Abstract
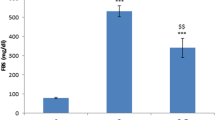
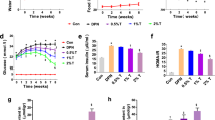
Neuroprotective effects of metformin have been increasingly recognized in both diabetic and non-diabetic conditions. Thus far, no information has been available on the potential beneficial effects of metformin on peripheral nerve regeneration in diabetes mellitus. The present study was designed to investigate such a possibility. Diabetes was established by a single injection of streptozotocin at 50 mg/kg in rats. After sciatic nerve crush injury, the diabetic rats were intraperitoneally administrated daily for 4 weeks with metformin (30, 200 and 500 mg/kg), or normal saline, respectively. The axonal regeneration was investigated by morphometric analysis and retrograde labeling. The functional recovery was evaluated by electrophysiological studies and behavioral analysis. It was found that metformin significantly enhanced axonal regeneration and functional recovery compared to saline after sciatic nerve injury in diabetic rats. In addition, metformin at 200 and 500 mg/kg showed better performance than that at 30 mg/kg. Taken together, metformin is capable of promoting nerve regeneration after sciatic nerve injuries in diabetes mellitus, highlighting its therapeutic values for peripheral nerve injury repair in diabetes mellitus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C et al (2011) IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 94:311–321
Kennedy JM, Zochodne DW (2005) Impaired peripheral nerve regeneration in diabetes mellitus. J Peripher Nerv Syst 10:144–157
Nishida N, Yamagishi S, Mizukami H et al (2013) Impaired nerve fiber regeneration in axotomized peripheral nerves in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. J Diabetes Investig 4:533–539
Kirpichnikov D, McFarlane SI, Sowers JR (2002) Metformin: an update. Ann Intern Med 137:25–33
Cahova M, Palenickova E, Dankova H et al (2015) Metformin prevents ischemia reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in the fatty liver by attenuation of reactive oxygen species formation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 309:G100–G111
Scheen AJ, Esser N, Paquot N (2015) Antidiabetic agents: potential anti-inflammatory activity beyond glucose control. Diabetes Metab 41:183–194
Morales DR, Morris AD (2015) Metformin in cancer treatment and prevention. Annu Rev Med 66:17–29
Melemedjian OK, Asiedu MN, Tillu DV et al (2011) Targeting adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in preclinical models reveals a potential mechanism for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 7:70
Taylor A, Westveld AH, Szkudlinska M et al (2013) The use of metformin is associated with decreased lumbar radiculopathy pain. J Pain Res 6:755–763
Melemedjian OK, Yassine HN, Shy A et al (2013) Proteomic and functional annotation analysis of injured peripheral nerves reveals ApoE as a protein upregulated by injury that is modulated by metformin treatment. Mol Pain 9:14
Tanaka Y, Uchino H, Shimizu T et al (1999) Effect of metformin on advanced glycation endproduct formation and peripheral nerve function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 376:17–22
Ma J, Yu H, Liu J et al (2015) Metformin attenuates hyperalgesia and allodynia in rats with painful diabetic neuropathy induced by Streptozotocin. Eur J Pharmacol 764:599–606
Bain JR, Mackinnon SE, Hunter DA (1989) Functional evaluation of complete sciatic, peroneal, and posterior tibial nerve lesions in the rat. Plast Reconstr Surg 83:129–138
Huang J, Lu L, Zhang J et al (2012) Electrical stimulation to conductive scaffold promotes axonal regeneration and remyelination in a rat model of large nerve defect. PLoS One 7:e39526
Huang J, Zhang Y, Lu L et al (2013) Electrical stimulation accelerates nerve regeneration and functional recovery in delayed peripheral nerve injury in rats. Eur J Neurosci 38:3691–3701
Wang Y, Qi F, Zhu S et al (2013) A synthetic oxygen carrier in fibrin matrices promotes sciatic nerve regeneration in rats. Acta Biomater 9:7248–7263
Zhu S, Ge J, Wang Y et al (2014) A synthetic oxygen carrier-olfactory ensheathing cell composition system for the promotion of sciatic nerve regeneration. Biomaterials 35:1450–1461
Huang J, Hu X, Lu L et al (2009) Electrical stimulation accelerates motor functional recovery in autograft-repaired 10 mm femoral nerve gap in rats. J Neurotrauma 26:1805–1813
Huang J, Lu L, Hu X et al (2010) Electrical stimulation accelerates motor functional recovery in the rat model of 15-mm sciatic nerve gap bridged by scaffolds with longitudinally oriented microchannels. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 24:736–745
Ma J, Liu J, Yu H (2013) Curcumin promotes nerve regeneration and functional recovery in rat model of nerve crush injury. Neurosci Lett 547:26–31
Currie CJ, Poole CD, Evans M et al (2013) Mortality and other important diabetes-related outcomes with insulin vs other antihyperglycemic therapies in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:668–677
Kamijo M, Merry AC, Akdas G et al (1996) Nerve fiber regeneration following axotomy in the diabetic biobreeding Worcester rat: the effect of ARI treatment. J Diabetes Complicat 10:183–191
Saito H, Sango K, Horie H et al (1999) Enhanced neural regeneration from transected vagus nerve terminal in diabetic mice in vitro. Neuroreport 10:1025–1028
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81501079), the Young Medical Scientists Training Project of Chinese PLA (14QNP002) and the Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Liaoning Province of China (201501028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no competing interest exists.
Additional information
Junxiong Ma and Jun Liu have equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Liu, J., Yu, H. et al. Beneficial Effect of Metformin on Nerve Regeneration and Functional Recovery After Sciatic Nerve Crush Injury in Diabetic Rats. Neurochem Res 41, 1130–1137 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1803-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1803-y