Abstract
Purpose
Since frameless stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) techniques have been recently introduced, hypofractionated SRS (HF-SRS) for large brain metastases (BMs) is gradually increasing. To verify the efficacy and safety of HF-SRS for large BMs, we aimed to perform a systematic review and compared them with SF-SRS.
Methods
We systematically searched the studies regarding SF-SRS or HF-SRS for large (> 2 cm) BM from databases including PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library on July 31, 2018. Biologically effective dose with the α/β ratio of 10 (BED10), 1-year local control (LC), and radiation necrosis (RN) were compared between the two groups, with the studies being weighted by the sample size.
Results
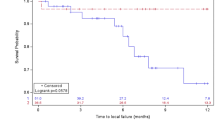
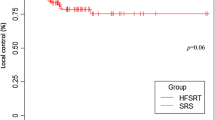
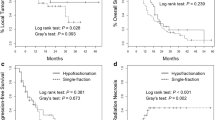
The 15 studies with 1049 BMs that described 1-year LC and RN were included. HF-SRS tended to be performed in larger tumors; however, higher mean BED10 (50.1 Gy10 versus 40.4 Gy10, p < 0.0001) was delivered in the HF-SRS group, which led to significantly improved 1-year LC (81.6 versus 69.0%, p < 0.0001) and 1-year overall survival (55.1 versus 47.2%, p < 0.0001) in the HF-SRS group compared to the SF-SRS group. In contrast, the incidence of radiation toxicity was significantly decreased in the HF-SRS group compared to the SF-SRS group (8.0 versus 15.6%, p < 0.0001).
Conclusion
HF-SRS results in better LC of large BMs while simultaneously reducing RN compared to SF-SRS. Thus, HF-SRS should be considered a priority for SF-SRS in patients with large BMs who are not suitable to undergo surgical resection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeong WJ, Park JH, Lee EJ, Kim JH, Kim CJ, Cho YH (2015) Efficacy and safety of fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for large brain metastases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58:217–224. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.217
Shiau CY, Sneed PK, Shu HKG, Lamborn KR, McDermott MW, Chang S, Nowak P, Petti PL, Smith V, Verhey LJ, Ho M, Park E, Wara WM, Gutin PH, Larson DA (1997) Radiosurgery for brain metastases: Relationship of dose and pattern of enhancement to local control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:375–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3016(96)00497-X
Breneman JC, Warnick RE, Albright RE Jr, Kukiatinant N, Shaw J, Armin D, Tew J Jr (1997) Stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of brain metastases. Results of a single institution series. Cancer 79:551–557
Matsuo T, Shibata S, Yasunaga A, Iwanaga M, Mori K, Shimizu T, Hayashi N, Ochi M, Hayashi K (1999) Dose optimization and indication of linac radiosurgery for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 45:931–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3016(99)00271-0
Gerosa M, Nicolato A, Foroni R, Tomazzoli L, Bricolo A (2005) Analysis of long-term outcomes and prognostic factors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases treated by gamma knife radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 102:75–80. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2005.102.s_supplement.0075
Sheehan J, Kondziolka D, Flickinger J, Lunsford LD (2005) Radiosurgery for patients with recurrent small cell lung carcinoma metastatic to the brain: outcomes and prognostic factors. J Neurosurg 102:247–254. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2005.102.s_supplement.0247
Muacevic A, Kreth FW, Tonn JC, Wowra B (2004) Stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases from breast carcinoma—feasibility and outcome of a local treatment concept. Cancer 100:1705–1711. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.20167
Selek U, Chang EL, Hassenbusch SJ, Shiu AS, Lang FF, Allen P, Weinberg J, Sawaya R, Maor MH (2004) Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment in 103 patients for 153 cerebral melanoma metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:1097–1106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.12.037
Muacevic A, Siebels M, Tonn JC, Wowra B (2005) Treatment of brain metastases in renal cell carcinoma: radiotherapy, radiosurgery, or surgery? World J Urol 23:180–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-004-0471-3
Alexander E 3rd, Moriarty TM, Davis RB, Wen PY, Fine HA, Black PM, Kooy HM, Loeffler JS (1995) Stereotactic radiosurgery for the definitive, noninvasive treatment of brain metastases. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/87.1.34
Mori Y, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Kirkwood JM, Agarwala S, Lunsford LD (1998) Stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral metastatic melanoma: Factors affecting local disease control and survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 42:581–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3016(98)00272-7
