barrier disruption and neurological deficits in stroke. Free Radic Biol Med 65:1012–1022
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Fasanaro P, Greco S, Ivan M, Capogrossi MC, Martelli F (2010) microRNA: emerging therapeutic targets in acute ischemic diseases. Pharmacol Ther 125:92–104
Huang Y, Shen XJ, Zou Q, Zhao QL (2010) Biological functions of microRNAs. Bioorg Khim 36:747–752
Zhao Y, Srivastava D (2007) A developmental view of microRNA function. Trends Biochem Sci 32:189–197
Dharap A, Bowen K, Place R, Li LC, Vemuganti R (2009) Transient focal ischemia induces extensive temporal changes in rat cerebral microRNAome. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:675–687
Tan JR, Koo YX, Kaur P, Liu F, Armugam A, Wong PT, Jeyaseelan K (2011) microRNAs in stroke pathogenesis. Curr Mol Med 11:76–92
Rink C, Khanna S (2011) MicroRNA in ischemic stroke etiology and pathology. Physiol Genomics 43:521–528
Zhang JF, Shi LL, Zhang L, Zhao ZH, Liang F, Xu X, Zhao LY, Yang PB, Zhang JS, Tian YF (2016) MicroRNA-25 negatively regulates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced cell apoptosis through Fas/FasL pathway. J Mol Neurosci. doi:10.1007/s12031-016-0712-0
Fabbri E, Borgatti M, Montagner G, Bianchi N, Finotti A, Lampronti I, Bezzerri V, Dechecchi MC, Cabrini G, Gambari R (2014) Expression of microRNA-93 and Interleukin-8 during Pseudomonas aeruginosa-mediated induction of proinflammatory responses. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 50:1144–1155
Singh B, Ronghe AM, Chatterjee A, Bhat NK, Bhat HK (2013) MicroRNA-93 regulates NRF2 expression and is associated with breast carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 34:1165–1172
Rouse M, Rao R, Nagarkatti M, Nagarkatti PS (2014) 3,3′-Diindolylmethane ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by promoting cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in activated T cells through microRNA signaling pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 350:341–352
Han RQ, Ouyang YB, Xu L, Agrawal R, Patterson AJ, Giffard RG (2009) Postischemic brain injury is attenuated in mice lacking the beta2-adrenergic receptor. Anesth Analg 108:280–287
Xiong X, Barreto GE, Xu L, Ouyang YB, Xie X, Giffard RG (2011) Increased brain injury and worsened neurological outcome in interleukin-4 knockout mice after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 42:2026–2032
Rodriguez R, Santiago-Mejia J, Gomez C, San-Juan ER (2005) A simplified procedure for the quantitative measurement of neurological deficits after forebrain ischemia in mice. J Neurosci Methods 147:22–28
Liu P, Zhao H, Wang R, Wang P, Tao Z, Gao L, Yan F, Liu X, Yu S, Ji X, Luo Y (2015) MicroRNA-424 protects against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in mice by suppressing oxidative stress. Stroke 46:513–519
Wang P, Liang J, Li Y, Li J, Yang X, Zhang X, Han S, Li S, Li J (2014) Down-regulation of miRNA-30a alleviates cerebral is-chemic injury through enhancing beclin 1-mediated autophagy. Neurochem Res 39:1279–1291
Zhao H, Tao Z, Wang R, Liu P, Yan F, Li J, Zhang C, Ji X, Luo Y (2014) MicroRNA-23a-3p attenuates oxidative stress injury in a mouse model of focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Brain Res 1592:65–72
Wang L, Wang Q, Li HL, Han LY (2013) Expression of MiR200a, miR93, metastasis-related gene RECK and MMP2/MMP9 in human cervical carcinoma–relationship with prognosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:2113–2118
Kim BH, Hong SW, Kim A, Choi SH, Yoon SO (2013) Prognostic implications for high expression of oncogenic microRNAs in advanced gastric carcinoma. J Surg Oncol 107:505–510
Ohta K, Hoshino H, Wang J, Ono S, Iida Y, Hata K, Huang SK, Colquhoun S, Hoon DS (2015) MicroRNA-93 activates c-Met/PI3K/Akt pathway activity in hepatocellular carcinoma by directly inhibiting PTEN and CDKN1A. Oncotarget 6:3211–3224
Li G, Ren S, Su Z, Liu C, Deng T, Huang D, Tian Y, Qiu Y, Liu Y (2015) Increased expression of miR-93 is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol 36:3949–3956
Montanini L, Lasagna L, Barili V, Jonstrup SP, Murgia A, Pazzaglia L, Conti A, Novello C, Kjems J, Perris R, Benassi MS (2012) MicroRNA cloning and sequencing in osteosarcoma cell lines: differential role of miR-93. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 35: 29–41
Yang IP, Tsai HL, Hou MF, Chen KC, Tsai PC, Huang SW, Chou WW, Wang JY, Juo SH (2012) MicroRNA-93 inhibits tumor growth and early relapse of human colorectal cancer by affecting genes involved in the cell cycle. Carcinogenesis 33:1522–1530
Tang Q, Zou Z, Zou C, Zhang Q, Huang R, Guan X, Li Q, Han Z, Wang D, Wei H, Gao X, Wang X (2015) MicroRNA-93 suppress colorectal cancer development via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway downregulating. Tumour Biol 36:1701–1710
Tasoulis MK, Douzinas EE (2016) Hypoxemic reperfusion of ischemic states: an alternative approach for the attenuation of oxidative stress mediated reperfusion injury. J Biomed Sci 23:7
Halladin NL (2015) Oxidative and inflammatory biomarkers of ischemia and reperfusion injuries. Dan Med J 62:B5054
Manzanero S, Santro T, Arumugam TV (2013) Neuronal oxidative stress in acute ischemic stroke: sources and contribution to cell injury. Neurochem Int 62:712–718
Jiang S, Deng C, Lv J, Fan C, Hu W, Di S, Yan X, Ma Z, Liang Z, Yang Y (2016) Nrf2 Weaves an Elaborate Network of Neuroprotection Against Stroke. Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-016-9707-7
Alfieri A, Srivastava S, Siow RC, Modo M, Fraser PA, Mann GE (2011) Targeting the Nrf2-Keap1 antioxidant defence pathway for neurovascular protection in stroke. J Physiol 589:4125–4136
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 81501017), Innovation Foundation for the Unversity Students (Grant No. 201510160000013) and the President Foundation of Jinzhou Medical University (Grant No. XZJJ20140105, XZJJ2015012). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Liang, X., Lu, Y. et al. MicroRNA-93 Downregulation Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemic Injury Through the Nrf2/HO-1 Defense Pathway. Neurochem Res 41, 2627–2635 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1975-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1975-0