Abstract
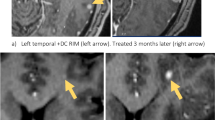
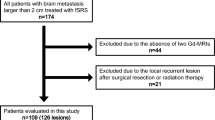
The number of brain metastases identified on diagnostic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a key factor in consideration of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). However, additional lesions are often detected on high-resolution SRS-planning MRI. We investigated pre-treatment clinical characteristics that are associated with finding additional metastases at SRS. Patients treated with SRS for brain metastases between the years of 2009–2014 comprised the study cohort. All patients underwent frame-fixed, 1 mm thick MRI on the day of SRS. Patient, tumor, and treatment characteristics were analyzed for an association with increase in number of metastases identified on SRS-planning MRI. 289 consecutive SRS cases were analyzed. 725 metastases were identified on pre-treatment MRI and 1062 metastases were identified on SRS-planning MRI. An increase in the number of metastases occurred in 34 % of the cases. On univariate analysis, more than four metastases and the diameter of the largest lesion were significantly associated with an increase in number of metastases on SRS-planning MRI. When stratified by the diameter of the largest lesion into <2, 2–3, or ≥3 cm, additional metastases were identified in 37, 29, and 18 %, respectively. While this increase in the number of metastases is largely due to the difference in imaging technique, the number and size of the metastases were also associated with finding additional lesions. These clinical factors may be considered when determining treatment options for brain metastases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Claus EB (2012) Neurosurgical management of metastases in the central nervous system. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 9(2):79–86. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.179
Mehta MP, Tsao MN, Whelan TJ, Morris DE, Hayman JA, Flickinger JC, Mills M, Rogers CL, Souhami L (2005) The American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ASTRO) evidence-based review of the role of radiosurgery for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63(1):37–46. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.05.023
Sperduto PW, Berkey B, Gaspar LE, Mehta M, Curran W (2008) A new prognostic index and comparison to three other indices for patients with brain metastases: an analysis of 1,960 patients in the RTOG database. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70(2):510–514. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.06.074
Mathieu D, Kondziolka D, Cooper PB, Flickinger JC, Niranjan A, Agarwala S, Kirkwood J, Lunsford LD (2007) Gamma knife radiosurgery in the management of malignant melanoma brain metastases. Neurosurgery 60(3):471–481. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000255342.10780.52 (discussion 481–472)
Kano H, Iyer A, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2011) Outcome predictors of gamma knife radiosurgery for renal cell carcinoma metastases. Neurosurgery 69(6):1232–1239. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e31822b2fdc
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG, Arbuckle RB, Swint JM, Shiu AS, Maor MH, Meyers CA (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10(11):1037–1044. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70263-3
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K, Kenjyo M, Oya N, Hirota S, Shioura H, Kunieda E, Inomata T, Hayakawa K, Katoh N, Kobashi G (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295(21):2483–2491. doi:10.1001/jama.295.21.2483
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, Werner-Wasik M, Demas W, Ryu J, Bahary JP, Souhami L, Rotman M, Mehta MP, Curran WJ Jr (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363(9422):1665–1672. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16250-8
Nagai A, Shibamoto Y, Mori Y, Hashizume C, Hagiwara M, Kobayashi T (2010) Increases in the number of brain metastases detected at frame-fixed, thin-slice MRI for gamma knife surgery planning. Neuro-oncology 12(11):1187–1192. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noq084
Engh JA, Flickinger JC, Niranjan A, Amin DV, Kondziolka DS, Lunsford LD (2007) Optimizing intracranial metastasis detection for stereotactic radiosurgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 85(4):162–168. doi:10.1159/000099075
Henley SJ, Singh SD, King J, Wilson R, O’Neil ME, Ryerson AB, Centers for Disease C, Prevention (2015) Invasive cancer incidence and survival—United States. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 64(9):237–242
Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, Vigneau FD, Lai P, Sawaya RE (2004) Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J Clin Oncol 22(14):2865–2872. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.12.149
Fabi A, Felici A, Metro G, Mirri A, Bria E, Telera S, Moscetti L, Russillo M, Lanzetta G, Mansueto G, Pace A, Maschio M, Vidiri A, Sperduti I, Cognetti F, Carapella CM (2011) Brain metastases from solid tumors: disease outcome according to type of treatment and therapeutic resources of the treating center. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 30:10. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-30-10
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villa S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortmann RD, Carrie C, Ben Hassel M, Kouri M, Valeinis E, van den Berge D, Collette S, Collette L, Mueller RP (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29(2):134–141. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.30.1655
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T, Akabane A, Higuchi Y, Kawagishi J, Yamanaka K, Sato Y, Jokura H, Yomo S, Nagano O, Kenai H, Moriki A, Suzuki S, Kida Y, Iwai Y, Hayashi M, Onishi H, Gondo M, Sato M, Akimitsu T, Kubo K, Kikuchi Y, Shibasaki T, Goto T, Takanashi M, Mori Y, Takakura K, Saeki N, Kunieda E, Aoyama H, Momoshima S, Tsuchiya K (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol 15(4):387–395. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70061-0
Schellinger PD, Meinck HM, Thron A (1999) Diagnostic accuracy of MRI compared to CCT in patients with brain metastases. J Neurooncol 44(3):275–281
Kim ES, Chang JH, Choi HS, Kim J, Lee SK (2010) Diagnostic yield of double-dose gadobutrol in the detection of brain metastasis: intraindividual comparison with double-dose gadopentetate dimeglumine. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31(6):1055–1058. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2010
Ba-Ssalamah A, Nobauer-Huhmann IM, Pinker K, Schibany N, Prokesch R, Mehrain S, Mlynarik V, Fog A, Heimberger K, Trattnig S (2003) Effect of contrast dose and field strength in the magnetic resonance detection of brain metastases. Invest Radiol 38(7):415–422. doi:10.1097/01.RLI.0000067488.57101.bd
Biswas J, Nelson CB, Runge VM, Wintersperger BJ, Baumann SS, Jackson CB, Patel T (2005) Brain tumor enhancement in magnetic resonance imaging: comparison of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) at 1.5 versus 3 tesla. Invest Radiol 40(12):792–797
Nobauer-Huhmann IM, Ba-Ssalamah A, Mlynarik V, Barth M, Schoggl A, Heimberger K, Matula C, Fog A, Kaider A, Trattnig S (2002) Magnetic resonance imaging contrast enhancement of brain tumors at 3 tesla versus 1.5 tesla. Invest Radiol 37(3):114–119
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank members of the Department of Radiation Oncology and Department of Neurosurgery at UT Southwestern Medical Center for their helpful critiques of this manuscript.
Funding
AA was supported by NCI 1F30CA168264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wardak, Z., Augustyn, A., Zhu, H. et al. Pre-treatment factors associated with detecting additional brain metastases at stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 128, 251–257 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2103-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2103-3