Abstract
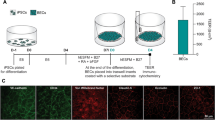
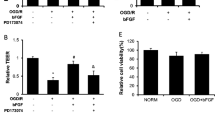
We have previously shown that activation of RhoA by bradykinin (BK) is associated with cytoskeleton rearrangement, tight junction (TJ) protein disassembly, and an increase in blood–tumor barrier (BTB) permeability in rat brain microvascular endothelial cells (RBMECs). Subsequently, we investigated whether Rho-kinases (ROCKs), a family of downstream effectors of activated RhoA known to stimulate F-actin rearrangement, play a key role in the above-mentioned processes in RBMECs. Our study uses primary RBMECs as an in vitro BTB model and a specific ROCK inhibitor (Y-27632) and ROCK II small interfering RNA (siRNA) to establish whether ROCK plays a role in the process of TJ opening by BK. Y-27632 and ROCK II siRNA could partially inhibit endothelial leakage and restored normal transendothelial electric resistance (TEER) values in RBMECs. A shift in occludin and claudin-5 distribution from insoluble to soluble fractions was prevented by Y-27632. Additionally, Y-27632 inhibited BK-induced relocation of occludin and claudin-5 from cellular borders into the cytoplasm as well as stress fiber formation in RBMECs. A time-dependent increase in phosphorylated myosin light chain (p-MLC) and phosphorylated cofilin (p-cofilin) by BK was observed, which was also inhibited by Y-27632. An increase in ROCK activity by BK was inhibited by Y-27632. ROCK’s contribution to BK-induced stress fiber formation is associated with TJ disassembly and an increase in BTB permeability.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black KL, Ningaraj NS (2004) Modulation of brain tumor capillaries for enhanced drug delivery selectively to brain tumor. Cancer Control 11:165–173
Samoto K, Perng GC, Ehtesham M, Liu Y, Wechsler SL, Nesburn AB, Black KL, Yu JS (2001) A herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant deleted for gamma 34.5 and LAT kills glioma cells in vitro and is inhibited for in vivo reactivation. Cancer Gene Therapy 8:269–277
Fenstermacher JK, Cowles AS (1977) Theoretic limitations of intracarotid infusions in brain tumor chemotherapy. Cancer Treat Rep 61:519–526
Muldoon LL, Soussain C, Jahnke K, Johanson C, Siegal T, Smith QR, Hall WA, Hynynen K, Senter PD, Peereboom DM, Neuwelt EA (2007) Chemotherapy delivery issues in central nervous system malignancy: a reality check. J Clin Oncol 25:2295–2305
Lockman PR, Mittapalli RK, Taskar KS, Rudraraju V, Gril B, Bohn KA, Adkins CE, Roberts A, Thorsheim HR, Gaasch JA, Huang S, Palmieri D, Steeg PS, Smith QR (2010) Heterogeneous blood-tumor barrier permeability determines drug efficacy in experimental brain metastases of breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16:5664–5678
Liu LB, Xue YX, Liu YH, Wang YB (2008) Bradykinin increases blood–tumor barrier permeability by down-regulating the expression levels of ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-5 and rearranging actin cytoskeleton. J Neurosci Res 86:1153–1168
Ma T, Xue Y (2010) RhoA-mediated potential regulation of blood-tumor barrier permeability by bradykinin. J Mol Neurosci 42:67–73
Yin J, Yu FS (2008) Rho kinases regulate corneal epithelial wound healing. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 295:C378–C387
Walsh SV, Hopkins AM, Chen J, Narumiya S, Parkos CA, Nusrat A (2001) Rho kinase regulates tight junction function and is necessary for tight junction assembly in polarized intestinal epithelia. Gastroenterology 121:566–579
Li B, Zhao WD, Tan ZM, Fang WG, Zhu L, Chen YH (2006) Involvement of Rho/ROCK signalling in small cell lung cancer migration through human brain microvascular endothelial cells. FEBS Lett 580:4252–4260
Calaminus SD, Auger JM, McCarty OJ, Wakelam MJ, Machesky LM, Watson SP (2007) MyosinIIa contractility is required for maintenance of platelet structure during spreading on collagen and contributes to thrombus stability. J Thromb Haemost 5:2136–2145
Wojciak-Stothard B, Ridley AJ (2002) Rho GTPases and the regulation of endothelial permeability. Vascul Pharmacol 39:187–199
Essler M, Staddon JM, Weber PC, Aepfelbacher M (2000) Cyclic AMP blocks bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced myosin light chain phosphorylation in endothelial cells through inhibition of Rho/Rho kinase signaling. J Immunol 164:6543–6549
van Nieuw Amerongen GP, van Delft S, Vermeer MA, Collard JG, van Hinsbergh VW (2000) Activation of RhoA by thrombin in endothelial hyperpermeability: role of Rho kinase and protein tyrosine kinases. Circ Res 87:335–340
Aepfelbacher M, Essler M (2001) Disturbance of endothelial barrier function by bacterial toxins and atherogenic mediators: a role for Rho/Rho kinase. Cell Microbiol 3:649–658
