Abstract
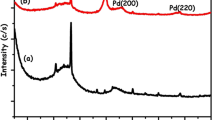
While Cr(VI), a hazardous industrial waste, is an acute toxic, carcinogenic, and proven mutagenic pollutant, Cr(III) is thought to be an essential element for living things. In this study, Pd(0)@Al2O3 nanoclusters supported on Al2O3 were reproducibly prepared in aqueous solution at 25 °C by a simple impregnation-reduction method. The results showed that Pd(0)@Al2O3 nanoclusters with average particle size of 3.01 ± 0.19 nm were formed, well dispersed over the Al2O3 surface. The Al2O3-supported Pd(0)@Al2O3 nanoclusters were used as heterogeneous nanocatalysts in the catalytic reduction of Cr(VI) in formic acid medium, which is a good reducing agent under mild conditions. It has been observed that catalyst Pd(0)@Al2O3 can catalyze the catalytic reduction of Cr(VI) with high selectivity (~ %99) and efficiency (TOF) (138 mol Cr2O72−/mol Pd min.). More importantly, the exceptional stability of the Pd(0)@Al2O3 nanocatalyst against flocculation, leaching, and CO poisoning showed that this catalyst is a reusable catalytic material in the catalytic reduction reaction of Cr(VI). It was observed that the Pd(0)@Al2O3 catalyst maintained a significant (> 84%) initial TOF value even after the 5th use. The Pd(0)@Al2O3 nanocatalyst was identified by advanced analytical methods (XPS, XRD, TEM, TEM–EDX, HR-TEM, ICP-OES). In addition, for the kinetic data of the catalytic reduction reaction of Cr(VI) catalyzed by Pd(0)@Al2O3, the rate equation and Ea, ΔH#, and ΔS# activation parameters were derived depending on the [catalyst], [Cr2O72−], [HCOOH], and [HCOONa] concentrations and temperature.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abass E, Alireza M, Reza V (2005) Chromium (III) removal and recovery from tannery wastewater by precipitation process. Am J Appl Sci 2(10):1471. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajassp.2005.1471.1473
Barakat T, Rooke JC, Genty E, Cousin R, Siffert S, Su BL (2013) Gold catalysts in environmental remediation and water-gas shift technologies. Energy Environ Sci 6(2):371–391. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ee22859a
Bhowmik K, Mukherjee A, Mishra MK, De G (2014) Stable Ni nanoparticle–reduced graphene oxide composites for the reduction of highly toxic aqueous Cr (VI) at room temperature. Langmuir 30:3209–3216. https://doi.org/10.1021/la500156e
Brieger G, Nestrick TJ (1974) Catalytic transfer hydrogenation. Chem Rev 74:567–580. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr60291a003
Buerge IJ, Hug SJ (1998) Influence of organic ligands on chromium(VI) reduction by ıron(II). Environ Sci Technol 32(14):2092–2099. https://doi.org/10.1021/es970932b
Bulut A, Yurderi M, Karatas Y, Zahmakiran M, Kivrak H, Gulcan M, Kaya M (2015) Pd-MnOx nanoparticles dispersed on amine-grafted silica: highly efficient nanocatalyst for hydrogen production from additive-free dehydrogenation of formic acid under mild conditions. App Catal b: Environ 164:324–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.09.041
Cao Y, Yin H, Fan T, Liu X, Chen S (2020) Morphology-dependent of nano sizes CdS toward efficient photocatalytic Cr (VI) reduction. J Nanopart Res 22:217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-04926-3
Celebi M, Yurderi M, Bulut A, Kaya M, Zahmakiran M (2016) Palladium nanoparticles supported on amine-functionalized SiO2 for the catalytic hexavalent chromium reduction. Appl Catal B 180:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.06.020
