Abstract
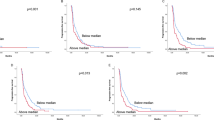
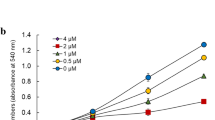
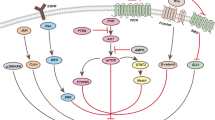
Glioma is one of the most malignant tumors in the central nervous system. As a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPAR-γ) activator, the thiazolidinediones (TZDs) induce growth arrest and cell death in a broad spectrum of tumor cells. In this study, we investigated the role of rosiglitazone in glioma cells. We found that rosiglitazone, a member of TZDs, suppresses growth of human glioma cell lines U87 and U251. Rosiglitazone also induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, which may be the mechanism of its anti-proliferation effect. Next, we found that rosiglitazone suppresses the expression of TGF-beta and its receptor TGF-betaR2, and suppresses phosphorylation of Smad3. Rosiglitazone also inhibits formation of the Smad3/Smad4 complex. Furthermore, Rosiglitazone affects the expression of Smad3/Smad4 associated regulators of gene expression, including p21 and c-Myc. These results suggest that rosiglitazone suppresses growth and cell cycle of human glioma cells by blocking the TGF-beta mediated pathway.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kazumoto K (2001) Brain tumor. Nihon Rinsho 59(Suppl 7):257–266
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2005) Epidemiology and etiology of gliomas. Acta Neuropathol 109:93–108
Wick W, Platten M, Weller M (2001) Glioma cell invasion: regulation of metalloproteinase activity by TGF-beta. J Neurooncol 53:177–185
Wick W, Naumann U, Weller M (2006) Transforming growth factor-beta: a molecular target for the future therapy of glioblastoma. Curr Pharm Des 12:341–349
Wrana JL, Attisano L, Carcamo J, Zentella A, Doody J, Laiho M, Wang XF, Massague J (1992) TGF beta signals through a heteromeric protein kinase receptor complex. Cell 71:1003–1014
Henry RR (1997) Thiazolidinediones. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 26:553–573
Saltiel AR, Olefsky JM (1996) Thiazolidinediones in the treatment of insulin resistance and type II diabetes. Diabetes 45:1661–1669
Feinstein DL (2003) Therapeutic potential of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists for neurological disease. Diabetes Technol Ther 5:67–73
Na HK, Surh YJ (2003) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) ligands as bifunctional regulators of cell proliferation. Biochem Pharmacol 66:1381–1391
Kim JA, Park KS, Kim HI, Oh SY, Ahn Y, Oh JW, Choi KY (2002) Troglitazone activates p21Cip/WAF1 through the ERK pathway in HCT15 human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett 179:185–195
Grommes C, Landreth GE, Heneka MT (2004) Antineoplastic effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists. Lancet Oncol 5:419–429
Posch MG, Zang C, Mueller W, Lass U, von Deimling A, Elstner E (2004) Somatic mutations in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma are rare events in human cancer cells. Med Sci Monit 10:BR250-4
Kubota T, Koshizuka K, Williamson EA, Asou H, Said JW, Holden S, Miyoshi I, Koeffler HP (1998) Ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (troglitazone) has potent antitumor effect against human prostate cancer both in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 58:3344–3352
Tsubouchi Y, Sano H, Kawahito Y, Mukai S, Yamada R, Kohno M, Inoue K, Hla T, Kondo M (2000) Inhibition of human lung cancer cell growth by the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists through induction of apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270:400–405
Fujimura S, Suzumiya J, Nakamura K, Ono J (1998) Effects of troglitazone on the growth and differentiation of hematopoietic cell lines. Int J Oncol 13:1263–1267
Hafner C, Reichle A, Vogt T (2005) New indications for established drugs: combined tumor-stroma-targeted cancer therapy with PPARgamma agonists, COX-2 inhibitors, mTOR antagonists and metronomic chemotherapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 5:393–419
Jan HJ, Lee CC, Lin YM, Lai JH, Wei HW, Lee HM (2009) Rosiglitazone reduces cell invasiveness by inducing MKP-1 in human U87 MG glioma cells. Cancer Lett 277:141–148
