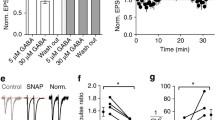
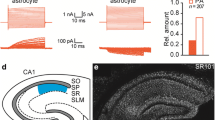
Abstract
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is considered to be the major inhibitory neurotransmitter that is synthesized in and released from GABA-ergic neurons in the brain. However, recent studies have shown that not only neurons but astrocytes contain a considerable amount of GABA, which can be released and activate the receptors responsive to GABA. In addition, astrocytes are themselves responsive to GABA by expressing GABA receptors. These exciting new findings raise more questions about the origin of GABA, whether it is synthesized or taken up, and about the role of astrocytic GABA and GABA receptors. In this review, we propose several potential pathways for astrocytes to accumulate GABA and discuss the evidence for functional expression of GABA receptors in astrocytes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG (1999) Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci 22:208–215
Fiacco TA, McCarthy KD (2006) Astrocyte calcium elevations: properties, propagation, and effects on brain signaling. Glia 54:676–690
Rousse I, Robitaille R (2006) Calcium signaling in Schwann cells at synaptic and extra-synaptic sites: active glial modulation of neuronal activity. Glia 54:691–699
Volterra A, Meldolesi J (2005) Astrocytes, from brain glue to communication elements: the revolution continues. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:626–640
Haydon PG, Carmignoto G (2006) Astrocyte control of synaptic transmission and neurovascular coupling. Physiol Rev 86:1009–1031
Oliet SH, Mothet JP (2006) Molecular determinants of d-serine-mediated gliotransmission: from release to function. Glia 54:726–737
Barakat L, Bordey A (2002) GAT-1 and reversible GABA transport in Bergmann glia in slices. J Neurophysiol 88:1407–1419
Hussy N (2002) Glial cells in the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system: key elements of the regulation of neuronal electrical and secretory activity. Prog Brain Res 139:95–112
Jimenez-Gonzalez C, Pirttimaki T, Cope DW, Parri HR (2011) Non-neuronal, slow GABA signalling in the ventrobasal thalamus targets delta-subunit-containing GABA (A) receptors. Eur J Neurosci 33:1471–1482
Lee S, Yoon BE, Berglund K, Oh SJ, Park H, Shin HS, Augustine GJ, Lee CJ (2010) Channel-mediated tonic GABA release from glia. Science 330:790–796
Yoon BE, Jo S, Woo J, Lee JH, Kim T, Kim D, Lee CJ (2011) The amount of astrocytic GABA positively correlates with the degree of tonic inhibition in hippocampal CA1 and cerebellum. Mol Brain 4:42
Lee M, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (2011) Mechanisms of GABA release from human astrocytes. Glia 59:1600–1611
Martin DL, Rimvall K (1993) Regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis in the brain. J Neurochem 60:395–407
Jakoby WB, Fredericks J (1959) Pyrrolidine and putrescine metabolism: gamma-aminobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 234:2145–2150
Lee M, Schwab C, Mcgeer PL (2011) Astrocytes are GABAergic cells that modulate microglial activity. Glia 59:152–165
Martin DL (1976) Carrier-mediated transport and removal of GABA from synaptic regions. In: Roberts E, Chase TN, Tower DR (eds) GABA in the central nervous system. Raven Press, New York, pp 347–386
Kang J, Jiang L, Goldman SA, Nedergaard M (1998) Astrocyte-mediated potentiation of inhibitory synaptic transmission. Nat Neurosci 1:683–692
Erlander MG, Tillakaratne NJ, Feldblum S, Patel N, Tobin AJ (1991) Two genes encode distinct glutamate decarboxylases. Neuron 7:91–100