Hirase T, Kawashima S, Wong EY, Ueyama T, Rikitake Y, Tsukita S, Yokoyama M, Staddon JM (2001) Regulation of tight junction permeability and occludin phosphorylation by Rhoa-p160ROCK-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem 276:10423–10431
Wojciak-Stothard B, Potempa S, Eichholtz T, Ridley AJ (2001) Rho and Rac but not Cdc42 regulate endothelial cell permeability. J Cell Sci 114:1343–1355
Hurst RD, Fritz IB (1996) Properties of an immortalised vascular endothelial/glioma cell co-culture model of the blood-brain barrier. J Cell Physiol 167:81–88
Easton AS, Abbott NJ (2002) Brandykinin increases permeability by calcium and 5-lipoxygenase in the ECV304/C6 cell culture model of the blood-brain barrier. Brain Res 953:157–169
Wong D, Dorovini-Zis K, Vincent SR (2004) Cytokines, nitric oxide, and cGMP modulate the permeability of an in vitro model of the human blood-brain barrier. Exp Neurol 190:446–455
Fuller E, Duckham C, Wood E (2007) Disruption of epithelial tight junctions by yeast enhances the paracellular delivery of a model protein. Pharm Res 24:37–47
Nunes KP, Rigsby CS, Webb RC (2010) RhoA/Rho-kinase and vascular diseases: what is the link? Cell Mol Life Sci 67:3823–3836
Liao JK, Seto M, Noma K (2007) Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 50:17–24
Davies SP, Reddy H, Caivano M, Cohen P (2000) Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J 351:95–105
Narumiya ST, Ishizaki M, Uehata (2000) Use and properties of ROCKspecific inhibitor Y-27632. Methods Enzymol 325:273–284
Ridley AJ (2001) Rho family proteins: coordinating cell responses. Trends Cell Biol 11:471–477
Nakagawa O, Fujisawa K, Ishizaki T, Saito Y, Nakao K, Narumiya S (1996) ROCK-I and ROCK-II, two isoforms of Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein serine/threonine kinase in mice. FEBS Lett 392:189–193
Di Cunto F, Imarisio S, Hirsch E, Broccoli V, Bulfone A, Migheli A, Atzori C, Turco E, Triolo R, Dotto GP, Silengo L, Altruda F (2000) Defective neurogenesis in citron kinase knockout mice by altered cytokinesis and massive apoptosis. Neuron 28:115–127
Wei L, Roberts W, Wang L, Yamada M, Zhang S, Zhao Z, Rivkees SA, Schwartz RJ, Imanaka-Yoshida K (2001) Rho kinases play an obligatory role in vertebrate embryonic organogenesis. Development 128:2953–2962
Liu PY, Liao JK (2008) A method for measuring Rho kinase activity in tissues and cells. Methods Enzymol 39:181–189
Rubenstein NM, Callahan JA, Lo DH, Firestone GL (2007) Selective glucocorticoid control of Rho kinase isoforms regulate cell–cell interactions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354:603–607
Mong PY, Wang Q (2009) Activation of Rho kinase isoforms in lung endothelial cells during inflammation. J Immunol 182:2385–2394
Harhaj NS, Antonetti DA (2004) Regulation of tight junctions and loss of barrier function in pathophysiology. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:1206–1237
Collares-Buzato CB, Jepson MA, Simmons NL, Hirst BH (1998) Increased tyrosine phosphorylation causes redistribution of adherens junction and tight junction proteins and perturbs paracellular barrier function in MDCK epithelia. Eur J Cell Biol 76:85–92
Keita AV, Söderholm JD (2010) The intestinal barrier and its regulation by neuroimmune factors. Neurogastroenterol Motil 22:718–733
Kubota K, Furuse M, Sasaki H, Sonoda N, Fujita K, Nagafuchi A, Tsukita S (1999) Ca(2 +)-independent cell-adhesion activity of claudins, a family of integral membrane proteins localized at tight junctions. Curr Biol 9:1035–1038
Mitic LL, Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM (2000) Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions I. Tight junction structure and function: lessons from mutant animals and proteins. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 279:G250–G254
Olivera D, Knall C, Boggs S, Seagrave J (2010) Cytoskeletal modulation and tyrosine phosphorylation of tight junction proteins are associated with mainstream cigarette smoke-induced permeability of airway epithelium. Exp Toxicol Pathol 62:133–143
Olivera DS, Boggs SE, Beenhouwer C, Aden J, Knall C (2007) Cellular mechanisms of mainstream cigarette smoke-induced lung epithelial tight junction permeability changes in vitro. Inhal Toxicol 19:13–22
Chen SH, Stins MF, Huang SH, Chen YH, Kwon-Chung KJ, Chang Y, Kim KS, Suzuki K, Jong AY (2003) Cryptococcus deformans induces alterations in the cytoskeleton of human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Med Microbiol 52:961–970
Tenenbaum T, Matalon D, Adam R, Seibt A, Wewer C, Schwerk C, Galla HJ, Schroten H (2008) Dexamethasone prevents alteration of tight junction-associated proteins and barrier function in porcine choroid plexus epithelial cells after infection with Streptococcus suis in vitro. Brain Res 1229:1–17
Li Q, Zhang Q, Wang C, Liu X, Qu L, Gu L, Li N, Li J (2009) Altered distribution of tight junction proteins after intestinal ischaemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Cell Mol Med 13:4061–4076
