Abstract
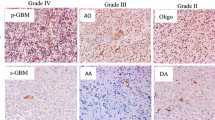
Overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is common in gliomas. Gliomas are infiltrating tumors in which neoplastic glial cells can be intermingled with reactive glial cells, particularly in diffuse low-grade gliomas. As overexpression of EGFR has also been described in gliosis, it can be difficult to evaluate EGFR immunolabeling in diffuse low-grade gliomas because of this cell mix. We compared EGFR immunolabeling between gliosis and low-grade gliomas in order to identify distinctive criteria. We studied EGFR expression in 28 cases of gliosis and 39 diffuse low-grade gliomas (23 astrocytomas and 16 oligodendrogliomas). EGFR immunohistochemistry staining was performed on paraffin-embedded sections with a mouse monoclonal antibody (clone 2-18C9; Dako). Co-expression of EGFR with Olig2, Mib-1, and p53 was assessed in seven cases of low-grade gliomas using double immunolabeling. Then, EGFR immunostaining was blindly tested on 22 small specimens of indeterminate glial lesions provided by a reference neuropathological center. Two pathologists of our local center were asked to classify the lesions into diffuse low-grade glioma or gliosis according to the pattern of EGFR expression. Weak expression of EGFR was commonly detected in gliosis (23/28 cases). Strongly-stained cells were absent. Positive cells had reactive glial cell morphology. EGFR expression in gliomas was characterized by constant strongly-stained cells (39/39 cases). All strongly-stained cells had a high nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratio, with minimal to moderate nuclear atypia. Most of the strongly EGFR-positive cells were Olig2-positive. All the cases displayed cells co-expressing EGFR and Mib-1. In three p53-positive tumors, many p53-positive cells were strongly EGFR-positive. On the basis of EGFR expression, 14 out of the 22 indeterminate cases were classified as gliomas and eight as gliosis by both pathologists. Concordance with the initial diagnosis established by the reference center and concordance between the pathologists were 100%. Our results confirm that weak EGFR expression can be detected by immunohistochemistry in gliosis. They show that strong EGFR expression may be specific for neoplastic glial cells. As all low-grade gliomas contained strongly-stained cells in our study, we believe that EGFR immunohistochemistry could be a useful tool for detection of neoplastic glial cells in case of indeterminate glial lesions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yano S, Kondo K, Yamaguchi M, Richmond G, Hutchison M, Wakeling A, Averbuch S, Wadsworth P (2003) Distribution and function of EGFR in human tissue and the effect of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition. Anticancer Res 23:3639–3650
Wong RW, Guillaud L (2004) The role of epidermal growth factor and its receptors in mammalian CNS. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 15:147–156
Nieto-Sampedro M, Gomez-Pinilla F, Knauer DJ, Broderick JT (1988) Epidermal growth factor receptor immunoreactivity in rat brain astrocytes. Response to injury. Neurosci Lett 91:276–282
Junier MP, Coulpier M, Le Forestier N, Cadusseau J, Suzuki F, Peschanski M, Dreyfus PA (1994) Transforming growth factor alpha (TGF alpha) expression in degenerating motoneurons of the murine mutant wobbler: a neuronal signal for astrogliosis? J Neurosci 14:4206–4216
Ferrer I, Alcantara S, Ballabriga J, Olive M, Blanco R, Rivera R, Carmona M, Berruezo M, Pitarch S, Planas AM (1996) Transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF-alpha) and epidermal growth factor-receptor (EGF-R) immunoreactivity in normal and pathologic brain. Prog Neurobiol 49:99–123
Planas AM, Justicia C, Soriano MA, Ferrer I (1998) Epidermal growth factor receptor in proliferating reactive glia following transient focal ischemia in the rat brain. Glia 23:120–129
Rabchevsky AG, Weinitz JM, Coulpier M, Fages C, Tinel M, Junier MP (1998) A role for transforming growth factor alpha as an inducer of astrogliosis. J Neurosci 18:10541–10552
Grandis JR, Sok JC (2004) Signaling through the epidermal growth factor receptor during the development of malignancy. Pharmacol Ther 102:37–46
Etienne MC, Formento JL, Lebrun-Frenay C, Gioanni J, Chatel M, Paquis P, Bernard C, Courdi A, Bensadoun RJ, Pignol JP, Francoual M, Grellier P, Frenay M, Milano G (1998) Epidermal growth factor receptor and labeling index are independent prognostic factors in glial tumor outcome. Clin Cancer Res 4:2383–2390
Feldkamp MM, Lala P, Lau N, Roncari L, Guha A (1999) Expression of activated epidermal growth factor receptors, Ras-guanosine triphosphate, and mitogen-activated protein kinase in human glioblastoma multiforme specimens. Neurosurgery 45:1442–1453
Korshunov A, Golanov A, Sycheva R, Pronin I (1999) Prognostic value of tumour associated antigen immunoreactivity and apoptosis in cerebral glioblastomas: an analysis of 168 cases. J Clin Pathol 52:574–580
Chakravarti A, Delaney MA, Noll E, Black PM, Loeffler JS, Muzikansky A, Dyson NJ (2001) Prognostic and pathologic significance of quantitative protein expression profiling in human gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 7:2387–2395
Shinojima N, Tada K, Shiraishi S, Kamiryo T, Kochi M, Nakamura H, Makino K, Saya H, Hirano H, Kuratsu J, Oka K, Ishimaru Y, Ushio Y (2003) Prognostic value of epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res 63:6962–6970
