Abstract
Background
In type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), cytokines have a central role in orchestrating multicellular relations between β-cells and immune cells. This study aims to investigate the role of interleukin (IL)-21, IL-23, and IL-2, and their association with dyslipidemia in T1DM children.
Methods
The sample population consisted of 30 healthy controls and 70 children with T1DM, the latter of which were split into two groups according to the duration of their T1DM diagnosis: recent (≤ 1 year; n = 21) and older (> 1 year; n = 49) diagnoses.
Results
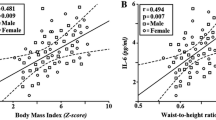
Fasting blood sugar and glycated hemoglobin levels in all diabetic children were significantly (P < 0.001) higher, whereas levels of plasma C-peptide were markedly (P < 0.001) lower in children with T1DM compared to healthy controls. In older T1DM diagnosis children, the levels of creatinine were noticeably (P < 0.05) increased relative to healthy controls. In all diabetic children, levels of total triglyceride, cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein were increased significantly (P < 0.001) than those of healthy controls. Furthermore, the IL-21 and IL-23 mRNA expressions of all children with T1DM were elevated significantly (P < 0.001) relative to healthy controls, whereas IL-2 levels revealed a significant (P < 0.001) decrease in all diabetic children.
Conclusion
There was a synergistic interplay between IL-21 and IL-23 with an antagonistic action of IL-2 in T1DM patients, and all three interleukins were associated with dyslipidemia in diabetic children. Importantly, therapies targeting IL-21 and IL-23 are promising targets for preventive strategies against the development of T1DM and its complications.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Brawerman G, Thompson PJ (2020) Beta cell therapies for preventing type 1 diabetes: from bench to bedside. Biomolecules 10:1681
Chalakova T, Yotov Y, Tzotchev K, Galcheva S, Balev B, Bocheva Y, Usheva N, Iotova V (2021) Type 1 diabetes mellitus—Risk factor for cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality. Curr Diabetes Rev 17:37–54
Uttra KM, Devrajani BR, Shah ZA, Devrajani T, Das T, Raza S (2011) Lipid profile of patients with diabetes mellitus (a multidisciplinary study). World Appl Sci J 12:1382–1384
d’Uscio LV, Baker TA, Mantilla CB, Smith L, Weiler D, Sieck GC, Katusic ZS (2001) Mechanism of endothelial dysfunction in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21:1017–1022
Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY (2004) Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351(13):1296–1305
Myasoedova E, Crowson CS, Kremers HM, Roger VL, Fitz-Gibbon PD, Therneau TM, Gabriel SE (2011) Lipid paradox in rheumatoid arthritis: the impact of serum lipid measures and systemic inflammation on the risk of cardiovascular disease. Ann Rheum Dis 70:482–487
Mathis D, Vence L, Benoist C (2001) β-Cell death during progression to diabetes. Nature 414:792–798
Fatima N, Faisal SM, Zubair S, Ajmal M, Siddiqui SS, Moin S, Owais M (2016) Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines and biochemical markers in the pathogenesis of type1diabetes: correlation with age and glycemic condition in diabetic human subjects. PLoS ONE 11(8):e0161548
Vogelzang A, McGuire HM, Yu D, Sprent J, Mackay CR, King C (2008) A fundamental role for interleukin-21 in the generation of T follicular helper cells. Immunity 29:127–137
McGuire HM, Vogelzang A, Ma CS, Hughes WE, Silveira PA, Tangye SG, Christ D, Fulcher D, Falcone M, King C (2011) A subset of interleukin-21+ chemokine receptor CCR9+ T helper cells target accessory organs of the digestive system in autoimmunity. Immunity 34:602–615
Ferreira RC, Simons HZ, Thompson WS, Cutler AJ, Dopico XC, Smyth DJ, Mashar M, Schuilenburg H, Walker NM, Dunger DB, Wallace C, Todd JA, Wicker LS, Pekalski ML (2015) IL-21 production by CD4+ effector T cells and frequency of circulating follicular helper T cells are increased in type 1 diabetes patients. Diabetologia 58:781–790
Lu J, Liang Y, Zhao J, Meng H, Zhang X (2019) Interleukin-33 prevents the development of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice. Int Immunopharmacol 70:9–15
Yen D, Cheung J, Scheerens H, Poulet F, McClanahan T, McKenzie B, Kleinschek MA, Owyang A, Mattson J, Blumenschein W, Murphy E, Sathe M, Cua DJ, Kastelein RA, Rennick D (2006) IL-23 is essential for T cell–mediated colitis and promotes inflammation via IL-17 and IL6. J Clin Investig 116(5):1310–1316
Mensah-Brown EP, Shahin A, Al-Shamsi M, Lukic ML (2006) New members of the interleukin-12 family of cytokines: IL-23andIL-27modulate autoimmune diabetes. Ann NY Acad Sci 1079:157–160
