Abstract
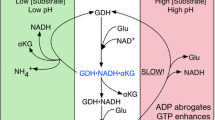
Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) is a homohexameric enzyme that catalyzes the reversible oxidative deamination of l-glutamate to 2-oxoglutarate. Only in the animal kingdom is this enzyme heavily allosterically regulated by a wide array of metabolites. The major activators are ADP and leucine and inhibitors include GTP, palmitoyl CoA, and ATP. Spontaneous mutations in the GTP inhibitory site that lead to the hyperinsulinism/hyperammonemia (HHS) syndrome have shed light as to why mammalian GDH is so tightly regulated. Patients with HHS exhibit hypersecretion of insulin upon consumption of protein and concomitantly extremely high levels of ammonium in the serum. The atomic structures of four new inhibitors complexed with GDH complexes have identified three different allosteric binding sites. Using a transgenic mouse model expressing the human HHS form of GDH, at least three of these compounds blocked the dysregulated form of GDH in pancreatic tissue. EGCG from green tea prevented the hyper-response to amino acids in whole animals and improved basal serum glucose levels. The atomic structure of the ECG–GDH complex and mutagenesis studies is directing structure-based drug design using these polyphenols as a base scaffold. In addition, all of these allosteric inhibitors are elucidating the atomic mechanisms of allostery in this complex enzyme.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hudson RC, Daniel RM (1993) l-Glutamate dehydrogenases: distribution, properties and mechanism. Comp Biochem Physiol 106B:767–792
Frieden C (1965) Glutamate dehydrogenase VI. Survey of purine nucleotides and other effects on the enzyme from various sources. J Biol Chem 240:2028–2037
George SA, Bell JE (1980) Effects of adenosine 5′-diphosphate on bovine glutamate dehydrogenase: diethyl pyrocarbonate modification. Biochemistry 19:6057–6061
Bailey JS, Bell ET, Bell JE (1982) Regulation of bovine glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 257:5579–5583
Iwatsubo M, Pantaloni D (1967) Regulation De L’ Activite’ De La glutamate dehydrogenase par les effecteurs GTP et ADP: ETUDE par “stopped flow”. Bull Soc Chem Biol 49:1563–1572
Koberstein R, Sund H (1973) The influence of ADP, GTP and l-glutamate on the binding of the reduced coenzyme to beef-liver glutamate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem 36:545–552
Dieter H, Koberstein R, Sund H (1981) Studies of glutamate dehydrogenase. The interaction of ADP, GTP, and NADPH in complexes with glutamate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem 115:217–226
Smith TJ, Schmidt T, Fang J, Wu J, Siuzdak G, Stanley CA (2002) The structure of apo human glutamate dehydrogenase details subunit communication and allostery. J Mol Biol 318:765–777
Banerjee S, Schmidt T, Fang J, Stanley CA, Smith TJ (2003) Structural studies on ADP activation of mammalian glutamate dehydrogenase and the evolution of regulation. Biochemistry 42:3446–3456
Yielding KL, Tomkins GM (1961) An effect of l-leucine and other essential amino acids on the structure and activity of glutamate dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci 47:983
Prough RA, Culver JM, Fisher HF (1973) The mechanism of activation of glutamate dehydrogenase-catalyzed reactions by two different, cooperatively bound activators. J Biol Chem 248:8528–8533
Fahien LA, Kmiotek E (1981) Regulation of glutamate dehydrogenase by palmitoyl-coenzyme A. Arch Biochem Biophys 212:247–253
Tomkins GM, Yielding KL, Curran JF (1962) The influence of diethylstilbestrol and adenosine diphosphate on pyridine nucleotide coenzyme binding by glutamic dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 237:1704–1708
Peterson PE, Smith TJ (1999) The structure of bovine glutamate dehydrogenase provides insights into the mechanism of allostery. Structure Fold Des 7:769–782
Smith TJ, Peterson PE, Schmidt T, Fang J, Stanley C (2001) Structures of bovine glutamate dehydrogenase complexes elucidate the mechanism of purine regulation. J Mol Biol 307:707–720
Frieden C (1963) Different structural forms of reversibly dissociated glutamic dehydrogenase: relation between enzymatic activity and molecular weight. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 10:410–415
Frieden C (1959) Glutamic dehydrogenase I. The effect of coenzyme on the sedimentation velocity and kinetic mechanism. J Biol Chem 234:809–814
Frieden C (1959) Glutamic dehydrogenase II The effect of various nucleotides on the association-disassociation and kinetic properties. J Biol Chem 234:815–819