Nighot PK, Moeser AJ, Ryan KA, Ghashghaei T, Blikslager AT (2009) ClC-2 is required for rapid restoration of epithelial tight junctions in ischemic-injured murine jejunum. Exp Cell Res 315:110–118
Dudek SM, Garcia JG (2001) Cytoskeletal regulation of pulmonary vascular permeability. J Appl Physiol 91:1487–1500
Birukova AA, Smurova K, Birukovm KG, Kaibuchi K, Garcia JG, Verin AD (2004) Role of Rho GTPases in thrombin-induced lung vascular endothelial cells barrier dysfunction. Microvasc Res 67:64–77
Breslin JW, Yuan SY (2004) Involvement of RhoA and Rho kinase in neutrophil-stimulated endothelial hyperpermeability. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H1057–H1062
Müller SL, Portwich M, Schmidt A, Utepbergenov DI, Huber O, Blasig IE, Krause G (2005) The tight junction protein occludin and the adherens junction protein alpha-catenin share a common interaction mechanism with ZO-1. J Biol Chem 280:3747–3756
Hopkins AM, Walsh SV, Verkade P, Boquet P, Nusrat A (2003) Constitutive activation of Rho proteins by CNF-1 influences tight junction structure and epithelial barrier function. J Cell Sci 116:725–742
Niwa R, Nagata-Ohashi K, Takeichi M, Mizuno K, Uemura T (2002) Control of actin reorganization by slingshot, a family of phosphatases that dephosphorylate ADF/cofilin. Cell 108:233–246
Brown M, Adyshev D, Bindokas V, Moitra J, Garcia JG, Dudek SM (2010) Quantitative distribution and colocalization of non-muscle myosin light chain kinase isoforms and cortactin in human lung endothelium. Microvasc Res 80:75–88
Ikebe M, Hartshorne DJ (1985) Phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin at two distinct sites by myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem 260:10027–10031
Kimura K, Ito M, Amano M, Chihara K, Fukata Y, Nakafuku M, Yamamori B, Feng J, Nakano T, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Kaibuchi K (1996) Regulation of myosin phosphatase by Rho and Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase). Science 273:245–248
Moyer RA, Wendt MK, Johanesen PA, Turner JR, Dwinell MB (2007) Rho activation regulates CXCL12 chemokine stimulated actin rearrangement and restitution in model intestinal epithelia. Lab Invest 87:807–817
Lui WY, Lee WM, Cheng CY (2003) Sertoli-germ cell adherens junction dynamics in the testis are regulated by RhoB GTPase via the ROCK/LIMK signaling pathway. Biol Reprod 68:2189–2206
Bamburg JR (1999) Proteins of the ADF/cofilin family: essential regulators of actin dynamics. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15:185–230
Nagumo Y, Han J, Bellila A, Isoda H, Tanaka T (2008) Cofilin mediates tight-junction opening by redistributing actin and tight-junction proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 377:921–925
Amano M, Ito M, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Chihara K, Nakano T, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K (1996) Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase(Rho-kinase). J Biol Chem 271:20246–20249
Easton AS, Abbott NJ (1997) The effects of bradykinin on a cell culture model of the blood-brain barrier. J Physiol 505:49–50
Manning TJ Jr, Parker JC, Sontheimer H (2000) Role of lysophosphatidic acid and rho in glioma cell motility. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 5:185–199
Liu C, Zuo J, Janssen LJ (2006) Regulation of airway smooth muscle RhoA/ROCK activities by cholinergic and bronchodilator stimuli. Eur Respir J 28:703–711
Arita R, Hata Y, Nakao S, Kita T, Miura M, Kawahara S, Zandi S, Almulki L, Tayyari F, Shimokawa H, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Ishibashi T (2009) Rho kinase inhibition by fasudil ameliorates diabetes-induced microvascular damage. Diabetes 58:215–226
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Lisa M. Abernathy, PhD pre-candidate (Department of Immunology and Microbiology, Wayne State University School of Medicine) and Mr. Arjun Dupati (College of Human Medicine, MSII Michigan State University) for critical reading of the manuscript. Contract grant sponsor: This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China, under contract nos. 30800451, 30872656, 30973079, 30670723, 81001029, and 30570650, the special fund for Scientific Research of Doctor-degree Subjects in Colleges and Universities no. 20092104110015, and Scientific and Technological Planning Projects of Shenyang nos. F10-205-1-22, F10-205-1-37, and 1081266-9-00.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, T., Liu, L., Wang, P. et al. Evidence for involvement of ROCK signaling in bradykinin-induced increase in murine blood–tumor barrier permeability. J Neurooncol 106, 291–301 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0685-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0685-3