Tapia-Perez JH, Kirches E, Mawrin C, Firsching R, Schneider T (2011) Cytotoxic effect of different statins and thiazolidinediones on malignant glioma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67:1193–1201
Seifer DB, MacLaughlin DT, Penzias AS, Behrman HR, Asmundson L, Donahoe PK, Haning RJ, Flynn SD (1993) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist-induced differences in granulosa cell cycle kinetics are associated with alterations in follicular fluid mullerian-inhibiting substance and androgen content. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 76:711–714
Coras R, Holsken A, Seufert S, Hauke J, Eyupoglu IY, Reichel M, Trankle C, Siebzehnrubl FA, Buslei R, Blumcke I, Hahnen E (2007) The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist troglitazone inhibits transforming growth factor-beta-mediated glioma cell migration and brain invasion. Mol Cancer Ther 6:1745–1754
Datto MB, Li Y, Panus JF, Howe DJ, Xiong Y, Wang XF (1995) Transforming growth factor beta induces the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 through a p53-independent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5545–5549
Okura T, Nakamura M, Takata Y, Watanabe S, Kitami Y, Hiwada K (2000) Troglitazone induces apoptosis via the p53 and Gadd45 pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol 407:227–235
Yin F, Bruemmer D, Blaschke F, Hsueh WA, Law RE, Herle AJ (2004) Signaling pathways involved in induction of GADD45 gene expression and apoptosis by troglitazone in human MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Oncogene 23:4614–4623
Qin C, Burghardt R, Smith R, Wormke M, Stewart J, Safe S (2003) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists induce proteasome-dependent degradation of cyclin D1 and estrogen receptor alpha in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 63:958–964
Sugimura A, Kiriyama Y, Nochi H, Tsuchiya H, Tamoto K, Sakurada Y, Ui M, Tokumitsu Y (1999) Troglitazone suppresses cell growth of myeloid leukemia cell lines by induction of p21WAF1/CIP1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 261:833–837
Perez-Ortiz JM, Tranque P, Vaquero CF, Domingo B, Molina F, Calvo S, Jordan J, Cena V, Llopis J (2004) Glitazones differentially regulate primary astrocyte and glioma cell survival. Involvement of reactive oxygen species and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. J Biol Chem 279:8976–8985
Zander T, Kraus JA, Grommes C, Schlegel U, Feinstein D, Klockgether T, Landreth G, Koenigsknecht J, Heneka MT (2002) Induction of apoptosis in human and rat glioma by agonists of the nuclear receptor PPARgamma. J Neurochem 81:1052–1060
Grommes C, Landreth GE, Schlegel U, Heneka MT (2005) The nonthiazolidinedione tyrosine-based peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligand GW7845 induces apoptosis and limits migration and invasion of rat and human glioma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313:806–813
Strakova N, Ehrmann J, Dzubak P, Bouchal J, Kolar Z (2004) The synthetic ligand of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ciglitazone affects human glioblastoma cell lines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309:1239–1247
Grommes C, Landreth GE, Sastre M, Beck M, Feinstein DL, Jacobs AH, Schlegel U, Heneka MT (2006) Inhibition of in vivo glioma growth and invasion by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist treatment. Mol Pharmacol 70:1524–1533
Cox PJ, Ryan DA, Hollis FJ, Harris AM, Miller AK, Vousden M, Cowley H (2000) Absorption, disposition, and metabolism of rosiglitazone, a potent thiazolidinedione insulin sensitizer, in humans. Drug Metab Dispos 28:772–780
Sugiyama D, Kusuhara H, Taniguchi H, Ishikawa S, Nozaki Y, Aburatani H, Sugiyama Y (2003) Functional characterization of rat brain-specific organic anion transporter (Oatp14) at the blood-brain barrier: high affinity transporter for thyroxine. J Biol Chem 278:43489–43495
Tran TT et al (2007) Inhibiting TGF-beta signaling restores immune surveillance in the SMA-560 glioma model. Neuro Oncol 9:259–270
