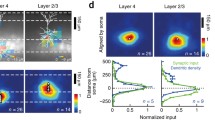
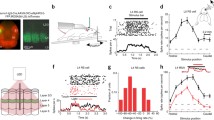
Ascending sensory information is conveyed from the thalamus to layers 4 and 6 of the sensory cortical areas. Interestingly, receptive field properties of cortical layer-6 neurons differ from those in layer 4. Do such differences reflect distinct inheritance patterns from the thalamus, or are they derived instead from local cortical circuits? To distinguish between these possibilities, we utilized in vitro slice preparations containing the thalamo-cortical pathways of the auditory and somatosensory systems. Responses from neurons in layers 4 and 6 that resided in the same column were recorded using whole-cell patch clamp. Laser-scanning photostimulation via uncaging of glutamate in the thalamus and cortex was used to map the functional topography of thalamo-cortical and intracortical inputs to each layer. In addition, we assessed the functional divergence of thalamo-cortical inputs by optical imaging of flavoprotein autofluorescence. We found that the thalamo-cortical inputs to layers 4 and 6 originated from the same thalamic domain, but the intracortical projections to the same neurons differed dramatically. Our results suggest that the intracortical projections, rather than the thalamic inputs, to each layer contribute more to the differences in their receptive field properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. L. Huang and J. A. Winer, “Auditory thalamocortical projections in the cat: laminar and areal patterns of input,” J. Comp. Neurol., 427, 302-331 (2000).
P. H. Smith, D. J. Uhlrich, K. A. Manning, and M. I. Banks, “Thalamocortical projections to rat auditory cortex from the ventral and dorsal divisions of the medial geniculate nucleus.,” J. Comp. Neurol., 520, 34-51 (2012).
P. Landry and M. Deschênes, “Intracortical arborizations and receptive fields of identified ventrobasal thalamocortical afferents to the primary somatic sensory cortex in the cat.,” J. Comp. Neurol., 199, 345-372 (1981).
A. L. Humphrey, M. Sur, D. J. Ulrich, and S. M. Sherman, “Termination patterns of individual X- and Y-cell axons in the visual cortex of the cat: projections to area 18, to the 17/18 border region, and to both areas 17 and 18,” J. Comp. Neurol., 233, 190-212 (1985).
M. Beierlein and B. W. Connors, “Short-term dynamics of thalamocortical and intracortical synapses onto layer 6 neurons in neocortex,” J. Neurophysiol., 88, 1924-1932 (2002).
H. J. Rose and R. Metherate, “Auditory thalamocortical transmission is reliable and temporally precise.,” J. Neurophysiol., 94, 2019-2030 (2005).
K. J. Stratford, K. Tarczy-Hornoch, K. A. Martin, et al., “Excitatory synaptic inputs to spiny stellate cells in cat visual cortex,” Nature, 382, 258-261 (1996).
J. N. MacLean, V. Fenstermaker, B. O. Watson, and R. Yuste, “A visual thalamocortical slice,” Nat. Methods, 3, 129-134 (2006).
C. C. Lee and S. M. Sherman, “Synaptic properties of thalamic and intracortical intputs to layer 4 of the first- and higher-order cortical areas in the auditory and somatosensory systems.,” J. Neurophysiol., 100, 317-326 (2008).
S. M. Sherman and R. W. Guillery, “On the actions that one nerve cell can have on another: distinguishing ‘drivers’ from ‘modulators’,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 7121-7126 (1998).
C. C. Lee and S. M. Sherman, “On the classification of pathways in the auditory midbrain, thalamus, and cortex.,” Hear. Res., 276, 79-87 (2011).
C. C. Lee and S. M. Sherman, “Drivers and modulators in the central auditory pathways,” Front. Neurosci., 4, 79-86 (2010).
C. D. Gilbert, “Laminar differences in receptive field properties of cells in cat primary visual cortex,” J. Physiol., 268, 391-421 (1977).
C. A. Atencio and C. E. Schreiner, “Laminar diversity of dynamic sound processing in cat primary auditory cortex,” J. Neurophysiol., 103, 192-205 (2010).
R. W. Dykes and Y. Lamour, “An electrophysiological study of single somatosensory neurons in rat granular cortex serving the limbs: a laminar analysis,” J. Neurophysiol., 70, 703-724 (1988).
