Abstract
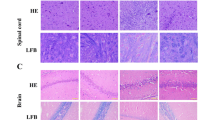
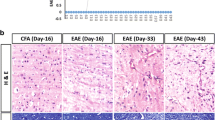
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is commonly induced with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)35–55; occasionally, EAE is not well induced despite MOG35–55 immunization. To confirm that EAE induction varies with difference in MOG35–55 properties, we compared three MOG35–55 from different commercial sources, which are MOG-A, MOG-B, and MOG-C. The peptides induced EAE disease with 100, 40, and 20 % incidence, respectively. Compared with others, MOG-A showed higher peptide purity (99.2 %) and content (92.2 %) and presented a sheet shape with additional sodium and chloride chemical elements. In MOG-A-treated group, MMP-9 activity and IL-6 levels were considerably higher than the other groups in CNS tissues, and significantly increased VCAM-1, IFN-γ, and decreased IL-4 were also shown compared to MOG-B- and/or MOG-C-treated group. In conclusion, the immunological and toxicological changes by the difference in MOG35–55 properties modulate EAE induction, and MOG35–55 which affects MMP-9 activity and IL-6 levels may be the most effective EAE-inducing antigen. This study can be potentially applied by researchers using MOG35-55 peptide and manufacturers for MOG35-55 synthesis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller SD, Karpus WJ, Davidson TS (2010) Chapter 15, Unit 15.1, Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the mouse. Curr Protoc Immunol 88:15.1.1–15.1.20
Gold R, Linington C, Lassmann H (2006) Understanding pathogenesis and therapy of multiple sclerosis via animal models: 70 years of merits and culprits in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis research. Brain 129:1953–1971
Clements CS, Reid HH, Beddoe T, Tynan FE, Perugini MA, Johns TG, Bernard CCA, Rossjohn J (2003) The crystal structure of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein, a key autoantigen in multiple sclerosis. P Natl Acad Sci USA 100:11059–11064
Mendel I, Kerlero de Rosbo N, Ben-Nun A (1995) A myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein peptide induces typical chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in H-2b mice: fine specificity and T cell receptor V beta expression of encephalitogenic T cells. Eur J Immunol 25:1951–1959
Ransohoff RM (2012) Animal models of multiple sclerosis: the good, the bad and the bottom line. Nat Neurosci 15:1074–1077
Leuenberger T, Paterka M, Reuter E, Herz J, Niesner RA, Radbruch H, Bopp T, Zipp F, Siffrin V (2013) The role of CD8 + T cells and their local interaction with CD4 + T cells in myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein35-55-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 191:4960–4968
Stromnes IM, Goverman JM (2006) Active induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Nat Protoc 1:1810–1819
Fletcher JM, Lalor SJ, Sweeney CM, Tubridy N, Mills KHG (2010) T cells in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Clin Exp Immunol 162:1–11
Goverman J (2009) Autoimmune T cell responses in the central nervous system. Nat Rev Immunol 9:393–407
Lalive PH, Molnarfi N, Benkhoucha M, Weber MS, Santiago-Raber ML (2011) Antibody response in MOG (35–55) induced EAE. J Neuroimmunol 240–241:28–33
Boullerne AI, Polak PE, Braun D, Sharp A, Pelligrino D, Feinstein DL (2014) Effects of peptide fraction and counter ion on the development of clinical signs in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurochem 129:696–703
Berer K, Mues M, Koutrolos M, Rasbi ZA, Boziki M, Johner C, Wekerle H, Krishnamoorthy G (2011) Commensal microbiota and myelin autoantigen cooperate to trigger autoimmune demyelination. Nature 479:538–541
Sharp AJ, Polak PE, Simonini V, Lin SX, Richardson JC, Bongarzone ER, Feinstein DL (2008) P2x7 deficiency suppresses development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroinflamm 5:33
Sinha S, Subramanian S, Proctor TM, Kaler LJ, Grafe M, Dahan R, Huan J, Vandenbark AA, Burrows GG, Offner H (2007) A promising therapeutic approach for multiple sclerosis: recombinant T-cell receptor ligands modulate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by reducing interleukin-17 production and inhibiting migration of encephalitogenic cells into the CNS. J Neurosci 27:12531–12539
Haque MM, Im HY, Seo JE, Hasan M, Woo K, Kwon OS (2013) Acute toxicity and tissue distribution of CdSe/CdS-MPA quantum dots after repeated intraperitoneal injection to mice. J Appl Toxicol 33:940–950