Faillot T, Magdelenat H, Mady E, Stasiecki P, Fohanno D, Gropp P, Poisson M, Delattre JY (1996) A phase I study of an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody for the treatment of malignant gliomas. Neurosurgery 39:478–483
Baselga J (2002) Why the epidermal growth factor receptor? The rationale for cancer therapy. Oncologist 7(Suppl 4):2–8
Jendrossek V, Belka C, Bamberg M (2003) Novel chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 12:1899–1924
Dancey J (2004) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in clinical development. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:1003–1007
Kapoor GS, O’Rourke DM (2003) Mitogenic signaling cascades in glial tumors. Neurosurgery 52:1425–1434 (discussion 1434–1425)
von Bossanyi P, Sallaba J, Dietzmann K, Warich-Kirches M, Kirches E (1998) Correlation of TGF-alpha and EGF-receptor expression with proliferative activity in human astrocytic gliomas. Pathol Res Pract 194:141–147
Kordek R, Biernat W, Alwasiak J, Maculewicz R, Yanagihara R, Liberski PP (1995) p53 protein and epidermal growth factor receptor expression in human astrocytomas. J Neurooncol 26:11–16
Orian JM, Vasilopoulos K, Yoshida S, Kaye AH, Chow CW, Gonzales MF (1992) Overexpression of multiple oncogenes related to histological grade of astrocytic glioma. Br J Cancer 66:106–112
Hwang SL, Chai CY, Lin HJ, Howng SL (1997) Expression of epidermal growth factor receptors and c-erbB-2 proteins in human astrocytic tumors. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 13:417–424
Mottolese M, Natali PG, Coli A, Bigotti G, Benevolo M, Cione A, Raus L, Carapella CM (1998) Comparative analysis of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and epidermal growth factor receptor expression in glial tumours: correlation with histological grading. Anticancer Res 18:1951–1956
Kleihues P, Davis RL, Ohgaki H, Burger PC, Westphal MM, Cavenee WK (2000) Diffuse astrocytoma. In: Kleihues P, Cavenee WK (eds) World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Nervous system. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 22–26
Reifenberger J, Reifenberger G, Ichimura K, Schmidt EE, Wechsler W, Collins VP (1996) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in oligodendroglial tumors. Am J Pathol 149:29–35
Broholm H, Bols B, Heegaard S, Braendstrup O (1999) Immunohistochemical investigation of p53 and EGFR expression of oligodendrogliomas. Clin Neuropathol 18:176–180
Hoang-Xuan K, He J, Huguet S, Mokhtari K, Marie Y, Kujas M, Leuraud P, Capelle L, Delattre JY, Poirier J, Broet P, Sanson M (2001) Molecular heterogeneity of oligodendrogliomas suggests alternative pathways in tumor progression. Neurology 57:1278–1281
Daumas-Duport C, Varlet P, Tucker ML, Beuvon F, Cervera P, Chodkiewicz JP (1997) Oligodendrogliomas: part I: patterns of growth, histological diagnosis, clinical and imaging correlations: a study of 153 cases. J Neurooncol 34:37–59
Cavenee WK, Furnari FB, Nagane M, Huang H-JS, Newcomb EW, Bigner DD, Weller M, Berens ME, Plate KH, Israel MA, Noble MD, Kleihues P (2000) Diffusely infiltrating astrocytomas. In: Kleihues P, Cavenee WK (eds) World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the nervous system. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 10–21
Yaziji H, Massarani-Wafai R, Gujrati M, Kuhns JG, Martin AW, Parker JCJ (1996) Role of p53 immunohistochemistry in differentiating reactive gliosis from malignant astrocytic lesions. Am J Surg Pathol 20:1086–1090
Prayson RA, Agamanolis DP, Cohen ML, Estes ML, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Abdul-Karim F, McClure SP, Sebek BA, Vinay R (2000) Interobserver reproducibility among neuropathologists and surgical pathologists in fibrillary astrocytoma grading. J Neurol Sci 175:33–39
Spaulding DC, Spaulding BO (2002) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression and measurement in solid tumors. Semin Oncol 29:45–54
Werner MH, Nanney LB, Stoscheck CM, King LE (1988) Localization of immunoreactive epidermal growth factor receptors in human nervous system. J Histochem Cytochem 36:81–86
Gomez-Pinilla F, Knauer DJ, Nieto-Sampedro M (1988) Epidermal growth factor receptor immunoreactivity in rat brain. Development and cellular localization. Brain Res 438:385–390
Damjanov I, Mildner B, Knowles BB (1986) Immunohistochemical localization of the epidermal growth factor receptor in normal human tissues. Lab Invest 55:588–592
Junier MP (2000) What role(s) for TGFalpha in the central nervous system? Prog Neurobiol 62:443–473
Sabattini E, Bisgaard K, Ascani S, Poggi S, Piccioli M, Ceccarelli C, Pieri F, Fraternali-Orcioni G, Pileri SA (1998) The EnVision++ system: a new immunohistochemical method for diagnostics and research. Critical comparison with the APAAP, ChemMate, CSA, LABC, and SABC techniques. J Clin Pathol 51:506–511
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Dominique Henin, Dr. Renaud Tamisier, and Dr. Brigitte Dunais for helping in the preparation of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Veronique Paquis-Flucklinger and Thierry Virolle contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burel-Vandenbos, F., Benchetrit, M., Miquel, C. et al. EGFR immunolabeling pattern may discriminate low-grade gliomas from gliosis. J Neurooncol 102, 171–178 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0308-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0308-4