L. M. Martinez, Q. Wang, R. C. Reid, et al., “Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary visual cortex,” Nat, Neurosci,, 8, 372-379 (2005).
J. C. Brumberg, D. J. Pinto, and D. J. Simons, “Cortical columnar processing in the rat whisker-to-barrel system,” J. Neurophysiol., 82, 1808-1817 (1999).
M. N. Wallace and A. R. Palmer, “Laminar differences in the response properties of cells in the primary auditory cortex,” Exp Brain Res, 184, 179-191 (2008).
C. C. Lee and J. A. Winer, “Connections of cat auditory cortex: III. Corticocortical system,” J. Comp. Neurol., 507, 1920-1943 (2008).
C. C. Lee and J. A. Winer, “Convergence of thalamic and cortical pathways in cat auditory cortex,” Hear. Res., 274, 85-94 (2011).
C. C. Lee and J. A. Winer, “A synthesis of auditory cortical connections: thalamocortical, commissural, and corticocortical systems,” in: The auditory cortex, J. A. Winer and C. E. Schreiner(eds.), Springer, New York (2011), pp. 147-170.
T. Binzegger, R. Douglas, and K. Martin, “A quantitative map of the circuit of cat primary visual cortex,” J. Neurosci., 24, 8441-8453 (2004).
B. Ahmed, J. C. Anderson, R. J. Douglas, et al., “Polyneuronal innervation of spiny stellate neurons in cat visual cortex,” J. Comp. Neurol., 341, 39-49 (1994).
C. C. Lee and S. M. Sherman, “Modulator property of the intrinsic cortical projections from layer 6 to layer 4,” Front. Syst. Neurosci., 3, 3 (2009).
C. C. Lee and S. M. Sherman, “Intrinsic modulators of auditory thalamocortical transmission,” Hear. Res., 287, 43-50 (2012).
C. C. Lee, Y. W. Lam, and S. M. Sherman, “Intracortical convergence of layer 6 neurons,” Neuroreport, 23, 736-740 (2012).
S. J. Cruikshank, H. J. Rose, and R. Metherate, “Auditory thalamocortical synaptic transmission in vitro,” J. Neurophysiol., 87, 361-384 (2002).
A. Agmon and B. W. Connors, “Thalamocortical responses of mouse somatosensory (barrel) cortex in vitro,” Neuroscience, 41, 365-379 (1991).
J. A. Winer and C. C. Lee, “The distributed auditory cortex,” Hear. Res., 229, 3-13 (2007).
J. A. Winer and J. J. Prieto, “Layer V in cat primary auditory cortex (AI): cellular architecture and identification of projection neurons,” J. Comp. Neurol., 434, 379-412 (2001).
C. C. Lee and S. M. Sherman, “Glutamatergic inhibition in sensory neocortex,” Cereb. Cortex, 19, 2281-2289 (2009).
B. A. Suter, T. O’Connor, V. Iyer, et al., “Ephus: multipurpose data acquisition software for neuroscience experiments,” Front. Neural Circuit., 4, 100 (2010).
C. C. Lee and S. M. Sherman, “Topography and physiology of ascending streams in the auditory tectothalamic pathway,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 107, 372-377 (2010).
B. B. Theyel, D. A. Llano, N. P. Issa, et al., “In vitro imaging using laser photostimulation with flavoprotein autofluorescence.,” Nat. Protoc., 6, 502-508 (2011).
B. B. Theyel, C. C. Lee, and S. M. Sherman, “Specific and nonspecific thalamocortical connectivity in the auditory and somatosensory thalamo-cortical slices,” Neuroreport, 21, 861-864 (2010).
D. A. Llano and S. M. Sherman, “Evidence for non-reciprocal organization of the mouse auditory thalamocortical-corticothalamic projections systems.,” J. Comp. Neurol., 507, 1209-1227 (2008).
J. A. Winer, J. J. Diehl, and D. T. Larue, “Projections of auditory cortex to the medial geniculate body of the cat,” J. Comp. Neurol., 430, 27-55 (2001).
I. Reichova and S. M. Sherman, “Somatosensory corticothalamic projections: distinguishing drivers from modulators,” J. Neurophysiol., 92, 2185-2197 (2004).
D. H. Sanes and V. C. Kotak, “Developmental plasticity of auditory cortical inhibitory synapses,” Hear. Res., 279, 140-148 (2011).
