Abstract
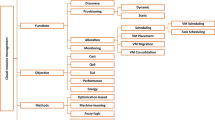
Cloud resources and their loads possess dynamic characteristics. Current research methods have utilized certain physical indicators and fixed thresholds to evaluate cloud resources, which cannot meet the dynamic needs of cloud resources or accurately reflect their resource states. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a Self-adaptive threshold based Dynamically Weighted load evaluation Method (termed SDWM). It evaluates the load state of the resource through a dynamically weighted evaluation method. First, the work proposes some dynamic evaluation indicators in order to evaluate the resource state more accurately. Second, SDWM divided the resource load into three states, including O v e r l o a d, N o r m a l and I d l e using the self-adaptive threshold. It then migrated those overload resources to a balance load, and releases the idle resources whose idle times exceeded a threshold to save energy, which could effectively improve system utilization. Finally, SDWM leveraged an energy evaluation model to describe energy quantitatively using the migration amount of the resource request. The parameters of the energy model were obtained from a linear regression model according to the actual experimental environment. Experimental results showed that SDWM is superior to other methods in energy conservation, task response time, and resource utilization, and the improvements are 31.5 %, 50 %, 50.8 %, respectively. These results demonstrate the positive effect of the dynamic self-adaptive threshold. More specially, SDWM shows great adaptability when resources dynamically join or exit.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong M, Lit H, Ota K et al (2014) HVSTO: Efficient privacy preserving hybrid storage in cloud data center. In: in Proc. of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS). IEEE, pp 529–534
Dong M, Li H, Ota K et al (2014) Multicloud-Based Evacuation Services for Emergency Management. IEEE Cloud Comp 1(4):50–59
Chang S. B., Jeun W. L., Youn C. H. (2011) Utility adaptive service brokering mechanism for personal cloud service. In: Proc. 2011 Military Communications Conference, Baltimore, MD, 7-10 Nov, pp 1622–1627
Hikita J, Hirano A, Nakashima H (2008) Saving 200kw and 200 dollar k/year by power-aware job/machine scheduling. In: Proc. 2008 IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing, Miami, FL, 14-18 Apr., 1-8
Bucur AID, Epema DHJ (2007) Scheduling Policies for Processor Collocation in Multi cluster System. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 18:958–962
Dai YS, Levitin G, Trivedi KS (2007) Performance and reliability of tree-structured grid services considering data dependence and failure correlation. IEEE Trans Comput 56(7):925–936
Song F, Xu CZ (2007) Exploring event correlation for failure prediction in coalitions of clusters. In: Proc. of the 2007 ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing, Reno, NV, USA, 10-16 Nov, pp 1–12
Beloglazov A., Buyya R. (2012) Optimal online deterministic algorithms and adaptive heuristics for energy and performance efficient dynamic consolidation of virtual machines in Cloud data centers. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience 24(13):1397–1420
Tang Z, Jiang L, Zhou J., Li K., Li K. (2015) A self-adaptive scheduling algorithm for reduce start time. Futur Gener Comput Syst 43(5):51–60
Tripathy B., Dash S., Padhy S. K. (2015) Dynamic task scheduling using a directed neural network. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing 75(3):101–106
Olivier B., Lionel E. D., Christopher T. C., Hejer R. (2013) Heterogeneous Resource Allocation under Degree Constraints. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 24(5):926–937
Islam S., Keung J., Lee K., Liu A. (2012) Empirical prediction models for adaptive resource provisioning in the cloud. Futur Gener Comput Syst 28(1):155–16
Zhang Q., Zhani M. F., Boutaba R. (2014) Dynamic Heterogeneity-Aware Resource Provisioning in the Cloud. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing 2(1):14–28
Bruneo D. (2014) A Stochastic Model to Investigate Data Center Performance and QoS in IaaS Cloud Computing Systems. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 25(3):560–569
Bera S., Misra S., Rodrigues J. J. P. C. (2015) Cloud Computing Applications for Smart Grid: A Survey. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 26(5):1477–1494
Pagani S., Chen J. J., Li M. M. (2015) Energy Efficiency on Multi-core Architectures with Multiple Voltage Islands. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 26(6):1608–1621
Cardosa M., Singh A., Pucha H., Chandra A. (2012) Exploiting spatio-temporal tradeoffs for energy-aware MapReduce in the Cloud. IEEE Trans Comput 61(12):1737–1751
Ghamkhari M., Mohsenian-Rad H. (2013) Energy and Performance Management of Green Data Centers: A Profit Maximization Approach. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 4(2):1017–1025
Mobius C., Dargie W., Schill A. (2013) Power Consumption Estimation Models for Processors, Virtual Machines, and Servers. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 25(6):1045–9219
Pedram M. (2012) Energy-Efficient Datacenters. IEEE Trans Comput Aided Des Integr Circuits Syst 31 (10):1465–1484
Guo Y., Fang Y. (2013) Electricity cost saving strategy in data centers by using energy storage. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 24(6):1149–1160
Farahnakian F., Liljeberg P., Plosila J. (2014) Energy-Efficient Virtual Machines Consolidation in Cloud Data Centers using Reinforcement Learning. In: Proc. of 2014 22nd Euromicro International Conference on Parallel, Distributed, and Network-Based Processing, Torino, 12-14 Feb , pp 500–507
Garraghan P., Moreno I. S., Townend P., Xu J. (2014) An Analysis of Failure-Related Energy Waste in a Large-Scale Cloud Environment. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing 2(2):166–180
