Abstract
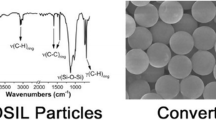
Silica and polysilsesquioxane particles are used as fillers in composites, catalyst supports, chromatographic separations media, and even as additives to cosmetics. The particles are generally prepared by hydrolysis and condensation of tetraalkoxysilanes and/or organotrialkoxysilanes, respectively, in aqueous alcohol solutions. In this study, we have discovered a new, non-aqueous approach to prepare silica and polysilsesquioxane particles. Spherical, nearly monodisperse, silica particles (600–6,000 nm) were prepared from the reaction of tetramethoxysilane with formic acid (4–8 equivalents) in toluene or toluene/tetrahydrofuran solutions. Polymerization of organotrialkoxysilanes with formic acid failed to afford particles, but bridged polysilsesquioxane particles were obtained from monomers with two trialkoxysilyl group attached to an organic-bridging group. The mild acidic conditions allowed particles to be prepared from monomers, such as bis(3-triethoxysilylpropyl)tetrasulfide, which are unstable to Stöber or base-catalyzed emulsion polymerization conditions. The bridged polysilsesquioxane particles were generally less spherical and more polydisperse than silica particles. Both silica and bridged polysilsesquioxane nanoparticles could be prepared in good yields at monomer concentrations considerably higher than used in Stöber or emulsion approaches.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboulaich A, Boury B, Mutin PH (2010) Reactive and organosoluble anatase nanoparticles by a surfactant-free nonhydrolytic synthesis. Chem Mater 22(16):4519–4521. doi:10.1021/Cm101191a
Aikawa K, Kaneko K, Tamura T, Fujitsu M, Ohbu K (1999) Formation of fractal porous silica by hydrolysis of TEOS in a bicontinuous microemulsion. Colloids Surf A 150(1–3):95–104. doi:10.1016/S0927-7757(98)00718-3
Arkhireeva A, Hay JN (2003) Synthesis of sub-200 nm silsesquioxane particles using a modified Stoeber sol–gel route. J Mater Chem 13(12):3122–3127. doi:10.1039/b306994j
Arkhireeva A, Hay JN, Lane JM, Manzano M, Masters H, Oware W, Shaw SJ (2004) Synthesis of organic–inorganic hybrid particles by sol–gel chemistry. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 31(1/2/3):31–36. doi:10.1023/b:jsst.0000047956.24117.89
Arkhireeva A, Hay JN, Manzano M (2005) Preparation of silsesquioxane particles via a nonhydrolytic sol–gel route. Chem Mater 17(4):875–880. doi:10.1021/cm049634l
Bailey JK, Mecartney ML (1992) Formation of colloidal silica particles from alkoxides. Colloids Surf 63(1–2):151–161. doi:10.1016/0166-6622(92)80081-c
Baumann F, Schmidt M, Deubzer B, Geck M, Dauth J (1994) On the preparation of organosilicon μ-spheres: a polycondensation in μ-emulsion? Macromolecules 27(21):6102–6105. doi:10.1021/ma00099a024
Boday DJ, Stover RJ, Muriithi B, Keller MW, Wertz JT, Obrey KAD, Loy DA (2009) Strong, low-density nanocomposites by chemical vapor deposition and polymerization of cyanoacrylates on aminated silica aerogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1(7):1364–1369. doi:10.1021/Am900240h
Boday DJ, Keng PY, Muriithi B, Pyun J, Loy DA (2010) Mechanically reinforced silica aerogel nanocomposites via surface initiated atom transfer radical polymerizations. J Mater Chem 20(33):6863–6865. doi:10.1039/C0jm01448f
Boday DJ, Stover RJ, Muriithi B, Loy DA (2011) Strong, low density, hexylene- and phenylene-bridged polysilsesquioxane aerogel–polycyanoacrylate composites. J Mater Sci 46(19):6371–6377. doi:10.1007/S10853-011-5584-7
Bourget L, Leclercq D, Vioux A (1999) Catalyzed nonhydrolytic sol–gel route to organosilsesquioxane gels. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 14(2):137–147
Carroll NJ, Pylypenko S, Atanassov PB, Petsev DN (2009) Microparticles with bimodal nanoporosity derived by microemulsion templating. Langmuir 25(23):13540–13544. doi:10.1021/La900988j
