Abstract
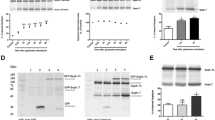
Calcium ion is essential for cellular functions including signal transduction. Uncontrolled calcium stress has been linked causally to a variety of neurodegenerative diseases. Thapsigargin, which inhibits Ca2+-ATPase in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and blocks the sequestration of calcium by the ER, induced apoptotic cell death (chromatin condensation and nuclear fragmentation) accompanied by GRP78 protein expression and caspase-3 activation in rat fetal cortical neurons (days in vitro 9–10). Blockade of N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors with NMDA antagonists induced apoptosis without GRP78 protein expression. Apoptosis accompanied both caspase-9 and caspase-3 activation. We then examined whether GSK-3 is involved in thapsigargin-induced cell death by using GSK-3 inhibitors. We assayed the effects of selective GSK-3 inhibitors, SB216763, alsterpaullone and 1-azakenpaullone, on thapsigargin-induced apoptosis. These inhibitors completely protected cells from thapsigargin-induced apoptosis. In addition, GSK-3 inhibitors inhibited caspase-9 and caspase-3 activation accompanied by thapsigargin-induced apoptosis. These results suggest that thapsigargin induces caspase-dependent apoptosis mediated through GSK-3β activation in rat cortical neurons.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ikonomidou C, Bosch F, Miksa M, Bittigau P, Vockler J, Dikranian K, Tenkova TI, Stefovska V, Turski L, Olney JW (1999) Blockade of NMDA receptors and apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Science 283:70–74
Takadera T, Matsuda I, Ohyashiki T (1999) Apoptotic cell death and caspase-3 activation induced by N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists and their prevention by insulin-like growth factor I. J Neurochem 73:548–556
Hwang JY, Kim YH, Ahn YH, Wie MB, Koh JY (1999). N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptor blockade induces neuronal apoptosis in cortical culture. Exp Neurol 159:124–130
Yoon WJ, Won SJ, Ryu BR, Gwag BJ (2003) Blockade of ionotropic glutamate receptors produces neuronal apoptosis through the Bax-cytochrome C-caspase pathway: the causative role of Ca2+ deficiency. J Neurochem 85:525–533
Olney JW, Wozniak DF, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Farber NB, Bittigau P, Ikonomidou C (2002) Drug-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Brain Pathol 12:488–498
Tsien RW, Tsien RY (1990) Calcium channels, stores, and oscillations. Annu Rev Cell Biol 6:715–760
Paschen W, Frandsen A (2001) Endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction—a common denominator for cell injury in acute and degenerative diseases of the brain? J Neurochem 79:719–725
Choi DW (1988) Calcium-mediated neurotoxicity: relationship to specific channel types and role in ischemic damage. Trends Neurosci 11:465–469
Lindholm D, Wootz H, Korhonen L (2006) ER stress and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Death Differ 13:385–392
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, Yuan J (2000) Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta. Nature 403:98–103
Lytton J, Westlin M, Hanley MR (1991) Thapsigargin inhibits the sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase family of calcium pumps. J Biol Chem 266:17067–17071
Thastrup O, Cullen PJ, Drobak BK, Hanley MR, Dawson AP (1990) Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:2466–2470
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA (1995) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 378:785–789
Hetman M, Cavanaugh JE, Kimelman D, Xia Z (2000) Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in neuronal apoptosis induced by trophic withdrawal. J Neurosci 20:2567–2574
Grimes CA, Jope RS (2001) The multifaceted roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in cellular signaling. Prog Neurobiol 65:391–426
Takadera T, Sakamoto Y, Ohyashiki T (2004) NMDA receptor 2B-selective antagonist ifenprodil-induced apoptosis was prevented by glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors in cultured rat cortical neurons. Brain Res 1020:196–203
Yao R, Cooper GM (1995) Requirement for phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase in the prevention of apoptosis by nerve growth factor. Science 267:2003–2006
Pap M, Cooper GM (1998) Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in the phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt cell survival pathway. J Biol Chem 273:19929–19932
Takadera T, Yoshikawa R, Ohyashiki T (2006) Thapsigargin-induced apoptosis was prevented by glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors in PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett 408:124–128
Dichter MA (1978) Rat cortical neurons in cell culture: culture methods, cell morphology, electrophysiology, and synapse formation. Brain Res 149:279–293
Coghlan MP, Culbert AA, Cross DA, Corcoran SL, Yates JW, Pearce NJ, Rausch OL, Murphy GJ, Carter PS, Roxbee Cox L, Mills D, Brown MJ, Haigh D, Ward RW, Smith DG, Murray KJ, Reith AD, Holder JC (2000) Selective small molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 modulate glycogen metabolism and gene transcription. Chem Biol 7:793–803
Cross DA, Culbert AA, Chalmers KA, Facci L, Skaper SD, Reith AD (2001) Selective small-molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity protect primary neurones from death. J Neurochem 77:94–102
Sandal T, Stapnes C, Kleivdal H, Hedin L, Doskeland SO (2002) A novel, extraneuronal role for cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 (CDK5): modulation of cAMP-induced apoptosis in rat leukemia cells. J Biol Chem 277:20783–20793
Leost M, Schultz C, Link A, Wu YZ, Biernat J, Mandelkow EM, Bibb JA, Snyder GL, Greengard P, Zaharevitz DW, Gussio R, Senderowicz AM, Sausville EA, Kunick C, Meijer L (2000) Paullones are potent inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and cyclin-dependent kinase 5/p25. Eur J Biochem 267:5983–5994
Song L, De Sarno P, Jope RS (2002) Central role of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced caspase-3 activation. J Biol Chem 277:44701–44708
Linseman DA, Butts BD, Precht TA, Phelps RA, Le SS, Laessig TA, Bouchard RJ, Florez-McClure ML, Heidenreich KA (2004) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta phosphorylates Bax and promotes its mitochondrial localization during neuronal apoptosis. J Neurosci 24:9993–10002
Takadera T, Ishida A, Ohyashiki T (2006) Ketamine-induced apoptosis in cultured rat cortical neurons. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 210:100–107
Balazs R, Jorgensen OS, Hack N (1988) N-methyl-d-aspartate promotes the survival of cerebellar granule cells in culture. Neuroscience 27:437–451
Yan GM, Ni B, Weller M, Wood KA, Paul SM (1994) Depolarization or glutamate receptor activation blocks apoptotic cell death of cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Brain Res 656:43–51
Feng XQ, You Y, Xiao J, Zou P (2006) Thapsigargin-induced apoptosis of K562 cells and its mechanism. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 14:25–30
Turner CP, Pulciani D, Rivkees SA (2002) Reduction in intracellular calcium levels induces injury in developing neurons. Exp Neurol 178:21–32
Brewster JL, Linseman DA, Bouchard RJ, Loucks FA, Precht TA, Esch EA, Heidenreich KA (2006) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and trophic factor withdrawal activate distinct signaling cascades that induce glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and a caspase-9-dependent apoptosis in cerebellar granule neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 32:242–253
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takadera, T., Fujibayashi, M., Kaniyu, H. et al. Caspase-dependent Apoptosis Induced by Thapsigargin was Prevented by Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Inhibitors in Cultured Rat Cortical Neurons. Neurochem Res 32, 1336–1342 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9310-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9310-4