Laurence A, Tato CM, Davidson TS, Lukic ML (2007) Interleukin-2 signaling via STAT5 constrains T helper 17 cell generation. Immunity 26:371–381
Diaz-de-Durana Y, Lau J, Knee D, Filippi C, Londei M, McNamara P, Nasoff M, DiDonato M, Glynne R, Herman AE (2013) IL-2 immunotherapy reveals potential for innate beta cell regeneration in the non-obese diabetic mouse model of autoimmune diabetes. PLoS ONE 8:e78483
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS (1972) Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18(6):499–502
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Teles SAS, Fornés NS (2012) Relationship between anthropometric and biochemical profiles in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Rev Paul Pediatr 30:65–71
Basu S, Larsson A, Vessby J, Vessby B, Berne C (2005) Type 1 diabetes is associated with increased cyclooxygenase- and cytokine-mediated inflammation. Diabetes Care 28(6):1371–1375
Lachin JM, McGee P, Palmer JP, DCCT/EDIC Research Group (2014) Impact of C- peptide preservation on metabolic and clinical outcomes in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes 63:739–748
Mannucci E, Dicembrini I, Lauria A, Pozzilli P (2013) Is glucose control important for prevention of cardiovascular disease in diabetes? Diabetes Care 36(2):S259–S263
Salem M, Moneir I, Adly AM, Esmat K (2011) Study of coronary artery calcification risk in Egyptian adolescents with type-1 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 48:41–53
Bielicki JK, Forte TM (1999) Evidence that lipid hydroperoxides inhibit plasma lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase activity. J Lipid Res 40:948–954
Cockerill GW, Huehns TY, Weerasinghe A et al (2001) Elevation of plasma high-density lipoprotein concentration reduces interleukin-1-induced expression of E-selectin in an in vivo model of acute inflammation. Circulation 103:108–112
Kuvin JT, Patel AR, Sidhu M (2003) Relation between high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and peripheral vasomotor function. Am J Cardiol 92:275–279
Mourad A, Soraya M, Mohammed K, Ahmed-Bakir B, Aziz H (2007) Naim AK2007: relationship between interleukin-1β and lipids in type1 diabetic patients. Med Sci Monit 13:372–378
Hartvigsen K, Chou MY, Hansen LF, Shaw PX, Tsimikas S, Binder CJ, Witztum JL (2009) The role of innate immunity in atherogenesis. J Lipid Res 50:S388–S393
Hakola L, Erlund I, Cuthbertson D, Miettinen ME, Autio R, Nucci AM, Härkönen T, Honkanen J, Vaarala O, Hyöty H, Knip M, Krischer JP, Niinistö S, Virtanen SM, Investigators TRIGR (2021) Serum fatty acids and risk of developing islet autoimmunity: a nested case-control study within the TRIGR birth cohort. Pediatr Diabetes. https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.13189
Lahdenpera S, Syvanne M, Kahri J, Taskinen MR (1996) Regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle size distribution in NIDDM and coronary disease: importance of serum triglycerides. Diabetologia 39:453–461
Arai K, Yokoyama H, Okuguchi F et al (2008) Association between body mass index and core components of metabolic syndrome in 1486 patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus in Japan (JDDM 13). Endocr J 55(6):1025–1032
Vaid S, Hanks L, Griffin R, Ashraf AP (2016) Body mass index and glycemic control influence lipoproteins in children with type 1 diabetes. J Clin Lipidol 10(5):1240–1247
Castro-Correia C, Santos-Silva R, Pinheiro M, Costa C, Fontoura M (2018) Metabolic risk factors in adolescent girls with type 1 diabetes. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 31(6):631–635
Fellinger P, Fuchs D, Wolf P et al (2019) Overweight and obesity in type 1 diabetes equal those of the general population. Wien Klin Wochenschr 131(3–4):55–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-018-1434-9
Murphy D, McCulloch CE, Lin F, Banerjee T, Bragg-Gresham JL, Eberhardt MS, Morgenstern H, Pavkov ME, Saran R, Powe NR, Hsu CY (2016) Centers for disease control and prevention chronic kidney disease surveillance team. Trends in prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. Ann Intern Med 165(7):473–481
Gonzalez Suarez ML, Thomas DB, Barisoni L, Fornoni A (2013) Diabetic nephropathy: is it time yet for routine kidney biopsy? World J Diabetes 4(6):245–255
Ruggenenti P, Remuzzi G (1998) Nephropathy of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:2157–2159
Bonner-Weir S, Li WC, Ouziel-Yahalom L, Guo L, Weir GC, Sharma A (2010) β-cell growth and regeneration: replication is only part of the story. Diabetes 59(10):2340–2348
Ozaki K, Spolski R, Ettinger R, Kim HP, Wang G, Qi CF, Hwu P, Shaffer DJ, Akilesh S, Roopenian DC, Morse HC 3rd, Lipsky PE, Leonard WJ (2004) Regulation of B cell differentiation and plasma cell generation by IL-21, a novel inducer of Blimp-1 and Bcl-6. J Immunol 173:5361–5371
