Abstract
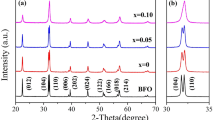
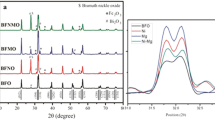
Bi1−x Nd x FeO3 (x = 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2) nanoparticles (about 20–50 nm) calcined at 500 and 600 °C, respectively, were prepared by an ethylene glycol-based sol–gel. The XRD analysis reveals that the BiFeO3 samples are in single phase, and their crystal structure is varied with the Nd content. Due to the small particle size, the uncompensated spin moments on the surface and the suppression of spin helical ordering structure result in a ferromagnetic phase of the BiFeO3 nanoparticles. The magnetization of the Nd-doped samples calcined at 600 °C is improved with the increase of Nd content, but for the Nd-doped samples calcined at 500 °C, it shows an opposite trend, which is ascribed to the interplay of size effect and the ratio of Fe2+:Fe3+ of samples calcined at different temperatures via XPS analysis. The dielectric properties were measured and analyzed for the samples calcined at 500 and 600 °C. Moreover, the leakage current value of the Bi1−x Nd x FeO3 samples can be modulated by the Nd doping, and it reaches a minimum at the Nd content around 0.1.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal RA, Ashima SS (2011) Rietveld analysis, dielectric and magnetic properties of Sr and Ti codoped BiFeO3 multiferroic. J Appl Phys 110:073909. doi:10.1063/1.3646557
Arya GS, Negi NS (2013) Effect of In and Mn co-doping on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of BiFeO3 nanoparticles. J Phys D 46:095004. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/46/9/095004
Arya GS, Kotnala RK, Negi NS (2013) Structural and multiferroic properties of Bi1−x In x FeO3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.20) nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 113:044107. doi:10.1063/1.4788668
Bi L, Taussig AR, Kim HS, Wang L, Dionne GF, Bono D, Persson K, Ceder G, Ross CA (2008) Structural, magnetic, and optical properties of BiFeO3 and Bi2FeMnO6 epitaxial thin films: An experimental and first-principles study. Phys Rev B 78:104106. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.78.104106
Chakrabarti K, Das K, Sarkar B, De SK (2011) Magnetic and dielectric properties of Eu-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles by acetic acid-assisted sol–gel method. J Appl Phys 110:103905. doi:10.1063/1.3662178
Chakrabarti K, Das K, Sarkar B, Ghosh S, De SK, Sinha G, Lahtinen J (2012) Enhanced magnetic and dielectric properties of Eu and Co co-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 101:042401. doi:10.1063/1.4738992
Cheong SW, Mostovoy M (2007) Multiferroics: a magnetic twist for ferroelectricity. Nat Mater 6:13–20. doi:10.1038/nmat1804
Cullity BD, Graham CD (2009) Introduction to magnetic materials, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 361–362
Das SR, Choudhary RNP, Bhattacharya P, Katiyara RS (2007) Structural and multiferroic properties of La-modified BiFeO3 ceramics. J Appl Phys 101:034104. doi:10.1063/1.2432869
Ederer C, Spaldin NA (2005) Weak ferromagnetism and magnetoelectric coupling in bismuth ferrite. Phys Rev B 71:060401. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.71.060401
Eerenstein W, Mathur ND, Scott JF (2006) Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature 442(17):759–765. doi:10.1038/nature05023
Hu GD, Cheng X, Wu WB, Yang CH (2007) Effects of Gd substitution on structure and ferroelectric properties of BiFeO3 thin films prepared using metal organic decomposition. Appl Phys Lett 91:232909. doi:10.1063/1.2822826
Huang FZ, Lu XM, Lin WW, Wu XM, Kan Y, Zhu JS (2006) Effect of Nd dopant on magnetic and electric properties of BiFeO3 thin films prepared by metal organic deposition method. Appl Phys Lett 89:242914. doi:10.1063/1.2404942
Jaiswal A, Das R, Vivekanand K, Abraham PM, Adyanthaya S, Poddar P (2010) Effect of reduced particle size on the magnetic properties of chemically synthesized BiFeO3 nanocrystals. J Phys Chem C 114:2108–2115. doi:10.1021/jp910745g
Khomchenko VA, Kiselev DA, Bdikin IK, Shvartsman VV, Borisov P, Kleemann W, Vieira JM, Kholkin AL (2008) Crystal structure and multiferroic properties of Gd-substituted BiFeO3. Appl Phys Lett 93:262905. doi:10.1063/1.3058708
Lotey GS, Verma NK (2012) Structural, magnetic, and electrical properties of Gd-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles with reduced particle size. J Nanopart Res 14:742. doi:10.1007/s11051-012-0742-7
Manna S, Ghoshal T, De SK (2010) Room temperature stabilized cubic zirconia nanocrystal: a giant dielectric material. J Phys D 43:295403. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/43/29/295403
Moulder JF, Stickle WF, Sobol PE, Bomben KD (1992) Handbook of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Perkin-Elmer, Eden Prairie
Park TJ, Papaefthymiou GC, Viescas AJ, Moodenbaugh AR, Wong SS (2007) Size dependent magnetic properties of single crystalline multiferroic BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Nano Lett 7(3):766–772. doi:10.1021/nl063039w
Patil RD, Lokare SA, Devan RS, Chougule SS, Kanamadi CM, Kokekar YD, Chougule BK (2007) Studies on electrical and dielectric properties of Ba1−x Sr x TiO3. Mater Chem Phys 104:254–257. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2007.02.027
Reddy VA, Pathak NP, Nath R (2012) Particle size dependent magnetic properties and phase transitions in multiferroic BiFeO3 nano-particles. J Alloy Compd 543:206–212. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.07.098
Singh A, Pandey V, Kotnala RK, Pandey D (2008) Direct evidence for multiferroic magnetoelectric coupling in 0.9BiFeO3–0.1BaTiO3. Phys Rev Lett 101:247602. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.247602
Spaldin NA, Fiebig M (2005) The renaissance of magnetoelectric multiferroics. Science 309:391–392. doi:10.1126/science.1113357
Wang J, Neaton JB, Zheng H, Nagarajan V, Ogale SB, Liu B, Viehland D, Vaithyanathan V, Schlom DG, Waghmare UV, Spaldin NA, Rabe KM, Wuttig M, Ramesh R (2003) Epitaxial BiFeO3 multiferroic thin film heterostructures. Science 299:1719. doi:10.1126/science.1080615
Yu BF, Li MY, Hu ZQ, Pei L, Guo DY, Zhao XZ, Dong SX (2008) Enhanced multiferroic properties of the high-valence Pr doped BiFeO3 thin film. Appl Phys Lett 93:182909. doi:10.1063/1.3020296
Yuan GL, Or SW (2006) Structural transformation and ferroelectromagnetic behavior in single-phase Bi1−x Nd x FeO3 multiferroic ceramics. Appl Phys Lett 89:052905. doi:10.1063/1.2266992
Zhang HW, Zhao TY, Zhang J, Rong CB, Zhang SY, Shen BG, Li L, Zhang LG (2003) Large coercivity in nanocrystalline TbMn6Sn6 permanent magnets prepared by mechanical milling. J Phys D 36:1769. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/36/15/303
Acknowledgments
This study has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11004148, 51074112, 11104202) and the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (11JCYBJC02700, 11JCZDJC21800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Liu, W.F., Wu, P. et al. Unusual magnetic behaviors and electrical properties of Nd-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles calcined at different temperatures. J Nanopart Res 16, 2205 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2205-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2205-1