Noel G, Simon JM, Valery CA, Cornu P, Boisserie G, Hasboun D, Ledu D, Tep B, Delattre JY, Marsault C, Baillet F, Mazeron JJ (2003) Radiosurgery for brain metastasis: impact of CTV on local control. Radiother Oncol 68:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8140(03)00207-X
Molenaar R, Wiggenraad R, Verbeek-de Kanter A, Walchenbach R, Vecht C (2009) Relationship between volume, dose and local control in stereotactic radiosurgery of brain metastasis. Br J Neurosurg 23:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1080/02688690902755613
van Leeuwen CM, Oei AL, Crezee J, Bel A, Franken NAP, Stalpers LJA, Kok HP (2018) The alfa and beta of tumours: a review of parameters of the linear-quadratic model, derived from clinical radiotherapy studies. Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-018-1040-z
McClelland S 3rd, Ford B, Senatus PB, Frucht SJ, Winfield LM, Yu Q, Du YE, Pullman SL, McKhann GM 2nd, Goodman RR (2009) Typical variations of subthalamic electrode location do not predict limb motor function improvement in Parkinson’s disease. J Clin Neurosci 16:771–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2008.10.011
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Onimaru R, Kagei K, Ikeda J, Ishii N, Sawamura Y, Miyasaka K (2003) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy alone without whole-brain irradiation for patients with solitary and oligo brain metastasis using noninvasive fixation of the skull. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 56:793–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00014-2
Ogura K, Mizowaki T, Ogura M, Sakanaka K, Arakawa Y, Miyamoto S, Hiraoka M (2012) Outcomes of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for metastatic brain tumors with high risk factors. J Neurooncol 109:425–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0912-6
Feuvret L, Vinchon S, Martin V, Lamproglou I, Halley A, Calugaru V, Chea M, Valery CA, Simon JM, Mazeron JJ (2014) Stereotactic radiotherapy for large solitary brain metastases. Cancer Radiotherapie 18:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canrad.2013.12.003
Murai T, Ogino H, Manabe Y, Iwabuchi M, Okumura T, Matsushita Y, Tsuji Y, Suzuki H, Shibamoto Y (2014) Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy using cyberknife for the treatment of large brain metastases: a dose escalation study. Clin Oncol 26:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2013.11.027
Nagai A, Shibamoto Y, Yoshida M, Wakamatsu K, Kikuchi Y (2014) Treatment of single or multiple brain metastases by hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy using helical tomotherapy. Int J Mol Sci 15:6910–6924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046910
Kim JW, Park HR, Lee JM, Kim JW, Chung HT, Kim DG, Jung HW, Paek SH (2016) Fractionated stereotactic gamma knife radiosurgery for large brain metastases: a retrospective Single Center Study. PLoS ONE 11(9):e0163304. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163304
Minniti G, Scaringi C, Paolini S, Lanzetta G, Romano A, Cicone F, Osti M, Enrici RM, Esposito V (2016) Single-fraction versus multifraction (3 x 9 Gy) stereotactic radiosurgery for large (> 2 cm) brain metastases: a comparative analysis of local control and risk of radiation-induced brain necrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 95:1142–1148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.03.013
Navarria P, Pessina F, Cozzi L, Ascolese AM, De Rose F, Fogliata A, Franzese C, Franceschini D, Tozzi A, D’Agostino G, Comito T, Iftode C, Maggi G, Reggiori G, Bello L, Scorsetti M (2016) Hypo-fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy alone using volumetric modulated arc therapy for patients with single, large brain metastases unsuitable for surgical resection. Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-016-0653-3
Marcrom SR, McDonald AM, Thompson JW, Popple RA, Riley KO, Markert JM, Willey CD, Bredel M, Fiveash JB (2017) Fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy for intact brain metastases. Adv Radiat Oncol 2:564–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adro.2017.07.006
Wiggenraad R, Verbeek-de Kanter A, Mast M, Molenaar R, Kal HB, Lycklama A, Nijeholt G, Vecht C, Struikmans H (2012) Local progression and pseudo progression after single fraction or fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for large brain metastases. A single centre study. Strahlenther Onkol 188:696–701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-012-0122-3
Kano H, Niranjan A, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2009) Stereotactic radiosurgery for pituitary metastases. Surg Neurol 72:248–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2008.06.003
