Abstract
Objective
Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) is a crucial cytokine that has been implicated in cancer and metastasis development. However, its possible mechanistic role in cervical cancer remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the functions of exogenous IL-1β in cervical cancer cell proliferation and migration.
Methods
HeLa cell proliferation and migration were measured using MTT and Transwell assays. A lentivirus-mediated packaging system was used to construct an IL-1β overexpressing cell line. MEK/ERK signal transduction was inhibited by pretreatment with the MEK inhibitor PD98059. qRT–PCR and Western blotting were used to test the expression of relevant genes.
Results
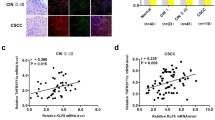
Exogenous IL-1β promoted the proliferation and migration of HeLa cells. In addition, overexpression of IL-1β in HeLa cells promoted cell proliferation. Mechanistically, exogenous IL-1β increased the phosphorylated MEK and ERK levels in HeLa cells and the expression of JUN, RELB, and NF-κB2. Alternatively, blockade of MEK inhibited the promoting proliferation effects of IL-1β and the expression of JUN, RELB, and NF-κB2.
Conclusions
Our data suggest that exogenous IL-1β regulates HeLa cell functions by regulating the MEK/ERK signaling pathway and by targeting JUN, RELB, and NF-κB2. Our study uncovered a potential association across IL-1β, cervical tumor development, and cancer progression.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data sets used or analyzed during the study are included in this published article.
References
Hu SY, Zheng RS, Zhao FH, Zhang SW, Chen WQ, Qiao YL (2014) Trend analysis of cervical cancer incidence and mortality rates in Chinese women during 19892008. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 36:119125
Tao J, Dai J, Hou S (2017) Association between B7-H1 and cervical cancer: B7-H1 impairs the immune response in human cervical cancer cells. Exp Ther Med 14(5):4125–4133
Sobti RC, Tamandani DMK, Shekari M, Kaur P, Malekzadeh K, Suri V (2008) Interleukin 1 beta gene polymorphism and risk of cervical cancer. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 101(1):47–52
Goodman A (2015) HPV testing as a screen for cervical cancer. BMJ 350:h2372
Canfell K (2019) Towards the global elimination of cervical cancer. Papillomavirus Res 8:100170
Kessler TA (2017) Cervical Cancer: Prevention and Early Detection. Semin Oncol Nurs 33(2):172–183
Burd EM (2003) Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. Clin Microbiol Rev 16(1):1–17
Burotto M, Chiou VL, Lee JM, Kohn EC (2014) The MAPK pathway across different malignancies: a new perspective. Cancer 120(22):3446–3456
Kim EK, Choi EJ (2010) Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802(4):396–405
Teng F, Ruan HJ, Xu J, Ni J, Qian B, Shen R, Gao LJ (2018) RBBP6 promotes human cervical carcinoma malignancy via JNK signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 101:399–405
Liu X, Yang Q, Yan J, Zhang X, Zheng M (2019) LncRNA MNX1-AS1 promotes the progression of cervical cancer through activating MAPK pathway. J Cell Biochem 120(3):4268–4277
Kumar V, Behera R, Lohite K, Karnik S, Kundu GC (2010) P38 kinase is crucial for osteopontin-induced furin expression that supports cervical cancer progression. Cancer Res 70(24):10381–10391
Zheng F, Zhang J, Luo S, Yi J, Wang P, Zheng Q, Wen Y (2016) MiR-143 is associated with proliferation and apoptosis involving ERK5 in HeLa cells. Oncol Lett 12(4):3021–3027
Guo YJ, Pan WW, Liu SB, Shen ZF, Xu Y, Hu LL (2020) ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med 19(3):1997–2007
Sun Y, Liu WZ, Liu T, Feng X, Yang N, Zhou HF (2015) Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 35(6):600–604
Malik A, Kanneganti TD (2018) Function and regulation of IL-1α in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Immunol Rev 281(1):124–137
Mantovani A, Barajon I, Garlanda C (2018) IL-1 and IL-1 regulatory pathways in cancer progression and therapy. Immunol Rev 281(1):57–61