R. S. Erzurumlu and P. Gaspar, “Development and critical period plasticity of the barrel cortex,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 35, 1540-1553 (2012).
A. M. Oswald and A. D. Reyes, “Development of inhibitory timescales in auditory cortex,” Cereb. Cortex, 21, 1351-1361 (2011).
Y. Zhou, B. H. Liu, G. K. Wu, et al., “Preceding inhibition silences layer 6 neurons in auditory cortex,” Neuron, 65, 706-717 (2010 ).
M. Wehr and A. M. Zador, “Balanced inhibition underlies tuning and sharpens spike timing in auditory cortex,” Nature, 426, 442-446 (2003).
I. Bureau, F. von Saint Paul, and K. Svoboda, “Interdigitated paralemniscal and lemniscal pathways in the mouse barrel cortex.,” PLoS Biol., 4, e382 (2006).
H. V. Oviedo, I. Bureau, K. Svoboda, and A. M. Zador, “The functional asymmetry of auditory cortex is reflected in the organization of local cortical circuits,” Nat. Neurosci., 13, 1413-1420 (2010).
V. C. Wimmer, R. M. Bruno, C. P. de Kock, et al., “Dimensions of a projection column and architecture of VPM and POm axons in rat vibrissal cortex,” Cereb. Cortex, 20, 2265-2276 (2010).
D. A. Llano, B. B. Theyel, A. K. Mallik, et al., “Rapid and sensitive mapping of long-range connections in vitro using flavoprotein autofluorescence imaging combined with laser photostimulation,” J. Neurophysiol., 101, 3325-3340 (2009).
S. Higashi, M. C. Crair, T. Kurotani, et al., “Altered spatial patterns of functional thalamocortical connections in the barrel cortex after neonatal infraorbital nerve cut revealed by optical recording,” Neuroscience, 91, 439-452 (1999).
N. Laaris, G. C. Carlson, and A. Keller, “Thalamicevoked synaptic interactions in barrel cortex revealed by optical imaging,” J. Neurosci., 20, 1529-1537 (2000).
T. A. Hackett, T. R. Barkat, B. M. O’Brien, et al., “Linking topography to tonotopy in the mouse auditory thalamocortical circuit,” J. Neurosci., 31, 2983-2995 (2011).
R. R. Llinas, E. Leznik, and F. J. Urbano, “Temporal binding via cortical coincidence detection of specific and nonspecific thalamocortical inputs: a voltagedependent dye-imaging study in mouse brain slices,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 449-454 (2002).
M. Beierlein, C. P. Fall, J. Rinzel, and R. Yuste, “Thalamo-cortical bursts trigger recurrent activity in neocortical networks: layer 4 as a frequency-dependent gate,” J. Neurosci., 22, 9885-9894 (2002).
M. Kubota and S. Sugimoto and J. Horikawa, et al., “Optical imaging of dynamic horizontal spread of excitation in rat auditory cortex slices,” Neuosci Lett, 237, 77-80 (1997).
M. Kubota, M. Nasu, and I. Taniguchi, “Layer-specific horizontal propagation of excitation in the auditory cortex,” Neuroreport, 10, 2865–2867 (1999).
T. Broicher and H. J. Bidmon and B. Kamuf, et al., “Thalamic afferent activation of supragranular layers in auditory cortex in vitro: a voltage sensitive dye study,” Neuroscience, 165, 371-385 (2010).
S. Kaur, H. J. Rose, R. Lazar, et al., “Spectral integration in primary auditory cortex: laminar processing of afferent input, in vivo and in vitro,” Neuroscience, 134, 1033-1045 (2005).
D. Contreras and R. Llinas, “Voltage-sensitive dye imaging of neocortical spatiotemporal dynamics to afferent activation frequency,” J. Neurosci., 21, 9403-9413 (2001).
D. L. Barbour and E. M. Callaway, “Excitatory local connections of superficial neurons in rat auditory cortex,” J. Neurosci., 28, 11174-11185 (2008).
D. A. Llano and S. M. Sherman, “Differences in intrinsic properties and local network connectivity of identified layer 5 and layer 6 adult mouse auditory corticothalamic neurons support a dual corticothalamic projection hypothesis,” Cereb. Cortex, 19, 2810-2826 (2009).