Flannery T, Kano H, Niranjan A, Monaco EA, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D (2010) Stereotactic radiosurgery as a therapeutic strategy for intracranial metastatic prostate carcinoma. J Neurooncol 96:369–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-9966-5
Prabhu RS, Press RH, Patel KR, Boselli DM, Symanowski JT, Lankford SP, McCammon RJ, Moeller BJ, Heinzerling JH, Fasola CE, Asher AL, Sumrall AL, Buchwald ZS, Curran WJ Jr, Shu HG, Crocker I, Burri SH (2017) Single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) alone versus surgical resection and SRS for large brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 99:459–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.04.006
Cummings M, Youn P, Bergsma DP, Usuki KY, Walter K, Sharma M, Okunieff P, Schell MC, Milano MT (2018) Single-fraction radiosurgery using conservative doses for brain metastases: durable responses in select primaries with limited toxicity. Neurosurgery 83:437–444. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyx427
Wolf A, Kvint S, Chachoua A, Pavlick A, Wilson M, Donahue B, Golfinos JG, Silverman J, Kondziolka D (2018) Toward the complete control of brain metastases using surveillance screening and stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 128:23–31. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.10.Jns161036
Kalkanis SN, Kondziolka D, Gaspar LE, Burri SH, Asher AL, Cobbs CS, Ammirati M, Robinson PD, Andrews DW, Loeffler JS, McDermott M, Mehta MP, Mikkelsen T, Olson JJ, Paleologos NA, Patchell RA, Ryken TC, Linskey ME (2010) The role of surgical resection in the management of newly diagnosed brain metastases: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol 96:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0061-8
Lehrer EJ, Peterson JL, Zaorsky NG, Brown PD, Sahgal A, Chiang VL, Chao ST, Sheehan JP, Trifiletti DM (2019) Single versus multifraction stereotactic radiosurgery for large brain metastases: an international meta-analysis of 24 trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 103:618–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.10.038
Masucci GL (2018) Hypofractionated radiation therapy for large brain metastases. Front Oncol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00379
Williams BJ, Suki D, Fox BD, Pelloski CE, Maldaun MV, Sawaya RE, Lang FF, Rao G (2009) Stereotactic radiosurgery for metastatic brain tumors: a comprehensive review of complications. J Neurosurg 111:439–448. https://doi.org/10.3171/2008.11.JNS08984
Blonigen BJ, Steinmetz RD, Levin L, Lamba MA, Warnick RE, Breneman JC (2010) Irradiated volume as a predictor of brain radionecrosis after linear accelerator stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:996–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.06.006
Minniti G, Clarke E, Lanzetta G, Osti MF, Trasimeni G, Bozzao A, Romano A, Enrici RM (2011) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717x-6-48
Nedzi LA, Kooy H, Alexander E 3rd, Gelman RS, Loeffler JS (1991) Variables associated with the development of complications from radiosurgery of intracranial tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 21:591–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-3016(91)90675-t
Korytko T, Radivoyevitch T, Colussi V, Wessels BW, Pillai K, Maciunas RJ, Einstein DB (2006) 12 GY gamma knife radiosurgical volume is a predictor for radiation necrosis in non-AVM intracranial tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:419–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.07.980
Santacroce A, Kamp MA, Budach W, Hanggi D (2013) Radiobiology of radiosurgery for the central nervous system. Biomed Res Int 2013:362761. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/362761
Jiang XS, Xiao JP, Zhang Y, Xu YJ, Li XP, Chen XJ, Huang XD, Yi JL, Gao L, Li YX (2012) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases larger than three centimeters. Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717x-7-36
Minniti G, D’Angelillo RM, Scaringi C, Trodella LE, Clarke E, Matteucci P, Osti MF, Ramella S, Enrici RM, Trodella L (2014) Fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases. J Neurooncol 117:295–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1388-3
Chon H, Yoon K, Lee D, Kwon DH, Cho YH (2019) Single-fraction versus hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for medium-sized brain metastases of 2.5 to 3 cm. J Neurooncol 145:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03265-1
Schlienger M, Nataf F, Huguet F, Pene F, Foulquier JN, Orthuon A, Roux FX, Touboul E (2010) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases. Cancer Radiother 14:119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canrad.2009.10.004