Chen JH, Hsu KC, Chang YM (2013) Surface modification of hydrophobic resin with tri capryl methylammonium chloride for the removal of trace hexavalent chromium. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(33):11685–11694. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie401233r
Connors KA (1990) Theory of Chemical Kinetics. VCH Publishers, New York
Dandapat A, Jana D, De G (2011) Pd nanoparticles supported mesoporous γ-Al2O3 film as a reusable catalyst for reduction of toxic Cr(VI) to Cr(III) in aqueous solution. Appl Catal A 396(1–2):34–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2011.01.032
Durap F, Zahmakiran M, Ozkar S (2009) Water-soluble laurate-stabilized rhodium(0) nanoclusters catalyst with unprecedented catalytic lifetime in the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia-borane. App Catal a: Gen 369(1–2):53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2009.08.031
Enthaler S, Langermann JV, Schmidt T (2010) Carbon dioxide and formic acid-the couple for environmental-friendly hydrogen-storage? Energy Environ. Sci 3:1207–1217. https://doi.org/10.1039/b907569k
Fu G-T, Jiang X, Wu R, Wei S-H, Sun D-M, Tang Y-W, Lu T-H, Chen Y (2014) Arginine-assisted synthesis and catalytic properties of single-crystalline palladium tetrapods. ACS Appl Mater & Inter 6(24):22790–22795. https://doi.org/10.1021/am506965f
Fu G-T, Jiang X, Wu R, Wei S-H, Sun D-M, Tang Y-W, Lu T-H, Chen Y (2014) Arginine-assisted synthesis and catalytic properties of single-crystalline palladium tetrapods. ACS Appl Mater & Inter 6:22790–22795. https://doi.org/10.1021/am506965f
Gu X, Lu Z-H, Jiang H-L, Akita T, Xu Q (2011) Synergistic catalysis of metal-organic framework-immobilized Au-Pd nanoparticles in dehydrogenation of formic acid for chemical hydrogen storage. J Am Chem Soc 13(31):1822–11825. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja200122f
Hsu LC, Wang SL, Lin YC, Wang MK, Chiang PN, Liu JC, Kuan WH, Chen CC, Tzou YM (2010) Cr(VI) Removal on fungal biomass of Neurospora crassa: the importance of dissolved organic carbons derived from the biomass to Cr(VI) reduction. Environ Sci Technol 44(16):6202–6208. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1017015
Hu X, Zhao Y, Wang H, Cai X, Hu X, Tang C, Liu Y, Yang Y (2018) Decontamination of Cr(VI) by graphene oxide@TiO2 in aerobic atmosphere: effects of pH, ferric ions, inorganic anions, and formate. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, Published Online in Wiley Online Library,. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5565
Huang Y, Ma H, Wang S, Shen M, Guo R, Cao X, Zhu M, Shi X (2012) Efficient catalytic reduction of hexavalent chromium using palladium nanoparticle-immobilized electrospun polymer nanofibers. ACS Appl Mater Inter 4(6):3054–3061. https://doi.org/10.1021/am300417s
Huang Y, Zhang X, Zhang K, Lu P, Zhang D (2018) Facile fabrication of sandwich-like BiOI/AgI/g-C3N4 composites for efficient photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange and reduction of Cr(VI). J Nanopart Res 20:328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4431-z
Humphries AC, Macaskie LE (2002) Reduction of Cr(VI) by Desulfovibrio vulgaris and Microbacterium sp. Biotech Lett 24:1261–1267. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1016257908574
Johnstone RA, Wilby AH, Entwistle ID (1985) Heterogeneous catalytic transfer hydrogenation and its relation to other methods for reduction of organic compounds. Chem Rev 85:129–170. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00066a003
Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (1991), JCPDS International Center for Diffraction Data, Pennsylvania.