Kastirr I, Maglie S, Paroni M, Alfen JS, Nizzoli G, Sugliano E, Crosti MC, Moro M, Steckel B, Steinfelder S, Stölzel K, Romagnani C, Botti F, Caprioli F, Pagani M, Abrignani S, Geginat J (2014) IL-21 is a central memory T cell–associated cytokine that inhibits the generation of pathogenic Th1/17 effector cells. J Immunol 193:3322–3331
Van Belle TL, Nierkens S, Arens R, von Herrath MG (2012) Interleukin-21 receptor-mediated signals control autoreactive T cell infiltration in pancreatic islets. Immunity 36:1060–1072
Viisanen T, Ihantola EL, Näntö-Salonen K, Hyöty H, Nurminen N, Selvenius J, Juutilainen A, Moilanen L, Pihlajamäki J, Veijola R, Toppari J, Knip M, Ilonen J, Kinnunen T (2017) Circulating CXCR5+PD-1+ICOS+ follicular T helper cells are increased close to the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in children with multiple autoantibodies. Diabetes 66:437–447
McGuire HM, Vogelzang A, Hill N, Flodström-Tullberg M, Sprent J, King C (2009) Loss of parity between IL-2 and IL-21 in the NOD Idd3 locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19438–19443
Sutherland AP, Van Belle T, Wurster AL, Suto A, Michaud M, Zhang D, Grusby MJ, von Herrath M (2009) Interleukin-21 is required for the development of type 1 diabetes in NOD mice. Diabetes 58:1144–1155
Duvallet E, Semerano L, Assier E, Falgarone G, Boissier MC (2011) Interleukin23: a key cytokine in inflammatory diseases. Ann Med 43:503–511
Villanueva MT (2017) Rheumatoid arthritis: IL-23 assists the transition from autoimmunity to inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol 13(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2016.197
Abu El-Nazar S, Ghoneim H, Abou-Shamaa L, Shalaby T, Merssal B, Abdelfattah Z, Elbigawy N (2020) Interleukin-23 and interleukin-25 activities following recombinant human interleukin-2 administration in an experimental model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. GSJ 8(6):1901–1930
Abbasi A, Corpeleijn E, Meijer E, Postmus D, Gansevoort RT, Gans RO, Struck J, Hillege HL, Stolk RP, Navis G, Bakker SJ (2012) Sex differences in the association between plasma copeptin and incident type 2 diabetes: the prevention of renal and vascular endstage disease (PREVEND) study. Diabetologia 55:1963–1970
Mus AM, Cornelissen F, Asmawidjaja PS, van Hamburg JP, Boon L, Hendriks RW, Lubberts E (2010) Interleukin-23 promotes Th17 differentiation by inhibiting T bet and FoxP3 and is required for elevation of interleukin-22, but not interleukin-21, in autoimmune experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 62:1043–1050
Mensah-Brown EP, Shahin A, Al-Shamisi M, Wei X, Lukic ML (2006) IL23 leads to diabetes induction after subdiabetogenic treatment with multiple low doses of streptozotocin. Eur J Immunol 36:216–223
Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM, Mattson J, Basham B, Sedgwick JD, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ (2005) IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med 201:233–240
Iwakura Y, Ishigame H, Saijo S, Nakae S (2011) Functional specialization of interleukin-17 Family Members. Immunity 34:149–162
Hulme MA, Wasserfall CH, Atkinson MA, Brusko TM (2012) Central role for interleukin-2 in type diabetes. Diabetes 61:14–22
Dogan Y, Akarsu S, Ustundag B, Yilmaz E, Gurgoze MK (2006) Serum IL-1β, IL-2, and IL-6 in insulin-dependent diabetic children. Mediat Inflamm 1:59206
Kukreja A, Cost G, Marker J, Zhang C, Sun Z, Lin-Su K, Ten S, Sanz M, Exley M, Wilson B, Porcelli S, Maclaren N (2002) Multiple immuno-regulatory defects in type-1 diabetes. J Clin Invest 109:131–140
Zhou L, Ivanov II, Spolski R, Min R, Shenderov K, Egawa T, Levy DE, Leonard WJ, Littman DR (2007) IL-6 programs T(H)-17 cell differentiation by promoting sequential engagement of the IL-21 and IL-23 pathways. Nat Immunol 8:967–974
Iwakura Y, Ishigame H (2006) The IL-23/IL 17axis in inflammation. J Clin Invest 116:1218–1222
Funding
None (no researches grant supported this work).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. RGK, HA, AIY and MIZ analyzed the data and interpreted the data and prepared the manuscript for publication. RGK, AA and AE reviewed the draft of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The research procedure was approved by the Hospital ethics committee in compliance with the Helsinki announcement and the recommendations for good clinical practice (BSU/FS/2016/12).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalil, R.G., Abdel-Moneim, A., Yousef, A.I. et al. Association of interleukin-2, interleukin-21 and interleukin-23 with hyperlipidemia in pediatric type 1 diabetes. Mol Biol Rep 48, 5421–5433 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06545-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06545-0