Abstract
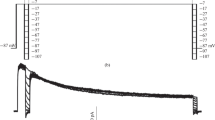
In freshly isolated neurons of the rat spinal ganglia, we studied the behavior of voltage-operated calcium channels of these cells under conditions of the absence of calcium ions in the extracellular solution; a patch-clamp technique in the whole-cell configuration was used. We found that such channels in a part of the studied neurons lose their selectivity in a calcium-free potassium-containing solution and become capable of passing an inward potassium current. This current was inhibited by blockers of voltage-operated calcium channels, nifedipine and nickel, and also was to some extent inhibited by caffeine. The latter effect is realized, perhaps, due to calcium-dependent inactivation of calcium channels induced by the action of calcium ions released from the endoplasmic reticulum upon caffeine-induced activation of ryanodine receptors. The peculiarities of current-voltage relationships and characteristics of activation/inactivation of calcium channels modified in calcium-free medium and the possible mechanisms of such modification are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. G. Kostyuk, V. L. Zima, I. S. Magura, et al., Biophysics [in Ukrainian], Oberegy, Kyiv (2001).
B. Hille, Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes, Univ. Washington, Sinauer Associates Inc. Publ., Sunderland, Massachusetts (1991).
W. A. Sather and E. W. McCleskey, “Permeation and selectivity in calcium channels,” Ann. Rev. Physiol., 65, 133–159 (2003).
P. G. Kostyuk and O. A. Krishtal, “Effects of calcium and calcium-chelating agents on the inward and outward current in the membrane of mollusc neurons,” J. Physiol., 270, 569–580 (1977).
P. Hess, J. B. Lansman, and R. W. Tsien, “Calcium channel selectivity for divalent and monovalent cations. Voltage and concentration dependence of single channel current in ventricular heart cells,” J. Gen. Physiol., 88, 293–319 (1986).
D. Yamamoto, “Sodium inward currents through calcium channels in mealworm muscle fibers,” Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol., 5, No. 4, 227–231 (1987).
B. D. Winegar, R. Kelly, and J. B. Lansman, “Block of current through single calcium channels by Fe, Co, and Ni. Location of the transition metal binding site in the pore,” J. Gen. Physiol., 97, 351–367 (1991).
B. Mlinar and J. J. Enyeart, “Block of current through T-type calcium channels by trivalent metal cations and nickel in neural rat and human cells,” J. Physiol., 469, 639–652 (1993).
J.-H. Lee, J. C. Gomora, L. L. Cribbs, and E. Perez-Reyes, “Nickel block of three cloned T-type calcium channels: low concentrations selectively block α1H,” Biophys. J., 77, 3034–3042 (1999).
L. Wang, A. Bhattacharjee, J. Fu, and M. Li, “Abnormally expressed low-voltage-activated calcium channels in beta-cells from NOD mice and a related clonal cell line,” Diabetes, 45, No. 12, 1678–1683 (1996).
P. G. Kostyuk and Ya. M. Shuba, “Examination of selectivity of calcium channels modified using EDTA with respect to monovalent cations,” Neirofiziologiya, 14, No. 5, 491–498 (1982).
B. Corry, T. W. Allen, S. Kuyucak, and S.-H. Chung, “Mechanisms of permeation and selectivity in calcium channels,” Biophys. J., 80, 195–214 (2001).
H. von Gersdorff and G. Matthews, “Calcium-dependent inactivation of calcium current in synaptic terminals of retinal bipolar neurons,” J. Neurosci., 16, No. 1, 115–122 (1996).
A. Ivanenko, M. D. Baring, J. A. Airey, et al., “A caffeine-and ryanodine-sensitive Ca2+ store in avian sensory neurons,” J. Neurophysiol., 70, No. 2, 710–722 (1993).
D. L. Bennett, M. D. Bootman, M. J. Berridge, and T. R. Cheek, “Ca2+ entry into PC12 cells initiated by ryanodine receptors or inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors,” Biochem. J., 329, 349–357 (1998).
S. Zhang, M. D. Ehlers, J. P. Bernhardt, et al., “Calmodulin mediates calcium-dependent inactivation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors,” Neuron, 21, 443–453 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Neirofiziologiya/Neurophysiology, Vol. 40, No. 2, pp. 93–99, March–April, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korol’, S.V., Korol’, T.Y., Kostyuk, E.P. et al. Potassium permeability of voltage-operated calcium channels of dorsal root ganglion neurons in a calcium-free medium. Neurophysiology 40, 79–85 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-008-9029-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-008-9029-0