Abstract
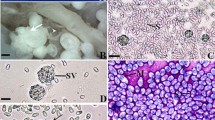
Saprolegnia brachydanis is described from zebra fish (Brachydanio rerio) in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China. The species is illustrated and compared with other species of the genus. The distinctive characteristics of S. brachydanis are the production of glomerulate oogonia wrapped around by predominantly monoclinous antheridia which can be up to eight in one oogonium. The oogonial stalks are short, straight, or curved and the antheridia, twisted, can enwind one or more oogonia. The oospores cannot mature or easily abort. Morphological features of the oomycete and the ITS sequence of its rDNA as well as the comparison with related species are discussed in this article.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruno DW, Wood BP. Saprolegnia and other Oomycetes. In: Woo PTK, Bruno DW, editors. Fish diseases and disorders, vol. 3, Viral, bacterial and fungal infections. Wallingford, Oxon, United Kingdom: CABI Publishing; 1999. p. 599–659.
Chen W, Hoy JW, Schneider RW. Species–specific polymorphisms in transcribed ribosomal DNA of five Pythium species. Exp Mycol. 1992;16:22–34. doi:10.1016/0147-5975(92)90038-S.
Chen W, Schneider RW, Hoy JW. Taxonomic and phylogenetic analyses of ten Pythium species using isozyme polymorphisms. Phytopathology. 1992;82:1234–44. doi:10.1094/Phyto-82-1234.
Coker WC. The Saprolegniaceae with notes on other water molds. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press; 1923.
Coker WC, Matthews VD. Saprolegniales. North Amer Flora. 1937;2:15–76.
Dick MW. Straminipilous fungi. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2001.
Diéguez-Uribeondo J, Cerenius L, Söderhäll K. Physiological characterisation of Saprolegnia parasitica isolates from brown trout. Aquaculture. 1996;140:247–57. doi:10.1016/0044-8486(95)01176-5.
Diéguez-Uribeondo J, Fregeneda-Grandes JM, Cerenius L, Pérez-Iniesta E, Miguel Aller-Gancedo J, Teresa Tellería M, et al. Re-evaluation of the enigmatic species complex Saprolegnia diclina–Saprolegnia parasitica based on morphological, physiological and molecular data. Fungal Genet Biol. 2007;44:585–601. doi:10.1016/j.fgb.2007.02.010.
Hughes GC. Saprolegniasis, then and now: a retrospective. In: Mueller GJ, editor. Salmon Saprolegniasis. Portland, Oregon: U.S. Department of Energy, Bonneville Power Administration; 1994.
Hussein MM, Hatai K. Saprolegnia Salmonis sp. nov. isolated from sockeye salmon, Onchrhynchus nerka. Mycoscience. 1999;40:387–91. doi:10.1007/BF02464392.
Inaba S, Tokumasu S. Saprolegnia semihypogyna sp. nov., a saprolegniaceous oomycete isolated from soil in Japan. Mycoscience. 2002;43:73–6. doi:10.1007/s102670200011.
John Jr TW, Seymour RL, Padgett DE. Biology and systematics of the saprolegniaceae. 2002. On-line publication: http://www.ilumina-dlib.org. 2002.
Molina FI, Jong SC, Ma GZ. Molecular characterization and identification of Saprolegnia by restriction analysis of genes coding for ribosomal RNA. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 1995;68:65–74. doi:10.1007/BF00873294.
Paul B, Steciow MM. Saprolegnia multispora, a new oomycete isolated from water samples taken in a river in the Burgundian region of France. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004;237:393–8.
Saprrow FK. Aquatic phycomycetes. 2nd ed. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press; 1960.
Steciow MM. Saprolegnia longicaulis (Saprolegniales, Straminipila), a new species from an Argentine stream. New Zeal J Bot. 2001;39:483–8.
Whisler HC. Identification of Saprolegnia spp. pathogenic in Chinook Salmon. Final Report, DE-AC79-90BP02836. Washington, DC: US Department of Energy; 1996. p. 43.
Willoughby LG. Sprolegnias of salmonid fish in windermere: a critical analysis. J Fish Dis. 1978;1:51–67. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2761.1978.tb00005.x.
Willoughby LG. Saprolegnia polymorpha sp. nov., a fungal parasite on Koi carp, in the UK. Nova Hedwigia. 1998;66:507–11.
Xiaoli K, Jianguo W, Zemao G, Ming L, Xiaoning G. Study on total DNA extraction methods of Saprolegnia. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica. 2008;32:67–72.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the group of molecular toxicology for the supply of fungal-infected zebra fish. This work was supported by “the Key Science–Technology Project of Hubei Province of China (Grant No. 2007AA203A01)’’ and the project of the 11th National Five-Year-Plan of Key Science and Technology 2006BAD03B04-08 and 2006BAK02A22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ke, X., Wang, J., Gu, Z. et al. Saprolegnia brachydanis, A New Oomycete Isolated from Zebra Fish. Mycopathologia 167, 107–113 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-008-9150-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-008-9150-z