Abstract
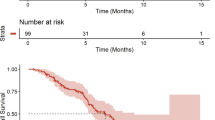
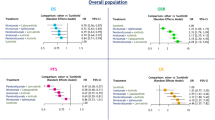
Malignant glioma treated with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) bevacizumab show progression patterns that vary with different mechanisms of resistance. We evaluated the clinico-radiological data of 71 patients with progressive malignant glioma treated with bevacizumab to determine the prognostic value of the differential outcome of each progression pattern. Progression patterns were categorized as three types based on the initial response to bevacizumab and serious changes of MR images i.e., non-enhancing infiltration, flare-up of contrast enhancement (CE) and primary non-responder progression. We analyzed the clinical outcome in each type of progression using Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. Analysis of progression patterns showed that incidence of non-enhancing infiltration progression (28.1 %) was less common than flare-up of CE or primary non-responder pattern. The time from initiation of bevacizumab to development of non-enhancing infiltration or flare-up of CE progression was longer than for progression in primary non-responders. There was no significant difference of overall survival, progression-free survival from start of bevacizumab therapy, survival after bevacizumab failure between non-enhancing infiltration and flare-up of CE patterns. However, in the non-enhancing infiltration pattern, early appearance of enhancement was observed after bevacizumab was discontinued, resulting in poor survival, as compared to flare-up of CE pattern (P = 0.01). Although the appearance of non-enhancing infiltration after bevacizumab does not imply a worse prognosis, discontinuation of therapy can aggravate the clinical course.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO, European Organisation for R, Treatment of Cancer Brain T, Radiotherapy G, National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials G (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. New Engl J Med 352:987–996. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043330
Gilbert MR, Wang M, Aldape KD, Stupp R, Hegi ME, Jaeckle KA, Armstrong TS, Wefel JS, Won M, Blumenthal DT, Mahajan A, Schultz CJ, Erridge S, Baumert B, Hopkins KI, Tzuk-Shina T, Brown PD, Chakravarti A, Curran WJ Jr, Mehta MP (2013) Dose-dense temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a randomized phase III clinical trial. J Clin Oncol 31:4085–4091. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.49.6968 (official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology)
Wong ET, Hess KR, Gleason MJ, Jaeckle KA, Kyritsis AP, Prados MD, Levin VA, Yung WK (1999) Outcomes and prognostic factors in recurrent glioma patients enrolled onto phase II clinical trials. J Clin Oncol 17:2572–2578 (official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology)
Lamborn KR, Yung WK, Chang SM, Wen PY, Cloughesy TF, DeAngelis LM, Robins HI, Lieberman FS, Fine HA, Fink KL, Junck L, Abrey L, Gilbert MR, Mehta M, Kuhn JG, Aldape KD, Hibberts J, Peterson PM, Prados MD, North American Brain Tumor C (2008) Progression-free survival: an important end point in evaluating therapy for recurrent high-grade gliomas. Neuro-Oncology 10:162–170. doi:10.1215/15228517-2007-062
Lamszus K, Ulbricht U, Matschke J, Brockmann MA, Fillbrandt R, Westphal M (2003) Levels of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor 1 in astrocytic tumors and its relation to malignancy, vascularity, and VEGF-A. Clini Cancer Res 9:1399–1405 (an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research)
Plate KH, Breier G, Weich HA, Risau W (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature 359:845–848. doi:10.1038/359845a0
Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, Mikkelsen T, Schiff D, Abrey LE, Yung WK, Paleologos N, Nicholas MK, Jensen R, Vredenburgh J, Huang J, Zheng M, Cloughesy T (2009) Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27:4733–4740. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.19.8721 (official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology)
Kreisl TN, Kim L, Moore K, Duic P, Royce C, Stroud I, Garren N, Mackey M, Butman JA, Camphausen K, Park J, Albert PS, Fine HA (2009) Phase II trial of single-agent bevacizumab followed by bevacizumab plus irinotecan at tumor progression in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27:740–745. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.16.3055 (official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology)