Itoh S, Hamada E, Kamoshida G, Takeshita K, Oku T, Tsuji T (2010) Staphylococcal superantigen-like protein 5 inhibits matrix metalloproteinase 9 from human neutrophils. Infect Immun 78:3298–3305
Nicolson K, Freland S, Weir C, Delahunt B, Flavell RA, Backstrom BT (2002) Induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the absence of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2. Int Immunol 14:849–856
Sestero CM, McGuire DJ, De Sarno P, Brantley EC, Soldevila G, Axtell RC, Raman C (2012) CD5-dependent CK2 activation pathway regulates threshold for T cell anergy. J Immunol 189:2918–2930
Yu M, Tang T, Takasu A, Higuchi M (2014) pH- and thermo-induced morphological changes of an amphiphilic peptide-grafted copolymer in solution. Polym J 46:52–58
Abdelwahed W, Degobert G, Stainmesse S, Fessi H (2006) Freeze-drying of nanoparticles: formulation, process and storage considerations. Adv Drug Deliver Rev 58:1688–1713
You Q, Cheng LL, Ju C (2010) Generation of T cell responses targeting the reactive metabolite of halothane in mice. Toxicol Lett 194:79–85
Bae H, Lee J (2015) Morphology control of eprosartan crystals via polymer-directed crystallization. J Pharm Invest 45:367–374
Seo J-E, Hasan M, Han J-S, Kang M-J, Jung B-H, Kwok S-K, Kim H-Y, Kwon O-S (2015) Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and age-related correlations of NADPH oxidase, MMP-9, and cell adhesion molecules: the increased disease severity and blood–brain barrier permeability in middle-aged mice. J Neuroimmunol 287:43–53
Gold SM, Sasidhar MV, Morales LB, Du S, Sicotte NL, Tiwari-Woodruff SK, Voskuhl RR (2009) Estrogen treatment decreases matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 in autoimmune demyelinating disease through estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha). Lab Invest 89:1076–1083
Yong VW (2005) Metalloproteinases: mediators of pathology and regeneration in the CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:931–944
Ninkovic M, Stevanovic I, Stojanovic I, Ljubisavljevic S, Basic J, Peric P (2015) The use of agmatine provides the new insight in an experimental model of multiple sclerosis. Neurochem Res. doi:10.1007/s11064-015-1655-5
Song J, Wu C, Korpos E, Zhang XL, Agrawal SM, Wang Y, Faber C, Schafers M, Korner H, Opdenakker G, Hallmann R, Sorokin L (2015) Focal MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity at the blood-brain barrier promotes chemokine-induced leukocyte migration. Cell Rep 10:1040–1054
Konnecke H, Bechmann I (2013) The role of microglia and matrix metalloproteinases involvement in neuroinflammation and gliomas. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:914104
Linker RA, Luhder F, Kallen KJ, Lee DH, Engelhardt B, Rose-John S, Gold R (2008) IL-6 transsignalling modulates the early effector phase of EAE and targets the blood-brain barrier. J Neuroimmunol 205:64–72
Eng LF, Ghirnikar RS, Lee YL (1996) Inflammation in EAE: role of chemokine/cytokine expression by resident and infiltrating cells. Neurochem Res 21:511–525
Jadidi-Niaragh F, Mirshafiey A (2011) Th17 cell, the new player of neuroinflammatory Process in multiple sclerosis. Scand J Immunol 74:1–13
Hofmann N, Lachnit N, Streppel M, Witter B, Neiss WF, Guntinas-Lichius O, Angelov DN (2002) Increased expression of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, MCP-1, and MIP-1 alpha by spinal perivascular macrophages during experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats. BMC Immunol 3:11
Minagar A, Alexander JS (2003) Blood-brain barrier disruption in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 9:540–549
Liblau R, Steinman L, Brocke S (1997) Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in IL-4-deficient mice. Int Immunol 9:799–803
Broberg EK, Salmi AA, Hukkanen V (2004) IL-4 is the key regulator in herpes simplex virus-based gene therapy of BALB/c experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurosci Lett 364:173–178
Weir C, Bernard CC, Backstrom BT (2003) IL-5-deficient mice are susceptible to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int Immunol 15:1283–1289
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Korea Institute of Science and Technology (2V03600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, JE., Hasan, M., Han, JS. et al. Dependency of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Induction on MOG35–55 Properties Modulating Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 and Interleukin-6. Neurochem Res 41, 666–676 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1732-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1732-9