Larsson B, Leksell L, Rexed B, Sourander P, Mair W, Andersson B (1958) High-energy proton beam as a neurosurgical tool. Nature 182:1222–1223. https://doi.org/10.1038/1821222a0
Zhao W, Robbins ME (2009) Inflammation and chronic oxidative stress in radiation-induced late normal tissue injury: therapeutic implications. Curr Med Chem 16:130–143. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986709787002790
Panganiban RA, Mungunsukh O, Day RM (2013) X-irradiation induces ER stress, apoptosis, and senescence in pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Int J Radiat Biol 89:656–667. https://doi.org/10.3109/09553002.2012.711502
Panganiban RA, Snow AL, Day RM (2013) Mechanisms of radiation toxicity in transformed and non-transformed cells. Int J Mol Sci 14:15931–15958. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140815931
Rothkamm K, Lobrich M (2003) Evidence for a lack of DNA double-strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low x-ray doses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5057–5062. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0830918100
Lindsay KJ, Coates PJ, Lorimore SA, Wright EG (2007) The genetic basis of tissue responses to ionizing radiation. Br J Radiol 80:S2–S6. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/60507340
Surova O, Zhivotovsky B (2013) Various modes of cell death induced by DNA damage. Oncogene 32:3789–3797. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.556
Friedman EJ (2002) Immune modulation by ionizing radiation and its implications for cancer immunotherapy. Curr Pharm Des 8:1765–1780. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612023394089
Mullins ME, Barest GD, Schaefer PW, Hochberg FH, Gonzalez RG, Lev MH (2005) Radiation necrosis versus glioma recurrence: conventional MR imaging clues to diagnosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1967–1972
Hall EJ, Brenner DJ (1993) The radiobiology of radiosurgery: rationale for different treatment regimes for AVMs and malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 25:381–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-3016(93)90367-5
Ling CC, Lo YC, Larson DA (1995) Radiobiophysical aspects of stereotaxic radiation treatment of central nervous system diseases. Semin Radiat Oncol 5:192–196. https://doi.org/10.1054/SRAO00500192
Suh JH, Kotecha R, Chao ST, Ahluwalia MS, Sahgal A, Chang EL (2020) Current approaches to the management of brain metastases. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 17:279–299. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-019-0320-3
Jiang T, Min W, Li Y, Yue Z, Wu C, Zhou C (2016) Radiotherapy plus EGFR TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: an update meta-analysis. Cancer Med 5:1055–1065. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.673
Tallet AV, Dhermain F, Le Rhun E, Noel G, Kirova YM (2017) Combined irradiation and targeted therapy or immune checkpoint blockade in brain metastases: toxicities and efficacy. Ann Oncol 28:2962–2976. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx408
Kotecha R, Kim JM, Miller JA, Juloori A, Chao ST, Murphy ES, Peereboom DM, Mohammadi AM, Barnett GH, Vogelbaum MA, Angelov L, Suh JH, Ahluwalia MS (2019) The impact of sequencing PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastasis. Neuro Oncol 21:1060–1068. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noz046
Knisely JP, Yu JB, Flanigan J, Sznol M, Kluger HM, Chiang VL (2012) Radiosurgery for melanoma brain metastases in the ipilimumab era and the possibility of longer survival. J Neurosurg 117:227–233. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.5.JNS111929
Schoenfeld JD, Mahadevan A, Floyd SR, Dyer MA, Catalano PJ, Alexander BM, McDermott DF, Kaplan ID (2015) Ipilmumab and cranial radiation in metastatic melanoma patients: a case series and review. J Immunother Cancer 3:50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-015-0095-8
Martin AM, Cagney DN, Catalano PJ, Alexander BM, Redig AJ, Schoenfeld JD, Aizer AA (2018) Immunotherapy and symptomatic radiation necrosis in patients with brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiation. JAMA Oncol 4:1123–1124. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3993
Jones B, Dale RG, Deehan C, Hopkins KI, Morgan DA (2001) The role of biologically effective dose (BED) in clinical oncology. Clin Oncol R Coll Radiol 13:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1053/clon.2001.9221
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, E.J., Choi, KS., Park, E.S. et al. Single- and hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for large (> 2 cm) brain metastases: a systematic review. J Neurooncol 154, 25–34 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03805-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03805-8