Zhang W, Borcherding N, Kolb R (2020) IL-1 signaling in tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol 1240:1–23
Lee CH, Chang JSM, Syu SH, Wong TS, Chan JYW, Tang YC, Yang ZP, Yang WC, Chen CT, Lu SC, Tang PH, Yang TC, Chu PY, Hsiao JR, Liu KJ (2015) IL-1β promotes malignant transformation and tumor aggressiveness in oral cancer. J Cell Physiol 230(4):875–884
Lee MK, Park JH, Gi SH, Hwang YS (2018) IL-1β induces fascin expression and increases cancer invasion. Anticancer Res 38(11):6127–6132
Liu B, Zhou Y, Chen X, Peng D (2017) IL-1β-mediated NF-κB signaling augments the osteosarcoma cell growth through modulating miR-376c/TGFA axis. Pharmazie 72(7):419–424
Hurmath KF, Ramaswamy P, Nandakumar DN (2014) IL-1β microenvironment promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of human glioma cells. Cell Biol Int 38(12):1415–1422
Lu L, Wang P, Zou Y, Zha Z, Huang H, Guan M, Wu Y, Liu G (2020) IL-1β promotes stemness of tumor cells by activating Smad/ID1 signaling pathway. Int J Med Sci 17(9):1257–1126
Ping PH, Bo TF, Li L, Hui YN, Hong Z (2016) IL-1β/NF-kb signaling promotes colorectal cancer cell growth through miR-181a/PTEN axis. Arch Biochem Biophys 604:20–26
Bent R, Moll L, Grabbe S, Bros M (2018) Interleukin-1 beta-A friend or foe in malignancies? Int J Mol Sci 19(8):2155
Qian N, Chen X, Han S, Qiang F, Jin G, Zhou X, Dong J, Wang X, Shen H, Hu Z (2010) Circulating IL-1beta levels, polymorphisms of IL-1B, and risk of cervical cancer in Chinese women. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136(5):709–716
Al-Tahhan MA, Etewa RL, Behery MME (2011) Association between circulating interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) levels and IL-1β C-511T polymorphism with cervical cancer risk in Egyptian women. Mol Cell Biochem 353(1–2):159–165
Tao L, Liu S, Xiong J, Yang H, Wu Y, Xu A, Gong Y (2021) IL-1β promotes cervical cancer through activating NF-κB/CCL-2. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 14(4):426–433
Chen L, Cai S, Wang JM, Huai YY, Lu PH, Chu Q (2020) BRDT promotes ovarian cancer cell growth. Cell Death Dis 11(11):1021
Liu W, Wang L, Zhang J, Qiao L, Liu Y, Yang X, Zhang J, Zheng W, Ma Z (2021) Purification of recombinant human chemokine CCL2 in E. coli and its function in ovarian cancer. 3 Biotech 11(1):8
Ibrahim EM, Stewart RL, Corke K, Blackett AD, Tidy JA, Wells M (2006) Upregulation of CD44 expression by interleukins 1, 4, and 13, transforming growth factor-beta1, estrogen, and progestogen in human cervical adenocarcinoma cell lines. Int J Gynecol Cancer 16(4):1631–1642
Adefuye AO, Sales KJ, Katz AA (2014) Seminal plasma induces the expression of IL-1α in normal and neoplastic cervical cells via EP2/EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway. J Mol Signal 9:8
Matamoros JA, Silva MIF, Moura PMMF, Leitão MCG, Coimbra EC (2019) Reduced Expression of IL-1β and IL-18 Proinflammatory Interleukins Increases the Risk of Developing Cervical Cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 20(9):2715–2721
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the Scientific and Technological Research Project of Henan Province (No. 212102310898), the Key scientific research project of Henan Province (No. 22A180017), the research start-up fund to topnotch talents of Henan Agricultural University (No. 30500424 and 30500618), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31802164).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.Z. and L.W. performed the experiments. Y.L. performed systematic research of the literature. Z.M. and L.W. designed the experiments. Z.M. wrote the manuscript. W.L. revised it. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wang, L., Liu, Y. et al. Exogenous interleukin-1 beta promotes the proliferation and migration of HeLa cells via the MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Mol Biol Rep 49, 3765–3772 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07216-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07216-4