Abstract
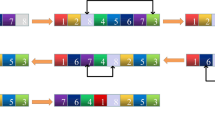
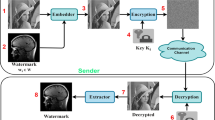
In this paper, we propose a reversible data hiding method for ordered dithered halftone images. To achieve reversibility and high capacity, the proposed method decomposes an ordered dithered halftone into a maximal number of subimage pairs with the same characteristic, and then hides data with a subimage-swapping operation, which converts a subimage pair into a subimage pair with opposite characteristic. Besides, this method maintains good visual quality by exchanging neighboring pixels instead of flipping individual pixels. Experimental results show that this method has the highest capacity among the existing reversible data hiding methods. A reversible authentication watermarking system is also proposed using this reversible watermarking method and it shows better visual quality compared to an existing method.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baharav Z, Shaked D (1998) Watermarking of Dither halftone images. Hewlett-Packard Labs Tech Rep, HPL-98-32
Fu MS, Au OC (2002) Data hiding watermarking for halftone images. IEEE Trans Image Process, pp 477–484
Guo JM, Pei SC, Lee H (2008) Paired subimage matching watermarking method on ordered Dither images and its high-quality progressive coding. IEEE Trans Multimedia 10(1):16–30
Hel-Or HZ (2001) Watermarking and copyright labeling of printed images. J Elect Imaging 10(3):794–803
Kim HY (2005) A new public-key authentication watermarking for binary document images resistant to parity attacks. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Image Processing, (Italy), vol. 2, pp 1074–1077
Lau DL, Ulichney R, Arce GR (2003) Blue- and green-noise halftoning models. IEEE Signal Process Mag 20(4):28–38
Liao PS, Pan JS, Chen YH, Liao BY (2005) A lossless watermarking technique for halftone images. In: Proc. Knowledge-Based Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems, vol. 2, pp 593–599
Lien BK, Chang CY (2007) Watermarking of ordered Dither halftone images by bit interleaving. In: Proc. IEEE, The 8th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology, vol. 1, pp 319–322
Lu ZM, Luo H, Pan JS (2006) Reversible watermarking for error diffused halftone image using statistical features. Lect Notes Comput Sci 4283:71–81
Ni Z, Shi YQ, Ansari N, Su W (2006) Reversible data hiding. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 16(3)
Pamboukian SVD, Kim HY (2006) Reversible data hiding and reversible authentication watermarking for binary images. In: VI Simpósio Brasileiro em Segurança da Informação e de Sistemas Computacionais (SBSeg), Santos, SP, Brasil
Pan JS, Luo H, Lu ZM (2006) A lossless watermarking scheme for halftone image authentication. Int J Comput Sci Netw Security 6(2b):147–151
Pei SC, Guo JM, Lee H (2005) Novel robust watermarking technique in Dithering halftone images. IEEE Signal Process 12(4):333–336
Schneier B (1996) Applied cryptography. Wiley
Tsaia CL, Chiang HF, Fan KC, Chung CD (2005) Reversible data hiding and lossless reconstruction of binary images using pair-wise logical computation mechanism. Pattern Recognit 38(11):1993–2006
Ulichney R (1987) Digital Halftoning. MIT, Cambridge
Ulichney R (1993) “The Void-and-Cluster Method for Generating Dither Arrays,” IS&T/SPIE Symposium on Electronic Imaging Science & Technology, San Jose, CA, vol. 1913, Feb. 1–5, pp 332–343
Wang CC, Chang CC, Zhang X, Jan JK (2007) Senary huffman compression - a reversible data hiding scheme for binary images. In: International Workshop on Multimedia Content Analysis and Mining (MCAM07), pp 351–360
Wong PW, Memon ND (2003) Image Processing for Halftones. IEEE Signal Process Mag 20(4):59–70
Wu M, Tang E, Liu B (2000) Data hiding in digital binary image. IEEE Int. Conf. Multimedia and Expo, ICME’00, New York, USA
Xuan G, Shi YQ, Chai P, Tong X, Teng J, Li J. Reversible binary image data hiding by run-length histogram modification. The 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR 2008), December 8–11, 2008, Tampa, Florida, USA
Yu FX, Luo H, Chu SC (2009) Lossless data hiding for halftone images. Inf Hiding Appl 227:181–203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lien, B.K., Lin, Ym. High-capacity reversible data hiding by maximum-span pairing. Multimed Tools Appl 52, 499–511 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-010-0497-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-010-0497-z