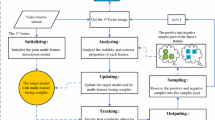
Abstract
In this paper, we present a robust and fast online object tracking algorithm, in which object tracking is achieved by combining L2-regularized least square (L2-RLS) and compressed Haar-like features matching in a Bayesian inference framework. Firstly, the extent of occlusion can be evaluated by L2 tracker. Secondly, the compressed features matching method is used to locate the target object if the extent of occlusion satisfies two inequality constraints. Finally, most of the insignificant samples are removed before computing the compressed features, which makes the computational load of our fused algorithm be only slightly higher than L2 tracker. Both qualitative and quantitative evaluations on numerous challenging image sequences demonstrate that the proposed method is more robust and stable than L2 tracker when the target object undergoes pose variation or rotation, and a paired T-test verifies that it significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art algorithms in terms of accuracy. In addition, our tracker meets the requirement of real-time tracking.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babenko B, Yang M.-H, Belongie S (2009) Visual tracking on-line multiple instance learning. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2009), 983–990
Bao CL, Wu Y, Ling HB, Ji H (2012) Real time robust ℓ tracker using accelerated proximal gradient approach. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2012), 1830–1837
Bay H, Tuytelaars T, Van Gool L (2006) Surf: speed up robust features. In: The 9th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2006), 404–417
Cai ZB, Gu ZH, Yu ZL, Liu H, Zhang K (2014) A real-time visual object tracking system based on Kalman filter and MB-LBP features matching. Multimed Tools Appl. doi:10.1007/s11042-014-2411-6
Chen XY, Yuan J, Nie LQ, Zha Z.-J, Yan SC, Chua T.-S (2010) TRECVID 2010 known-item search by NUS. In: 2010 TREC Video Retrieval Evaluation Notebook Papers
Grabner H, Bischof H (2006) On-line boosting and vision. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2006), 260–267
Grabner H, Leistner C, Bischof H (2008) Semi-supervised on-line boosting for robust tracking. In: The 10th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2008), 234–247
Hong RC, Li GD, Nie LQ, Tang JH, Chua T.-S (2010) Exploring large scale data for multimedia QA: an initial study. In: ACM International Conference on Image and Video Retrieval (CIVR’10), 74–81
Jia X, Lu HC, Yang M.-H (2012) Visual tracking via adaptive structural local sparse appearance model. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2012), 1822–1829
Jiang XD, Yu H, Lu Y, Liu HH (2015) A fusion method for robust face tracking. Multimed Tools Appl. doi:10.1007/s11042-015-2659-5
Kalal Z, Matas J, Mikolajczyk K (2010) P-N learning: bootstrapping binary classifiers by structural constraints. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2010), 49–56
Kwon J, Lee K. M (2010) Visual tracking decomposition. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2010), 1269–1276
Li X, Hu WM, Zhang ZF, Zhang XQ, Luo G (2007) Robust visual tracking based on incremental tensor subspace learning. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2007), 1–7
Li GR, Liang DW, Huang QM, Jiang SQ, Gao W (2008) Object tracking using incremental 2d-lda learning and bayes inference. In: International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP 2008), 1568–1571
Li S, Zhang ZQ (2004) Floatboost learning and statistical face detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 26(9):1112–1123
Liu BY, Huang JZ, Yang L, Kulikowski CA (2011) Robust tracking using local sparse appearance model and k-selection. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2011), 1313–1320
Liu HP, Sun FC (2012) Fusion tracking in color and infrared images using joint sparse representation. Sci China Inf Sci 55(3):590–599
Lower DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. J Comput Vis 60(2):91–110
Mei X, Ling HB (2009) Robust visual tracking using ℓ minimization. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2009), 1436–1443.