Choi JY, Kim CH, Kim DK (1998) Formation and characterization of monodisperse, spherical organo-silica powders from organo-alkoxysilane–water system. J Am Ceram Soc 81(5):1184–1188
Cintron JM, Colon LA (2002) Organo-silica nano-particles used in ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography. Analyst 127(6):701–704. doi:10.1039/B203236h
Framery E, Mutin PH (2002) Si-29 MAS–NMR study of silica gels and xerogels: influence of the catalyst. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 24(3):191–195. doi:10.1023/A:1015391922572
Ghassemzadeh L, Pace G, Di Noto V, Muller K (2011) Effect of SiO2 on the dynamics of proton conducting [Nafion/(SiO2)(X)] composite membranes: a solid-state F-19 NMR study. PCCP 13(20):9327–9334. doi:10.1039/C0cp02316g
Hay JN, Raval HM (2001) Synthesis of organic–inorganic hybrids via the nonhydrolytic sol–gel process. Chem Mater 13(10):3396–3403. doi:10.1021/cm011024n
Hench LL, West JK (1990) The sol–gel process. Chem Rev 90(1):33–72
Hu L-C, Khiterer M, Huang S-J, Chan JCC, Davey JR, Shea KJ (2010) Uniform, spherical bridged polysilsesquioxane nano- and microparticles by a non-emulsion method. Chem Mater 22 (Copyright (C) 2012 American Chemical Society (ACS). All Rights Reserved):5244–5250. doi:10.1021/cm101243m
Jansen M, Guenther E (1995) Oxide gels and ceramics prepared by a nonhydrolytic sol–gel process. Chem Mater 7(11):2110–2114. doi:10.1021/cm00059a019
Jesson DA, Abel ML, Hay JN, Smith PA, Watts JF (2006) Organic–inorganic hybrid nanoparticles: surface characteristics and interactions with a polyester resin. Langmuir 22(11):5144–5151. doi:10.1021/La053101p
Jiang CY, Mark JE (1984) The effects of various catalysts in the in situ precipitation of reinforcing silica in poly(dimethylsiloxane) networks. Makromol Chem 185(12):2609–2617
Khiterer M, Shea KJ (2006) Monodisperse, spherical micro and nanosized bridged polysilsesquioxanes. Polym Prep (Am Chem Soc Div Polym Chem) 47(2):889–890
Li Z, Tolbert S, Loy DA (2013) Hybrid organic–inorganic membranes on porous supports by size exclusion and thermal sintering of fluorescent polyphenylsilsesquioxane nanoparticles. Macromol Mater Eng 298(7):715–721. doi:10.1002/mame.201200091
Liu Q, DeShong P, Zachariah MR (2012) One-step synthesis of dye-incorporated porous silica particles. J Nanopart Res 14(7), Artn 923. doi:10.1007/S11051-012-0923-4
Loy DA, Carpenter JP, Myers SA, Assink RA, Small JH, Greaves J, Shea KJ (1996) Intramolecular condensation reactions of alpha, omega-bis(triethoxysilyl)alkanes. Formation of cyclic disilsesquioxanes. J Am Chem Soc 118(35):8501–8502. doi:10.1021/Ja961409k
Loy DA, Russick EM, Yamanaka SA, Baugher BM, Shea KJ (1997) Direct formation of aerogels by sol–gel polymerizations of alkoxysilanes in supercritical carbon dioxide. Chem Mater 9(11):2264–2268. doi:10.1021/cm970326f
Loy DA, Carpenter JP, Alam TM, Shaltout R, Dorhout PK, Greaves J, Small JH, Shea KJ (1999) Cyclization phenomena in the sol–gel polymerization of alpha, omega-bis(triethoxysilyl) alkanes and incorporation of the cyclic structures into network silsesquioxane polymers. J Am Chem Soc 121(23):5413–5425. doi:10.1021/Ja982751v
Loy DA, Baugher BM, Baugher CR, Schneider DA, Rahimian K (2000) Substituent effects on the sol–gel chemistry of organotrialkoxysilanes. Chem Mater 12(12):3624–3632
Mark JE (2006) Some novel polymeric nanocomposites. Acc Chem Res 39 (Copyright (C) 2012 American Chemical Society (ACS). All Rights Reserved):881–888. doi:10.1021/ar040062k
Matsoukas T, Gulari E (1988) Dynamics of growth of silica particles from ammonia-catalyzed hydrolysis of tetra-ethyl-orthosilicate. J Colloid Interface Sci 124(1):252–261. doi:10.1016/0021-9797(88)90346-3
Matsoukas T, Gulari E (1989) Monomer-addition growth with a slow initiation step: a growth model for silica particles from alkoxides. J Colloid Interface Sci 132 (Copyright (C) 2012 American Chemical Society (ACS). All Rights Reserved):13–21. doi:10.1016/0021-9797(89)90210-5