Keith LH, Telliard WA (1979) ES&T Special Report: priority pollutants: I-a perspective view. Environ Sci Technol 13(4):416–423. https://doi.org/10.1021/es60152a601
Kim J-H, Kim J-H, Bokare V, Kim E-J, Chang Y-Y, Chang Y-S (2012) Enhanced removal of chromate from aqueous solution by sequential adsorption-reduction on mesoporous iron-iron oxide nanocomposites. J Nanopart Res 14:1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1010-6
Kim SM, Lee YJ, Kim JW, Lee SY (2014) Facile synthesis of Pt-Pd bimetallic nanoparticles by plasma discharge in liquid and their electrocatalytic activity toward methanol oxidation in alkaline media. Thin Solid Films 572:260–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2014.07.067
Kotas J, Stasicka Z (2000) Chromium occurrence in the environment and methods of its speciation. Environ Pollut 107(3):263–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(99)00168-2
Krishnani KK, Srinives S, Mohapatra B (2013) Hexavalent chromium removal mechanism using conducting polymers. J Hazard Mater 252:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.01.079
Kyung H, Lee J, Choi W (2005) Simultaneous and synergistic conversion of dyes and heavy metal ions in aqueous TiO2 suspensions under visible-light ıllumination. Environ Sci Technol 39(7):2376–2382. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0492788
Lan Y, Deng B, Kim C, Thornton EC, Xu H (2005) Redox ınteractions of Cr(VI) and substituted phenols: kinetic investigation environ. Sci Technol 39(7):2087–2094. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00061a026
Li S, Tang L, Zeng G, Wang J, Deng Y, Wang J, Xie Z, Zhou Y (2016) Catalytic reduction of hexavalent chromium by a novel nitrogen-functionalized magnetic ordered mesoporous carbon doped with Pd nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:22027–22036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7439-x
Liang M, Su R, Qi W, Zhang Y, Huang R, Yu Y, Wang L, He Z (2014) Reduction of hexavalent chromium using recyclable Pt/Pd nanoparticles ımmobilized on procyanidin-grafted eggshell membrane. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(35):13635–13643. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie5021552
Liang M, Wang L, Liu X, Qi W, Su R, Huang R, Yu Y, He Z (2013) Cross-linked lysozyme crystal templated synthesis of Au nanoparticles as high-performance recyclable catalysts. Nanotechnology 24
Liu Y-G, Hu X-J, Wang H, Chen A-W, Liu S-M, Guo Y-M, He Y, Hu X, Li J, Liu S-h, Wang Y-Q, Zhou L (2013) Photoreduction of Cr(VI) from acidic aqueous solution using TiO2-impregnated glutaraldehyde-crosslinked alginate beads and the effects of Fe(III) ions. Chem Eng J 226:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.048
Madiwale S, Bashte B, Dindorkar S, Dhawal P, More1 P (2020) Green mediated synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extract of Gymnema sylvestre for catalytic reduction of Cr (VI), SN Applied Sciences 2:1854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03663-5
Omole MA, K’Owino IO, Sadik OA (2007) Palladium nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of Cr(VI) using formic acid. Appl Catal B 76(1–2):158–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.05.018
Prabhakaran SK, Vijayaraghavan K, Balasubramanian R (2009) Removal of Cr(VI) ions by spent tea and coffee dusts: reduction to Cr(III) and biosorption Ind. Eng Chem Res 48(4):2113–2117. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie801380h
Qian A, Liao P, Yuan S, Luo M (2014) Efficient reduction of Cr(VI) in groundwater by a hybrid electro-Pd process. Water Res 48:326–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.09.043
Roucoux A, Schulz J, Patin H (2002) Aminopropyltriethoxysilane stabilized ruthenium(0) nanoclusters as an isolable and reusable heterogeneous catalyst for the dehydrogenation of dimethylamine-borane. Chem Rev 102(10):3757–3778. https://doi.org/10.1039/c000419g
Schlotterbeck U, Aymonier C, Thomann R, Hofmeister H, Tromp M, Richtering W, Mecking S (2014) Shape-selective synthesis of palladium nanoparticles stabilized by highly branched amphiphilic polymers. Adv Func Mater 14(10):999–1004. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200400053
Shaikh A, Mishra SP, Mohapatra P, Parida S (2017) One-step solvothermal synthesis of TiO2-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites with enhanced visible light photoreduction of Cr(VI). J Nanopart Res 19:206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3894-7
Shirzad-Siboni M, Farrokhi M, Soltani RDC, Khataee A, Tajassosi S (2014) Photocatalytic reduction of hexavalent chromium over ZnO nanorods immobilized on Kaolin. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(3):1079–1087. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie4032583
Su N, Chen X, Ren Y, Yue B, Wang H, Cai W, He H (2015) The facile synthesis of single-crystalline palladium arrow-headed tripods and their application in formic acid electro-oxidation. Chem Commun 51:7195–7198. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cc00353a
Sumayya PK, Subrahmanian SK, Mullakkattuthodi S, Sugunan S, Narayanan BN (2021) Green in situ preparation of novel graphene-wrapped ethyl cellulose submicro spherical capsules and its effective use in Cr (VI) removal. J Nanopart Res 23:104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05212-6