Wen PY, Junck L (2014) Bevacizumab for glioblastoma: what can we learn from patterns of progression? Neurology 82:1670–1671. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000421
Quant EC, Norden AD, Drappatz J, Muzikansky A, Doherty L, Lafrankie D, Ciampa A, Kesari S, Wen PY (2009) Role of a second chemotherapy in recurrent malignant glioma patients who progress on bevacizumab. Neuro-Oncology 11:550–555. doi:10.1215/15228517-2009-006
Chinot OL, Wick W, Mason W, Henriksson R, Saran F, Nishikawa R, Carpentier AF, Hoang-Xuan K, Kavan P, Cernea D, Brandes AA, Hilton M, Abrey L, Cloughesy T (2014) Bevacizumab plus radiotherapy-temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. New Engl J Med 370:709–722. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1308345
Gilbert MR, Dignam JJ, Armstrong TS, Wefel JS, Blumenthal DT, Vogelbaum MA, Colman H, Chakravarti A, Pugh S, Won M, Jeraj R, Brown PD, Jaeckle KA, Schiff D, Stieber VW, Brachman DG, Werner-Wasik M, Tremont-Lukats IW, Sulman EP, Aldape KD, Curran WJ Jr, Mehta MP (2014) A randomized trial of bevacizumab for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. New Engl J Med 370:699–708. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1308573
Iwamoto FM, Abrey LE, Beal K, Gutin PH, Rosenblum MK, Reuter VE, DeAngelis LM, Lassman AB (2009) Patterns of relapse and prognosis after bevacizumab failure in recurrent glioblastoma. Neurology 73:1200–1206. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bc0184
Pope WB, Xia Q, Paton VE, Das A, Hambleton J, Kim HJ, Huo J, Brown MS, Goldin J, Cloughesy T (2011) Patterns of progression in patients with recurrent glioblastoma treated with bevacizumab. Neurology 76:432–437. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e31820a0a8a
Narayana A, Kelly P, Golfinos J, Parker E, Johnson G, Knopp E, Zagzag D, Fischer I, Raza S, Medabalmi P, Eagan P, Gruber ML (2009) Antiangiogenic therapy using bevacizumab in recurrent high-grade glioma: impact on local control and patient survival. J Neurosurg 110:173–180. doi:10.3171/2008.4.17492
Zuniga RM, Torcuator R, Jain R, Anderson J, Doyle T, Ellika S, Schultz L, Mikkelsen T (2009) Efficacy, safety and patterns of response and recurrence in patients with recurrent high-grade gliomas treated with bevacizumab plus irinotecan. J Neuro-Oncol 91:329–336. doi:10.1007/s11060-008-9718-y
Wick A, Dorner N, Schafer N, Hofer S, Heiland S, Schemmer D, Platten M, Weller M, Bendszus M, Wick W (2011) Bevacizumab does not increase the risk of remote relapse in malignant glioma. Ann Neurol 69:586–592. doi:10.1002/ana.22336
Wick W, Wick A, Weiler M, Weller M (2011) Patterns of progression in malignant glioma following anti-VEGF therapy: perceptions and evidence. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 11:305–312. doi:10.1007/s11910-011-0184-0
Nowosielski M, Wiestler B, Goebel G, Hutterer M, Schlemmer HP, Stockhammer G, Wick W, Bendszus M, Radbruch A (2014) Progression types after antiangiogenic therapy are related to outcome in recurrent glioblastoma. Neurology 82:1684–1692. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000402
Soffietti R, Trevisan E, Bertero L, Cassoni P, Morra I, Fabrini MG, Pasqualetti F, Lolli I, Castiglione A, Ciccone G, Ruda R (2014) Bevacizumab and fotemustine for recurrent glioblastoma: a phase II study of AINO (Italian Association of Neuro-Oncology). J Neuro-Oncol 116:533–541. doi:10.1007/s11060-013-1317-x
Verhoeff JJ, van Tellingen O, Claes A, Stalpers LJ, van Linde ME, Richel DJ, Leenders WP, van Furth WR (2009) Concerns about anti-angiogenic treatment in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. BMC Cancer 9:444. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-9-444
Norden AD, Drappatz J, Wen PY (2008) Novel anti-angiogenic therapies for malignant gliomas. Lancet Neurol 7:1152–1160. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70260-6
de Groot JF, Fuller G, Kumar AJ, Piao Y, Eterovic K, Ji Y, Conrad CA (2010) Tumor invasion after treatment of glioblastoma with bevacizumab: radiographic and pathologic correlation in humans and mice. Neuro-Oncology 12:233–242. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nop027
Kunkel P, Ulbricht U, Bohlen P, Brockmann MA, Fillbrandt R, Stavrou D, Westphal M, Lamszus K (2001) Inhibition of glioma angiogenesis and growth in vivo by systemic treatment with a monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. Cancer Res 61:6624–6628
Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA, Cloughesy TF, Sorensen AG, Galanis E, Degroot J, Wick W, Gilbert MR, Lassman AB, Tsien C, Mikkelsen T, Wong ET, Chamberlain MC, Stupp R, Lamborn KR, Vogelbaum MA, van den Bent MJ, Chang SM (2010) Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol 28:1963–1972. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.26.3541 (official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology)