Matsuda A, Sasaki T, Tanaka T, Tatsumisago M, Minami T (2002) Preparation of copolymerized phenylsilsesquioxane–benzylsilsesquioxane particles. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 23(3):247–252
Mauritz KA, Hassan MK (2007) Nanophase separated perfluorinated ionomers as sol–gel polymerization templates for functional inorganic oxide nanoparticles. Polym Rev 47(4):543–565. doi:10.1080/15583720701638393
Nandiyanto ABD, Okuyama K (2011) Progress in developing spray-drying methods for the production of controlled morphology particles: from the nanometer to submicrometer size ranges. Adv Powder Technol 22(1):1–19. doi:10.1016/J.Apt.09.011
Nicotera I, Coppola L, Rossi CO, Youssry M, Ranieri GA (2009) NMR investigation of the dynamics of confined water in Nafion-based electrolyte membranes at subfreezing temperatures. J Phys Chem B 113(42):13935–13941. doi:10.1021/Jp904691g
Noda I, Isikawa M, Yamawaki M, Sasaki Y (1997) A facile preparation of spherical methyl silsesquioxane particles by emulsion polymerization. Inorg Chim Acta 263(1–2):149–152. doi:10.1016/s0020-1693(97)05608-9
Nostell P, Roos A, Karlsson B (1999) Optical and mechanical properties of sol–gel antireflective films for solar energy applications. Thin Solid Films 351(1–2):170–175
Obrey KAD, Wilson KV, Loy DA (2011) Enhancing mechanical properties of silica aerogels. J Non-Cryst Solids 357(19–20):3435–3441. doi:10.1016/J.Jnoncrysol.06.014
O’gara JE, Wyndham KD (2006) Porous hybrid organic–inorganic particles in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 29(7–8):1025–1045. doi:10.1080/10826070600574747
Pal R, Kundu D (2009) Sol–gel synthesis of porous and dense silica microspheres. J Non-Cryst Solids 355(1):76–78. doi:10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2008.03.052
Sharp KG (1994) A two-component, non-aqueous route to silica gel. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 2 (Copyright (C) 2012 American Chemical Society (ACS). All Rights Reserved):35–41. doi:10.1007/bf00486210
Sharp KG, Michalczyk MJ (1997) Star gels: new hybrid network materials from polyfunctional single component precursors. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 8(1/2/3):541–546. doi:10.1007/bf02436896
Shea KJ, Loy DA (2001) Bridged polysilsesquioxanes. Molecular-engineered hybrid organic–inorganic materials. Chem Mater 13(10):3306–3319. doi:10.1021/cm011074s
Stober W, Fink A, Bohn E (1968) Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 26(1):62–69.
Sui R, Rizkalla AS, Charpentier PA (2004) Synthesis and formation of silica aerogel particles by a novel sol–gel route in supercritical carbon dioxide. J Phys Chem B 108(32):11886–11892. doi:10.1021/jp036973d
Vartuli JC, Schmitt KD, Kresge CT, Roth WJ, Leonowicz ME, Mccullen SB, Hellring SD, Beck JS, Schlenker JL, Olson DH, Sheppard EW (1994) Development of a formation mechanism for M41s Materials. Zeolites Relat Microporous Mater State Art 84:53–60
Vioux PA (1997) Nonhydrolytic sol–gel routes to oxides. Chem Mater 9 (Copyright (C) 2012 American Chemical Society (ACS). All Rights Reserved):2292–2299. doi:10.1021/cm970322a
Wooldridge MS, Danczyk SA, Wu JF (1999) Demonstration of gas-phase combustion synthesis of nanosized particles using a hybrid burner. Nanostruct Mater 11(7):955–964
Zhang YP, Jin Y, Dai P, Yu H, Yu DH, Ke YX, Liang XM (2009) Phenylene-bridged hybrid silica spheres for high performance liquid chromatography. Anal Methods 1(2):123–127. doi:10.1039/B9ay00073a
Zhao L, Loy DA, Shea KJ (2006) Photodeformable spherical hybrid nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 128(44):14250–14251. doi:10.1021/ja066047n
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boday, D.J., Tolbert, S., Keller, M.W. et al. Non-hydrolytic formation of silica and polysilsesquioxane particles from alkoxysilane monomers with formic acid in toluene/tetrahydrofuran solutions. J Nanopart Res 16, 2313 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2313-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2313-6