Mei X, Ling HB, Wu Y, Blasch E, Bai L (2012) Minimum error bounded efficient l1 tracker with occlusion detection. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2011), 1257–1264
Mei X, Ling HB, Wu Y, Blasch E, Bai L (2013) Efficient minimum error bounded particle resampling l1 tracker with occlusion. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(7):2661–2675
Nie LQ, Wang M, Gao Y, Zha Z-J, Chua T-S (2012) Beyond text QA: multimedia answer generation by harvesting web information. IEEE Trans Multimed 15(2):426–441
Nie LQ, Wang M, Zha Z.-J, Li GD, Chua T.-S (2011) Multimedia answering: enriching text QA with media information. In: the 34th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR’11), 695–704
Nie LQ, Zhao Y-L, Wang XY (2014) Learning to recommend descriptive tags for questions in social forums. ACM Trans Inf Syst 32(1):1–23
Ross D, Lim J, Lin R, Yang M (2008) Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int J Comput Vis 77(1):125–141
Shi QF, Eriksson A, Van den Hengel A, Shen CH (2011) Is face recognition really a compressive sensing problem? In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2011), 553–560
Viola P, Jones M (2001) Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2001), 511–518
Wang D, Lu HC (2012) Object tracking via 2DPCA and ℓ regularization. IEEE Signal Process Lett 19(11):711–714
Wang D, Lu HC, Bo CW (2014) Online visual tracking via two view sparse representation. IEEE Signal Process Lett 21(9):1031–1034
Wang D, Lu HC, Chen YW (2010) Incremental mpca for color object tracking. In: International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR 2010), 1751–1754
Wang D, Lu HC, Yang M-H (2013) Online object tracking with sparse prototypes. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(1):314–325
Wang D, Lu HC, Yang M.-H (2013) Least soft-thresold squares tracking. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2013), 2371–2378
Williams O, Blake A, Clipolla R (2005) Sparse bayesian learning for efficient visual tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(8):1292–1304
Xiao ZY, Lu HC, Wang D (2014) L2-RLS based object tracking. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 24(8):1301–1309
Yan Y, Ricci E, Liu GW, Sebe N (2015) Egocentric daily activity recognition via multitask clustering. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(10):2984–2995
Yan Y, Ricci E, Subramanian R, Liu GW, Lanz O, Sebe N (2016) A multi-task learning framework for head pose estimation under target motion. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2477843
Yan Y, Ricci E, Subramanian R, Liu GW, Sebe N (2014) Multitask linear discriminant analysis for view invariant action recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(12):5599–5611
Yang F, Lu HC, Yang M-H (2013) Robust visual tracking via multiple kernel boosting with affinity constraints. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 24(2):242–254
Zeng FX, Liu X, Huang ZT, Ji Y (2013) Kernel based multiple cue adaptive appearance model for robust real-time visual tracking. IEEE Signal Process Lett 20(11):1094–1097
Zhang LM, Gao Y, Xia YJ, Dai QH, Li XL (2015) A fine-grained image categorization system by cellet-encoded spatial pyramid modeling. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(1):564–571
Zhang LM, Han YH, Yang Y, Song ML, Yan SC, Tian Q (2013) Discovering discriminative graphlets for aerial image categories recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(12):5071–5084
Zhang HL, Tao F, Yang GB (2015) Robust visual tracking based on structured sparse representation model. Multimed Tools Appl 74(3):1021–1043
Zhang LM, Yang Y, Gao Y, Yu Y, Wang CB, Li XL (2014) A probabilistic associative model for segmenting weakly supervised images. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(9):4150–4159
Zhang L, Yang M, Feng XC (2011) Sparse representation or collaborative representation: Which helps face recognition? In: International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2011), 471–478
Zhang SP, Yao HX, Sun X, Liu SH (2010) Robust object tracking based on sparse representation. In: SPIE International Conference on Visual Communication and Image Processing (VCIP), 77441N-1-8
Zhang KH, Zhang L, Yang M.-H (2012) Real-time compressive tracking. In: The 12th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2012), 864–877
Zhang KH, Zhang L, Yang M-H (2013) Real-time object tracking via online discriminative feature selection. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(12):4664–4677
Zhong W, Lu HC, Yang M.-H (2012) Robust object tracking via sparsity-based collaborative model. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2012), 1838–1845
Zhuang BH, Lu HC, Xiao ZY, Wang D (2014) Visual tracking via discriminative sparse similarity map. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(4):1872–1881
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Science Foundation of China(NSFC) under Grand 51479159 and Soft Science Project of China’s Ministry of Transport under Grand 2013-322-811-470.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Yang, J., Liu, H. et al. A real-time object tracking via L2-RLS and compressed Haar-like features matching. Multimed Tools Appl 75, 9427–9443 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3356-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3356-8