Shafer JA, Chiancone E, Vittorelli LM, Spagnuolo C, Machler B, Antonini E (1972) Binding of reduced cofactor to glutamate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem 31:166–171
Limuti CM (1983) Glutamate dehydrogenase: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Ph.D., University of Rochester
Batra SP, Colman RF (1986) Isolation and identification of cysteinyl peptide labeled by 6-[(4-bromo-2,3-dioxobutyl)thio]-6-deaminoadenosine 5′-diphosphate in the reduced diphosphopyridine nucleotide inhibitory site of glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry 25:3508–3515
Stanley CA, Lieu YK, Hsu BY, Burlina AB, Greenberg CR, Hopwood NJ, Perlman K, Rich BH, Zammarchi E, Poncz M (1998) Hyperinsulinism and hyperammonemia in infants with regulatory mutations of the glutamate dehydrogenase gene. N Engl J Med 338:1352–1357
Sener A, Malaisse WJ (1980) l-Leucine and a nonmetabolized analogue activate pancreatic islet glutamate dehydrogenase. Nature 288:187–189
Sener A, Malaisse-Lagae F, Malaisse WJ (1981) Stimulation of pancreatic islet metabolism and insulin release by a nonmetabolizable amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:5460–5464
Fahien LA, MacDonald MJ, Kmiotek EH, Mertz RJ, Fahien CM (1988) Regulation of insulin release by factors that also modify glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 263:13610–13614
Li C, Najafi H, Daikhin Y, Nissim I, Collins HW, Yudkoff M, Matschinsky FM, Stanley CA (2003) Regulation of leucine stimulated insulin secretion and glutamine metabolism in isolated rat islets. J Biol Chem 278:2853–2858
Li C, Buettger C, Kwagh J, Matter A, Daihkin Y, Nissiam I, Collins HW, Yudkoff M, Stanley CA, Matschinsky FM (2004) A signaling role of glutamine in insulin secretion. J Biol Chem 279:13393–13401
Stanley CA (2000) The hyperinsulinism-hyperammonemia syndrome: gain-of-function mutations of glutamate dehydrogenase. In: O’Rahilly S, Dunger DB (eds) Genetic insights in paediatric endocrinology and metabolism. BioScientifica Ltd., Bristol, pp 23–30
Stanley CA, Fang J, Kutyna K, Hsu BYL, Ming JE, Glaser B, Poncz M (2000) Molecular basis and characterization of the hyperinsulinism/hyperammonemia syndrome of the glutamate dehydrogenase gene. Diabetes 49:667–673
MacMullen C, Fang J, Hsu BYL, Kelly A, deLonlay-Debeney P, Saudubray JM, Ganguly A, Smith TJ, Stanley CA (2001) The Hyperinsulinism/hyperammonemia Contributing Investigators. Hyperinsulinism/hyperammonemia syndrome in children with regulatory mutations in the inhibitory guanosine triphosphate-binding domain of glutamate dehydrogenase. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:1782–1787
Hsu BY, Kelly A, Thornton PS, Greenberg CR, Dilling LA, Stanley CA (2001) Protein-sensitive and fasting hypoglycemia in children with the hyperinsulinism/hyperammonemia syndrome. J Pediatr 138:383–389
Bahi-Buisson N, Roze E, Dionisi C, Escande F, Valayannopoulos V, Feillet F, Heinrichs C (2008) Neurological aspects of hyperinsulinism-hyperammonaemia syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol 50:945–949
Herrero-Yraola A, Bakhit SM, Franke P, Weise C, Schweiger M, Jorcke D, Ziegler M (2001) Regulation of glutamate dehydrogenase by reversible ADP-ribosylation in mitochondria. EMBO J 20:2404–2412
Haigis MC, Mostoslavsky R, Haigis KM, Fahie K, Christodoulou DC, Murphy AJ, Valenzuela DM, Yancopoulos GD, Karow M, Blander G, Wolberger C, Prolla TA, Weindruch R, Alt FW, Guarente L (2006) SIRT4 inhibits glutamate dehydrogenase and opposes the effects of calorie restriction in pancreatic beta cells. Cell 126:941–954
Hussain K, Clayton PT, Krywawych S, Chatziandreou I, Mills P, Ginbey DW, Geboers AJ, Berger R, van den Berg IE, Eaton S (2005) Hyperinsulinism of infancy associated with a novel splice site mutation in the SCHAD gene. J Pediatr 146:706–708
Jackson S, Bartlett K, Land J, Moxon ER, Pollitt RJ, Leonard JV, Turnbull DM (1991) Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Pediatr Res 29:406–411
Molven A, Matre GE, Duran M, Wanders RJ, Rishaug U, Njolstad PR, Jellum E, Sovik O (2004) Familial hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia caused by a defect in the SCHAD enzyme of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. Diabetes 53:221–227
Kapoor RR, James C, Flanagan SE, Ellard S, Eaton S, Hussain K (2009) 3-Hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency and hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia: characterization of a novel mutation and severe dietary protein sensitivity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:2221–2225