Soghomonian JJ, Martin DL (1998) Two isoforms of glutamate decarboxylase: why? Trends Pharmacol Sci 19:500–505
Wilson SH, Schrier BK, Farber JL, Thompson EJ, Rosenberg RN, Blume AJ, Nirenberg MW (1972) Markers for gene expression in cultured cells from the nervous system. J Biol Chem 247:3159–3169
Schrier BK, Thompson EJ (1974) On the role of glial cells in the mammalian nervous system. Uptake, excretion, and metabolism of putative neurotransmitters by cultured glial tumor cells. J Biol Chem 249:1769–1780
Ochi S, Lim JY, Rand MN, During MJ, Sakatani K, Kocsis JD (1993) Transient presence of GABA in astrocytes of the developing optic nerve. Glia 9:188–198
De Mello FG, Bachrach U, Nirenberg M (1976) Ornithine and glutamic acid decarboxylase activities in the developing chick retina. J Neurochem 27:847–851
Seiler N, al-Therib MJ, Kataoka K (1973) Formation of GABA from putrescine in the brain of fish (Salmo irideus Gibb.). J Neurochem 20:699–708
Hokoc JN, Ventura AL, Gardino PF, De Mello FG (1990) Developmental immunoreactivity for GABA and GAD in the avian retina: possible alternative pathway for GABA synthesis. Brain Res 532:197–202
Barres BA, Koroshetz WJ, Swartz KJ, Chun LL, Corey DP (1990) Ion channel expression by white matter glia: the O-2A glial progenitor cell. Neuron 4:507–524
Sequerra EB, Gardino P, Hedin-Pereira C, de Mello FG (2007) Putrescine as an important source of GABA in the postnatal rat subventricular zone. Neuroscience 146:489–493
Laschet J, Grisar T, Bureau M, Guillaume D (1992) Characteristics of putrescine uptake and subsequent GABA formation in primary cultured astrocytes from normal C57BL/6 J and epileptic DBA/2 J mouse brain cortices. Neuroscience 48:151–157
Wu PH, Durden DA, Hertz L (1979) Net production of gamma-aminobutyric acid in astrocytes in primary cultures determined by a sensitive mass spectrometric method. J Neurochem 32:379–390
Yeung JY, Canning KJ, Zhu G, Pennefather P, MacDonald JF, Orser BA (2003) Tonically activated GABAA receptors in hippocampal neurons are high-affinity, low-conductance sensors for extracellular GABA. Mol Pharmacol 63:2–8
Rossi DJ, Hamann M, Attwell D (2003) Multiple modes of GABAergic inhibition of rat cerebellar granule cells. J Physiol 548:97–110
Chiu CS, Brickley S, Jensen K, Southwell A, McKinney S, Cull-Candy S, Mody I, Lester HA (2005) GABA transporter deficiency causes tremor, ataxia, nervousness, and increased GABA-induced tonic conductance in cerebellum. J Neurosci 25:3234–3245
Wu Y, Wang W, Diez-Sampedro A, Richerson GB (2007) Nonvesicular inhibitory neurotransmission via reversal of the GABA transporter GAT-1. Neuron 56:851–865
Hosli E, Mohler H, Richards JG, Hosli L (1980) Autoradiographic localization of binding sites for [3H]gamma-aminobutyrate, [3H]muscimol,(+)[3H]bicuculline methiodide and [3H] flunitrazepam in cultures of rat cerebellum and spinal cord. Neuroscience 5:1657–1665
Hosli L, Hosli E, Redle S, Rojas J, Schramek H (1990) Action of baclofen, GABA and antagonists on the membrane potential of cultured astrocytes of rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 117:307–312
Ossola L, DeFeudis FV, Mandel P (1980) Lack of Na”-independent binding of [3H]GABA or [3H]muscimol to particulate fractions of cultured astroblasts. J Neurochem 34:1026–1029
Fraser DD, Duffy S, Angelides KJ, Perez-Velazquez JL, Kettenmann H, MacVicar BA (1995) GABAA/benzodiazepine receptors in acutely isolated hippocampal astrocytes. J Neurosci 15:2720–2732
von Blankenfeld G, Kettenmann H (1991) Glutamate and GABA receptors in vertebrate glial cells. Mol Neurobiol 5:31–43
Clark B, Mobbs P (1992) Transmitter-operated channels in rabbit retinal astrocytes studied in situ by whole-cell patch clamping. J Neurosci 12:664–673