Greenwood M (1926) A report on the natural duration of cancer. Her Majesty’s Stationary Office, London
Bergers G, Hanahan D (2008) Modes of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 8:592–603. doi:10.1038/nrc2442
de Groot JF (2011) High-dose antiangiogenic therapy for glioblastoma: less may be more? Clin Cancer Res 17:6109–6111. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1853 (an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research)
Lorgis V, Maura G, Coppa G, Hassani K, Taillandier L, Chauffert B, Apetoh L, Ladoire S, Ghiringhelli F (2012) Relation between bevacizumab dose intensity and high-grade glioma survival: a retrospective study in two large cohorts. J Neuro-Oncol 107:351–358. doi:10.1007/s11060-011-0748-5
Bloch O, Safaee M, Sun MZ, Butowski NA, McDermott MW, Berger MS, Aghi MK, Parsa AT (2013) Disseminated progression of glioblastoma after treatment with bevacizumab. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115:1795–1801. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2013.04.017
Clark AJ, Lamborn KR, Butowski NA, Chang SM, Prados MD, Clarke JL, McDermott MW, Parsa AT, Berger MS, Aghi MK (2012) Neurosurgical management and prognosis of patients with glioblastoma that progresses during bevacizumab treatment. Neurosurgery 70:361–370. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182314f9d
DeLay M, Jahangiri A, Carbonell WS, Hu YL, Tsao S, Tom MW, Paquette J, Tokuyasu TA, Aghi MK (2012) Microarray analysis verifies two distinct phenotypes of glioblastomas resistant to antiangiogenic therapy. Clin Cancer Res 18:2930–2942. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2390 (an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research)
Ellingson BM, Cloughesy TF, Lai A, Mischel PS, Nghiemphu PL, Lalezari S, Schmainda KM, Pope WB (2011) Graded functional diffusion map-defined characteristics of apparent diffusion coefficients predict overall survival in recurrent glioblastoma treated with bevacizumab. Neuro-Oncology 13:1151–1161. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nor079
Norden AD, Young GS, Setayesh K, Muzikansky A, Klufas R, Ross GL, Ciampa AS, Ebbeling LG, Levy B, Drappatz J, Kesari S, Wen PY (2008) Bevacizumab for recurrent malignant gliomas: efficacy, toxicity, and patterns of recurrence. Neurology 70:779–787. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000304121.57857.38
Keunen O, Johansson M, Oudin A, Sanzey M, Rahim SA, Fack F, Thorsen F, Taxt T, Bartos M, Jirik R, Miletic H, Wang J, Stieber D, Stuhr L, Moen I, Rygh CB, Bjerkvig R, Niclou SP (2011) Anti-VEGF treatment reduces blood supply and increases tumor cell invasion in glioblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:3749–3754. doi:10.1073/pnas.1014480108
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2011) Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 473:298–307. doi:10.1038/nature10144
Soda Y, Marumoto T, Friedmann-Morvinski D, Soda M, Liu F, Michiue H, Pastorino S, Yang M, Hoffman RM, Kesari S, Verma IM (2011) Transdifferentiation of glioblastoma cells into vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:4274–4280. doi:10.1073/pnas.1016030108
Gutman DA, Cooper LA, Hwang SN, Holder CA, Gao J, Aurora TD, Dunn WD Jr, Scarpace L, Mikkelsen T, Jain R, Wintermark M, Jilwan M, Raghavan P, Huang E, Clifford RJ, Mongkolwat P, Kleper V, Freymann J, Kirby J, Zinn PO, Moreno CS, Jaffe C, Colen R, Rubin DL, Saltz J, Flanders A, Brat DJ (2013) MR imaging predictors of molecular profile and survival: multi-institutional study of the TCGA glioblastoma data set. Radiology 267:560–569. doi:10.1148/radiol.13120118
Jain R, Poisson L, Narang J, Gutman D, Scarpace L, Hwang SN, Holder C, Wintermark M, Colen RR, Kirby J, Freymann J, Brat DJ, Jaffe C, Mikkelsen T (2013) Genomic mapping and survival prediction in glioblastoma: molecular subclassification strengthened by hemodynamic imaging biomarkers. Radiology 267:212–220. doi:10.1148/radiol.12120846
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Byung Sup Kim and Sung Kwon Kim have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, B.S., Kim, S.K., Choi, S.H. et al. Prognostic implication of progression pattern after anti-VEGF bevacizumab treatment for recurrent malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol 124, 101–110 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1808-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1808-z