Tian Y, Huang L, Zhou X, Wu C (2012) Electroreduction of hexavalent chromium using a polypyrrole-modified electrode under potentiostatic and potentiodynamic conditions. J Hazard Mater 225:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.04.057
Tu W, Li K, Shu X, Yu WW (2013) Reduction of hexavalent chromium with colloidal and supported palladium nanocatalysts. J Nanopart Res 15:1593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1593-6
Veerakumar P, Lin K-C (2020) An overview of palladium supported on carbon-based materials: synthesis, characterization, and its catalytic activity for reduction of hexavalent chromium. Chemosphere 253
Veerakumar P, Thanasekaran P, Lin K-C, Liu S-B (2017) Biomass derived sheet-like carbon/palladium nanocomposite: an excellent opportunity for reduction of toxic hexavalent chromium, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng 5:5302–5312. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00645
Wang L, Zan L (2020) Noble metal-free MoS2-modified In2S3 for excellent visible-NIR-light-driven photocatalytic of Cr6+ removal in alkaline wastewater. J Nanopart Res 22:325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05057-5
Wei L-L, Gu R, Lee J-M (2015) Highly efficient reduction of hexavalent chromium on amino-functionalized palladium nanowires. App Catal b: Environ 176:325–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.03.056
World Health Organization 2008 Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality WHO Press, Geneva
Yadav M, Singh AK, Tsumori N, Xu Q (2012) Palladium silica nanosphere-catalyzed decomposition of formic acid for chemical hydrogen storage. J Mater Chem 22:19146–19150. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm32776g
Yadav M, Xu Q (2012) Liquid-phase chemical hydrogen storage materials. Energy Environ Sci 5:9698–9725. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ee22937d
Yadav M, Xu Q (2013) Catalytic chromium reduction using formic acid and metal nanoparticles immobilized in a metal-organic framework. Chemical Commun 49:3327–3329. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc00293d
Yang C, Manocchi AK, Lee B, Yi H (2010) Viral templated palladium nanocatalysts for dichromate reduction. App Catal b: Environ 93(3–4):282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.10.001
Yang S, Shen C, Tian Y, Zhang X, Gao H-J (2014) Synthesis of cubic and spherical Pd nanoparticles on graphene and their electrocatalytic performance in the oxidation of formic acid. Nanoscale 6:13154–13162. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr04349a
Yurderi M, Bulut A, Zahmakiran M, Kaya M (2014) Carbon supported trimetallic PdNiAg nanoparticles as highly active, selective and reusable catalyst in the formic acid decomposition. App Catal b: Environ 160:514–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.06.004
Zahmakiran M, Leshkov YR, Zhang Y (2012) Rhodium(0) Nanoparticles supported on nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite: highly effective catalytic system for the solvent-free hydrogenation of aromatics at room temperature. Langmuir 28(1):60–64. https://doi.org/10.1021/la2044174
Zahmakiran M, Ozkar S (2006) Water dispersible acetate stabilized ruthenium(0) nanoclusters as catalyst for hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. J Mol Catal a: Chem 258(1–2):95–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2006.05.037
Zahmakiran M, Ozkar S (2011) Metal nanoparticles in liquid phase catalysis; from recent advances to future goals. Nanoscale 3:3462–3481. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1nr10201j
Zhang L, Guo Y, Iqbal A, Li B, Deng M, Gong D, Liu W, Qin W (2017) Palladium nanoparticles as catalysts for reduction of Cr(VI) and Suzuki coupling reaction. J Nanopart Res 19:150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3829-3
Zhang Y, Gao H, Kuai Y, Han Y, Wang J, Sun B, Gu S, You W (2013) Effects of Y additions on the precipitation and recrystallization of Al-Zr alloys. Sci Rep 86:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2013.09.004
Zhitkovich A (2011) Chromium in drinking water: Sources, metabolism, and cancer risks. Chem Res Toxicol 24(10):1617–1629. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx200251t
Zhu Q-L, Xu Q (2015) Liquid organic and inorganic chemical hydrides for high-capacity hydrogen storage. Energ Environ Sci 8:478–512. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ee03690e
Funding
This study was supported by the Van Yüzüüncü Yıl University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit as a project numbered FDK-2019–8195.
This study was supported by the Van Yüzüüncü Yıl University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit as a project numbered FDK-2019–8195.,FDK-2019–8195,Mehmet Tunç
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gözeten, İ., Tunç, M. Palladium nanoparticles supported on aluminum oxide (Al2O3) for the catalytic hexavalent chromium reduction. J Nanopart Res 24, 13 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05389-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05389-w