Muller T, Fritschy JM, Grosche J, Pratt GD, Mohler H, Kettenmann H (1994) Developmental regulation of voltage-gated K + channel and GABAA receptor expression in Bergmann glial cells. J Neurosci 14:2503–2514
Riquelme R, Miralles CP, De Blas AL (2002) Bergmann glia GABA (A) receptors concentrate on the glial processes that wrap inhibitory synapses. J Neurosci 22:10720–10730
Fraser DD, Mudrick-Donnon LA, MacVicar BA (1994) Astrocytic GABA receptors. Glia 11:83–93
Bovolin P, Santi MR, Puia G, Costa E, Grayson D (1992) Expression patterns of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor subunit mRNAs in primary cultures of granule neurons and astrocytes from neonatal rat cerebella. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:9344–9348
Hoppe D, Kettenmann H (1989) GABA triggers a Cl- efflux from cultured mouse olinodendrocvtes. Neurosci Lett 97:334–339
MacVicar BA, Tse FW, Crichton SA, Kettenmann H (1989) GABA-activated Cl-channels in astrocytes of hippocampal slices. J Neurosci 9:3577–3583
Backus KH, Kettenmann H, Schachner M (1988) Effect of benzodiazepines and pentobarbital on the GABA-induced depolarization in cultured astrocytes. Glia 1:132–140
Kettenmann H, Schachner M (1985) Pharmacological properties of GABA, glutamate and aspartate induced depolarizations in cultured astrocytes. J Neurosci 5:3295–3301
Matsutani S, Yamamoto N (1997) Neuronal regulation of astrocyte morphology in vitro is mediated by GABAergic signaling. Glia 20:1–9
Matsutani S, Yamamoto N (1998) GABAergic neuron-to-astrocyte signaling regulates dendritic branching in coculture. J Neurobiol 37:251–264
Bekar LK, Jabs R, Walz W (1999) GABAA receptor agonists modulate K+ currents in adult hippocampal glial cells in situ. Glia 26:129–138
Barres BA, Chun LL, Corey DP (1989) Calcium current in cortical astrocytes: induction by cAMP and neurotransmitters and permissive effect of serum factors. J Neurosci 9:3169–3175
MacVicar BA (1984) Voltage-dependent calcium channels in glial cells. Science 226:1345–1347
Nilsson M, Hansson E, Ronnback L (1992) Agonist evoked calcium transients in primary astroglia culture modulatory effects of valproic acid. Glia 5:201–209
Perea G, Navarrete M, Araque A (2009) Tripartite synapses: astrocytes process and control synaptic information. Trends Neurosci 32:421–431
Albrecht J, Pearce B, Murphy S (1986) Evidence for an interaction between GABA, and glutamate receptors in astrocytes as revealed by changes in Ca2+ flux. Eur J Pharmacol 125:463–464
Charles KJ, Deuchars J, Davies CH, Pangalos MN (2003) GABA B receptor subunit expression in glia. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:214–223
Oka M, Wada M, Wu Q, Yamamoto A, Fujita T (2006) Functional expression of metabotropic GABAB receptors in primary cultures of astrocytes from rat cerebral cortex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 341:874–881
Pearce B, Murphy S (1998) PNeurotransmitter receptors coupled to inositol phospholipid turnover and Ca2 + flux: consequences for astrocyte function. In: Kimelberg H (ed) Glial cell receptors. Raven Press, New York, pp 197–221
Nilsson M, Eriksson PS, Ronnback L, Hansson E (1993) GABA induces Ca2+ transients in astrocytes. Neuroscience 54:605–614
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue: In Honor of Leif Hertz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, BE., Woo, J. & Justin Lee, C. Astrocytes as GABA-ergic and GABA-ceptive Cells. Neurochem Res 37, 2474–2479 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0808-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0808-z