Hosseinimotlagh S., Khunjush F., Hosseinimotlagh S. (2014) A Cooperative Two-Tier Energy-Aware Scheduling for Real-Time Tasks in Computing Clouds. In: Proc. of 2014 22nd Euromicro International Conference on Parallel, Distributed, and Network-Based Processing, Torino, 12-14 Feb, pp 178–182
Zhu XM, Yang T, Chen HK, Wang J, Yin S, Liu XC (2014) Real-Time Tasks Oriented Energy-Aware Scheduling in Virtualized Clouds. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2014 2(2):180–198
Luo J. Y., Rao L., Liu X. (2014) Temporal Load Balancing with Service Delay Guarantees for Data Center Energy Cost Optimization. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 25(3):775–784
Ye K. J., WU Z. H., Jiang X. H., He Q. M. (2012) Power management of virtualized cloud computing platform. Chin J Comput Phys 35(6):1262–1283
Kansal A., Zhao F., Liu J., Kothari N., Bhattacharya A. A. (2010) Virtual machine power metering and provisioning. In: Proc. of the 1st ACM symposium on Cloud computing. Indianapolis, Indiana, USA, ACM. 10-11 June, pp 39–50
Owusu F., Pattinson C. (2012) The current state of understanding of the energy efficiency of cloud computing. In: Proc. of 2012 IEEE 11th International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom), Liverpool, 25-27 June, pp 1948–1953
Kliazovich D., Bouvry P., Khan S. U. (2012) GreenCloud: a packet-level simulator of energy-aware cloud computing data centers. J Supercomput 62(3):1263–1283
Bessis N., Sotiriadis S., Pop F. et al (2013) Using a novel message-exchanging optimization (MEO) model to reduce energy consumption in distributed systems. Simul Model Pract Theory 39(3):104–120
Nathuji R., Schwan K. (2007) VirtualPower: coordinated power management in virtualized enterprise systems. ACM SIGOPS Operating Systems Review 41(6):265–278
Cao J. W., Li K. Q. (2014) Optimal Power Allocation and Load Distribution for Multiple Heterogeneous Multicore Server Processors across Clouds and Data Centers. IEEE Trans Comput 63(1):45–58
Verma A., Ahuja P., Neogi A (2008) pMapper: power and migration cost aware application placement in virtualized systems. Middleware 2008. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp 243–264
Zhu X., Young D., Watson BJ et al (2008) 1000 islands: Integrated capacity and workload management for the next generation data center. In: Proc. of 2008 International Conference on Autonomic Computing, Chicago, IL, 2-6 June, pp 172–181
Gmach D., Rolia J., Cherkasova L. et al (2008) An integrated approach to resource pool management: Policies, efficiency and quality metrics. In: Proc. of IEEE International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks With FTCS and DCC, Anchorage, AK, 24-27 June, pp 326–335
Beloglazov A., Abawajy J., Buyya R. (2012) Energy-aware resource allocation heuristics for efficient management of data centers for cloud computing. Futur Gener Comput Syst 28(5):755–768
Beloglazov A., Buyya R. (2013) Managing overloaded hosts for dynamic consolidation of virtual machines in cloud data centers under quality of service constraints. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 24(7):1366–1379
Xiao Z., Song W., Chen Q. (2013) Dynamic Resource Allocation Using Virtual Machines for Cloud Computing Environment. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 24(6):1107–1116
Liu H. K., He B. S. (2015) VMbuddies: Coordinating Live Migration of Multi-Tier Applications in Cloud Environments. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 26(4):1192–1205
Hu Z. J. (2010) The resource availability evaluation in service grid environment for QoS. Ph.D. dissertation
Baliga J., Ayre R. W. A., Hinton K., Tucker RS (2011) Green cloud computing: Balancing energy in processing, storage, and transport. Proc IEEE 99(1):149–167
Dong M, Li H, Ota K et al (2015) Rule caching in SDN-enabled mobile access networks. IEEE Netw 29 (4):40–45
Zuo L., Dong S., Zhu C., Shu L., Han G. (2015) A Cloud Resource Evaluation Model Based on Entropy Optimization and Ant Colony Clustering. Comput J 58(6):1254–1266
Zuo L., Shu L., Zhu C., Zhou Z. (2013) A Resource Evaluation Model Based on Entropy Optimization toward Green Cloud. In: Proc. of 2013 Semantics, Knowledge and Grids 2013, Beijing, Oct, pp 74–81
Valls M G, Alonso A, Ruiz J et al (2003) An architecture of a quality of service resource manager middleware for flexible embedded multimedia systems. In: Software Engineering and Middleware, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp 36–55
Palopoli L, Cucinotta T, Marzario L et al (2009) AQuoSAadaptive quality of service architecture. In: Software: Practice and Experience, vol. 39 no. 1, 1-31
Calheiros R. N., Ranjan R., Beloglazov A., Cesar A. F., De R., Buyya R. (2011) CloudSim: A Toolkit for Modeling and Simulation of Cloud Computing Environments and Evaluation of Resource Provisioning Algorithms. Software: Practice and Experience, Wiley 41(1):23–50
He X., Sun X. (2003) QoS Guided Min-Min Heuristic for Grid Task Scheduling. J Comput Sci Technol 18 (4):442–451
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China Project No. 2014A030313729, 2013 Special Fund of Guangdong Higher School Talent Recruitment, 2013 top Level Talents Project in Sailing Plan of Guangdong Province, National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant NO. 61401107), and 2014 Guangdong Province Outstanding Young Professor Project, Science and Technology Key Project of Guangdong No. 2014B010112006, Natural Science Fund of Guangdong No. 2015A030308017. Lei Shu and Shoubin Dong are the corresponding authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, L., Shu, L., Dong, S. et al. Dynamically Weighted Load Evaluation Method Based on Self-adaptive Threshold in Cloud Computing. Mobile Netw Appl 22, 4–18 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-016-0679-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-016-0679-7