Stanley C, Bennett MJ, Mayatepek E (2006) Disorders of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and related metabolic pathways. In: Fernandes J, Saudubray J-M, van den Berg G, Walter JH (eds) Inborn metabolic diseases, 4th edn. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 177–188
Li C, Chen P, Palladino A, Narayan S, Russell LK, Sayed S, Xiong G, Chen J, Stokes D, Butt YM, Jones PM, Collins HW, Cohen NA, Cohen AS, Nissim I, Smith TJ, Strauss AW, Matschinsky FM, Bennett MJ, Stanley CA (2010) Mechanism of hyperinsulinism in short-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency involves activation of glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 285:31806–31818
Filling C, Kelier B, Hirschberg D, Marschall H-U, Jörnvall H, Bennett MJ, Oppermann U (2008) Role of short-chain hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenases in SCHAD deficiency. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 368:6–11
Allen A, Kwagh J, Fang J, Stanley CA, Smith TJ (2004) Evolution of glutamate dehydrogenase regulation of insulin homeostasis is an example of molecular exaptation. Biochemistry 43:14431–14443
Gerhardt B (1992) Fatty acid degradation in plants. Prog Lipid Res 31:417–446
Erdmann R, Veenhuis M, Kunau WH (1997) Peroxisomes: organelles at the crossroads. Trends Cell Biol 7:400–407
Muller M, Hogg JF, De Duve C (1968) Distribution of tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes and glyoxylate cycle enzymes between mitochondria and peroxisomes in Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Biol Chem 243:5385–5395
Blum JJ (1973) Localization of some enzymes of β-oxidation of fatty acids in the peroxisomes of Tetrahymena. J Protozool 20:688–692
Reddy JK, Mannaerts GP (1994) Peroxisomal lipid metabolism. Ann Rev Nutrition 14:343–370
Hashimoto T (1999) Peroxisomal beta-oxidation enzymes. Neurochem Res 24:551–563
Kibbey RG, Pongratz RL, Romanelli AJ, Wollheim CB, Cline GW, Shulman GI (2007) Mitochondrial GTP regulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Cell Metab 5:253–264
Stanley CA, Baker L (1976) Hyperinsulinism in infants and children: diagnosis and therapy. Adv Pediatr 23:315–355
Li M, Allen A, Smith TJ (2007) High throughput screening reveals several new classes of glutamate dehydrogenase inhibitors. Biochemistry 46:15089–15102
Li M, Smith CJ, Walker MT, Smith TJ (2009) Novel inhibitors complexed with glutamate dehydrogenase: allosteric regulation by control of protein dynamics. J Biol Chem 284:22988–23000
Tomita T, Kuzuyama T, Nishiyama M (2011) Structural basis for leucine-induced allosteric activation of glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 286:37406–37413
Li C, Li M, Narayan S, Matschinsky FM, Bennet MJ, Stanley CA, Smith TJ (2011) Green tea polyphenols control dysregulated glutamate dehydrogenase in transgenic mice by hijacking the ADP activation site. J Biol Chem 286:34164–34174
Li C, Allen A, Kwagh K, Doliba NM, Qin W, Najafi H, Collins HW, Matschinsky FM, Stanley CA, Smith TJ (2006) Green tea polyphenols modulate insulin secretion by inhibiting glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 281:10214–10221
Smith TJ (2011) Green tea polyphenols in drug discovery—a success or failure? Expert Opin Drug Discov 6:589–595
Yang C, Sudderth J, Dang T, Bachoo RG, McDonald JG, DeBerardinis RJ (2009) Glioblastoma cells require glutamate dehydrogenase to survive impairments of glucose metabolism or Akt signaling. Cancer Res 69:7986–7993
Choo AY, Kim SG, Vander Heiden MG, Mahoney SJ, Vu H, Yoon S-O, Cantley LC, Blenis J (2010) Glucose addiction of TSC null cells Is caused by failed mTORC1-dependent balancing of metabolic demand with supply. Mol Cell 38:487–499
Han SJ, Choi S-E, Yi S-A, Lee S-J, Kim HK, Kim DJ, Lee HC, Lee KW, Kang Y (2012) β-Cell-protective effect of 2-aminobicyclo-(2,2,1)-heptane-2-carboxylic acid as a glutamate dehydrogenase activator in db/db mice. J Endocrinol 212:307–315
Smith TJ, Stanley CA (2008) Untangling the glutamate dehydrogenase allosteric nightmare. Trends Biol Chem 33:557–564
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) Grant DK072171 (to T.J.S.), NIH Grant DK53012 and American Diabetes Association Research Award 1-05-RA-128 (to C.A.S.), and NIH Grant DK19525 for islet biology and radioimmunoassay cores. A special thanks goes to Blue California (www.bluecal-ingredients.com) for the generous gift of EGCG used for the whole animal studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Li, C., Allen, A. et al. Glutamate Dehydrogenase: Structure, Allosteric Regulation, and Role in Insulin Homeostasis. Neurochem Res 39, 433–445 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1173-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1173-2