Wick W, Grimmel C, Wild-Bode C, Platten M, Arpin M, Weller M (2001) Ezrin-dependent promotion of glioma cell clonogenicity, motility, and invasion mediated by BCL-2 and transforming growth factor-beta2. J Neurosci 21:3360–3368
Merzak A, McCrea S, Koocheckpour S, Pilkington GJ (1994) Control of human glioma cell growth, migration and invasion in vitro by transforming growth factor beta 1. Br J Cancer 70:199–203
Uhl M, Aulwurm S, Wischhusen J, Weiler M, Ma JY, Almirez R, Mangadu R, Liu YW, Platten M, Herrlinger U, Murphy A, Wong DH, Wick W, Higgins LS, Weller M (2004) SD-208, a novel transforming growth factor beta receptor I kinase inhibitor, inhibits growth and invasiveness and enhances immunogenicity of murine and human glioma cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 64:7954–7961
Friese MA, Wischhusen J, Wick W, Weiler M, Eisele G, Steinle A, Weller M (2004) RNA interference targeting transforming growth factor-beta enhances NKG2D-mediated antiglioma immune response, inhibits glioma cell migration and invasiveness, and abrogates tumorigenicity in vivo. Cancer Res 64:7596–7603
Hjelmeland MD, Hjelmeland AB, Sathornsumetee S, Reese ED, Herbstreith MH, Laping NJ, Friedman HS, Bigner DD, Wang XF, Rich JN (2004) SB-431542, a small molecule transforming growth factor-beta-receptor antagonist, inhibits human glioma cell line proliferation and motility. Mol Cancer Ther 3:737–745
Kawataki T, Naganuma H, Sasaki A, Yoshikawa H, Tasaka K, Nukui H (2000) Correlation of thrombospondin-1 and transforming growth factor-beta expression with malignancy of glioma. Neuropathology 20:161–169
Kjellman C, Olofsson SP, Hansson O, Von Schantz T, Lindvall M, Nilsson I, Salford LG, Sjogren HO, Widegren B (2000) Expression of TGF-beta isoforms, TGF-beta receptors, and SMAD molecules at different stages of human glioma. Int J Cancer 89:251–258
Yamada N, Kato M, Yamashita H, Nister M, Miyazono K, Heldin CH, Funa K (1995) Enhanced expression of transforming growth factor-beta and its type-I and type-II receptors in human glioblastoma. Int J Cancer 62:386–392
Demuth T, Rennert JL, Hoelzinger DB, Reavie LB, Nakada M, Beaudry C, Nakada S, Anderson EM, Henrichs AN, McDonough WS, Holz D, Joy A, Lin R, Pan KH, Lih CJ, Cohen SN, Berens ME (2008) Glioma cells on the run: the migratory transcriptome of 10 human glioma cell lines. BMC Genomics 9:54
Brown KA, Pietenpol JA, Moses HL (2007) A tale of two proteins: differential roles and regulation of Smad2 and Smad3 in TGF-beta signaling. J Cell Biochem 101:9–33
Soucek L, Evan GI (2010) The ups and downs of Myc biology. Curr Opin Genet Dev 20:91–95
Claassen GF, Hann SR (2000) A role for transcriptional repression of p21CIP1 by c-Myc in overcoming transforming growth factor beta -induced cell-cycle arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9498–9503
Feng XH, Liang YY, Liang M, Zhai W, Lin X (2002) Direct interaction of c-Myc with Smad2 and Smad3 to inhibit TGF-beta-mediated induction of the CDK inhibitor p15(Ink4B). Mol Cell 9:133–143
Feng XH, Lin X, Derynck R (2000) Smad2, Smad3 and Smad4 cooperate with Sp1 to induce p15(Ink4B) transcription in response to TGF-beta. EMBO J 19:5178–5193
Moustakas A, Kardassis D (1998) Regulation of the human p21/WAF1/Cip1 promoter in hepatic cells by functional interactions between Sp1 and Smad family members. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6733–6738
Pardali K, Moustakas A (2007) Actions of TGF-beta as tumor suppressor and pro-metastatic factor in human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1775:21–62
Seoane J, Pouponnot C, Staller P, Schader M, Eilers M, Massague J (2001) TGFbeta influences Myc, Miz-1 and Smad to control the CDK inhibitor p15INK4b. Nat Cell Biol 3:400–408
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant from Tianjin Municipal Health Bureau (07KC79), Tianjin, China.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Yu, J., Yin, Q. et al. Rosiglitazone Suppresses Glioma Cell Growth and Cell Cycle by Blocking the Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Mediated Pathway. Neurochem Res 37, 2076–2084 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0828-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0828-8