B. M. Hooks, S. A. Hires, Y. X. Zhang, et al., “Laminar analysis of excitatory local circuits in vibrissal motor and sensory cortical areas,” PLoS Biol., 9, e1000572 (2011).
A. Zarrinpar and E. M. Callaway, “Local connections to specific types of layer 6 neurons in the rat visual cortex,” J. Neurophysiol., 95, 1751-1761 (2006).
Y. Yoshimura, J. L. Dantzker, and E. M. Callaway, “Excitatory cortical neurons form fine-scale functional networks,” Nature, 433, 868-873 (2005).
F. Briggs and E. M. Callaway, “Layer-specific input to distinct cell types in layer 6 of monkey primary visual cortex,” J. Neurosci., 15, 3600-3608 (2001).
G. M. Shepherd, A. Stepanyants, I. Bureau, et al., “Geometric and functional organization of cortical circuits,” Nat. Neurosci., 8, 782-790 (2005).
G. M. Shepherd, T. A. Pologruto, and K. Svoboda, “Circuit analysis of experience-dependent plasticity in the developing rat barrel cortex,” Neuron, 38, 277-289 (2003).
H. Ojima, C. N. Honda, and E. G. Jones, “Patterns of axon collateralization of identified supragranular pyramidal neurons in the cat auditory cortex,” Cereb. Cortex, 1, 80-94 (1991).
H. Ojima, C. N. Honda, and E. G. Jones, “Characteristics of intracellularly injected infragranular pyramidal neurons in cat primary auditory cortex,” Cereb. Cortex, 2, 197-216 (1992).
J. A. Winer, “Anatomy of layer IV in cat primary auditory cortex (AI),” J. Comp. Neurol., 224, 535-567 (1984).
J. A. Winer, “The non-pyramidal neurons in layer III of cat primary auditory cortex (AI),” J. Comp. Neurol., 229, 512-530 (1984).
J. A. Winer, “The pyramidal cells in layer III of cat primary auditory cortex,” J. Comp. Neurol., 229, 476-496 (1984).
J. J. Prieto and J. A. Winer, “Layer VI in cat primary auditory cortex: Golgi study and sublaminar origins of projection neurons,” J. Comp. Neurol., 404, (1999).
J. A. Winer, L. M. Miller, C. C. Lee, and C. E. Schreiner, “Auditory thalamo-cortical transformation: structure and function,” Trends Neurosci, 28, 255-263 (2005).
L. M. Miller, M. A. Escabí, H. L. Read, and C. E. Schreiner, “Functional convergence of response properties in the auditory thalamo-cortical system,” Neuron, 32, 151-160 (2001).
C. C. Lee and J. A. Winer, “Connections of cat auditory cortex: I. Thalamo-cortical system,” J. Comp. Neurol., 507, 1879-1900 (2008).
J. W. Scannell, C. Blakemore, and M. P. Young, “Analysis of connectivity in the cat cerebral cortex,” J. Neurosci., 15, 1463-1483 (1995).
R. M. Bruno and B. Sakmann, “Cortex is driven by weak but synchronously active thalamo-cortical synapses,” Science, 312, 1622-1627 (2006).
R. J. Douglas, C. Koch, M. Mahowald, et al., “Recurrent excitation in neocortical circuits,” Science, 269, 981-985 (1995).
R. Ben-Yishai, R. L. Bar-Or, and H. Sompolinsky, “Theory of orientation tuning in visual cortex,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 3844-3848 (1995).
B. H. Liu, G. K. Wu, R. Arbuckle, et al., “Defining cortical frequency tuning with recurrent excitatory circuitry,” Nat. Neurosci., 10, 1594-1600 (2007).
J. N. MacLean, B. O. Watson, G. B. Aaron, and R. Yuste, “Internal dynamics determine the cortical response to thalamic stimulation,” Neuron, 8, 811-823 (2005).
C. R. Stoelzel, Y. Bereshpolova, A. G. Gusev, and H. A. Swadlow, “The impact of an LGNd impulse on the awake visual cortex: synaptic dynamics and the sustained/transient distinction,” J. Neurosci., 28, 5018-5028 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, C.C., Imaizumi, K. Functional Convergence of Thalamic and Intrinsic Projections to Cortical Layers 4 and 6. Neurophysiology 45, 396–406 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-013-9385-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-013-9385-2