Abstract
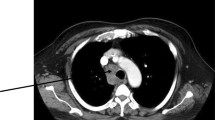
Temozolomide (TMZ) is a cytotoxic agent of the imidazotetrazine class, chemically related to dacarbazine. Its use poses higher risks of lymphopenia and opportunistic infections. Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis jiroveci must be considered up to 12 months after treatment discontinuation. The due literature (MEDLINE) makes no mention of a possible connection between the use of TMZ and tuberculosis (TB). A female patient, aged 59, featuring glioblastoma multiforme and having undergone solely a brain biopsy, was submitted to TMZ along with radiotherapy. After the first TMZ maintenance cycle, the referred patient was admitted displaying a background of a 40-day afternoon fever and productive coughing. She was thus submitted to a bronchoscopy and LBA, which resulted BAAR 1+/4+. TMZ was then suspended, and rifampicin, isoniazid, and pyrazinamide introduced. Considerations on prophylaxis with isoniazide in cancer patients are long-lived and scarce. Some subgroups are likely to benefit from the prophylactic administration of isoniazide during TMZ treatment, such as those patients under high doses of corticoids, patients with past medical history of TB, the malnourished, patients from endemic regions, and patients with highly reactive tuberculinic tests. That, nevertheless, must not restrict the administration of TMZ, but, rather, stand for a warning about its possible toxicity, and thus mitigate complications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352(10):987–996. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043330
Su YB, Sohn S, Krown SE, Livingston PO, Wolchok JD, Quinn C et al (2004) Selective CD4+ lymphopenia in melanoma patients treated with temozolomide: toxicity with therapeutic implications. J Clin Oncol 22(4):610–616. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.07.060
Schwarzberg AB, Stover EH, Sengupta T, Michelini A, Vincitore M, Baden LR et al (2007) Selective lymphopenia and opportunistic infections in neuroendocrine tumor patients receiving temozolomide. Cancer Invest 25(4):249–255. doi:10.1080/07357900701206380
Wick W, Weller M (2005) How lymphotoxic is dose-intensified temozolomide? The glioblastoma experience. J Clin Oncol 23(18):4235–4236. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.00.8417 author reply 4236
Henson JW, Jalaj JK, Walker RW, Stover DE, Fels AO (1991) Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with primary brain tumors. Arch Neurol 48(4):406–409
Maher D, Raviglione M (2005) Global epidemiology of tuberculosis. Clin Chest Med 26(2):167–182. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2005.02.009
Kamboj M, Sepkowitz KA (2006) The risk of tuberculosis in patients with cancer. Clin Infect Dis 42(11):1592–1595. doi:10.1086/503917
Hughes MA, Parisi M, Grossman S, Kleinberg L (2005) Primary brain tumors treated with steroids and radiotherapy: low CD4 counts and risk of infection. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 62(5):1423–1426. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.12.085
Targeted tuberculin testing and treatment of latent tuberculosis infection (2000). This is a Joint Statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161:S221
Fisch P, Handgretinger R, Schaefer HE (2000) Pure red cell aplasia. Br J Haematol 111(4):1010–1022. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.2000.02429.x
Thompson DF, Gales MA (1996) Drug-induced pure red cell aplasia. Pharmacotherapy 16(6):1002–1008
Loulergue P, Mir O, Dhote R (2007) Pure red blood cell aplasia and isoniazid use. Emerg Infect Dis 13(9):1427–1428
Maekawa K (1989) Nippon Naika Gakkai Zasshi 78(7):1002–1003
Tauchi T (1999) Remission of pure-red-cell aplasia associated with operative cure of lung cancer. Am J Hematol 61(2):157–158. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8652(199906)61:2<157::AID-AJH20>3.0.CO;2-8
Iannucci A (1983) Acquired pure red cell aplasia associated with thyroid carcinoma: case report. Acta Haematol 69(1):62–63
Kobayashi M (2005) Pure red cell aplasia in a prostate cancer patient treated with leuprolide acetate and chlormadinone acetate. Int J Urol 12(11):1010–1011. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2042.2005.01195.x
Doyle TJ, Mikkelsen T, Croteau D et al (2005) Fatal hematologic toxicity with prolonged continuous administration of temozolomide during radiation therapy in the treatment of newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme: report of a phase II trial. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 23:125S. Abstract
Villano JL, Collins CA, Manasanch EE, Ramaprasad C, van Besien K (2006) Aplastic anaemia in patient with glioblastoma multiforme treated with temozolomide. Lancet Oncol 7(5):436–438. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70696-9
Jalali R, Singh P, Menon H, Gujral S (2007) Unexpected case of aplastic anaemia in a patient with glioblastoma multiforme treated with temozolomide. J Neurooncol 85(1):105–107. doi:10.1007/s11060-007-9398-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Paiva, T.F., de Barros e Silva, M.J., Rinck, J.A. et al. Tuberculosis in a patient on temozolomide: a case report. J Neurooncol 92, 33–35 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9724-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9724-0