Abstract
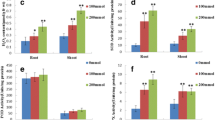
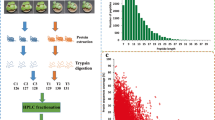
Salinity and drought are two major environmental factors that limit the growth and yield of many forage crops in semi-arid and arid regions. Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) is one of the most important forage crops in many countries. We aim to investigate the molecular mechanisms of alfalfa in response to salt and drought stresses in this study. Physiological and proteomic analyses were applied to examine the Zhongmu NO.3 alfalfa seed germination stage with 200 mM NaCl and 180 g·L−1 polyethylene glycol (PEG) treatments. The germination ability of the seed and the accumulation of osmotic solutes were quite different between the NaCl and PEG treatments. More than 800 protein spots were detected by proteomics technology on two-dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE) gels. The abundance of twenty-eight proteins were decreased or increased after salt and drought stress. Seventeen of these proteins were identified and classified into six functional categories through mass spectrometry (MS). The six groups involved in salt- and PEG-mediated stress included defense response, energy metabolism, protein synthesis and degradation, oxidative stress, carbohydrate metabolism-associated proteins, and unknown proteins. We discovered that some proteins related to carbohydrate metabolism and energy production increased in abundance under salt- and PEG-mediated drought stress. This demonstrates a common mechanism of energy consumption during abiotic stresses. Further study of these proteins with unknown function will provide insights into the molecular mechanisms of abiotic stress and the discovery of new candidate markers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alksne L, Warner J (1993) A novel cloning strategy reveals the gene for the yeast homologue to Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S12. J Biol Chem 268:10813–10819
Aranjuelo I, Tcherkez G, Molero G, Gilard F, Avice JC, Nogues S (2013) Concerted changes in N and C primary metabolism in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) under water restriction. J Exp Bot 64:885–897
Bader N, Grune T (2006) Protein oxidation and proteolysis. Biol Chem 387:1351–1355
Bates L, Waldren R, Teare I (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Bianchi MW, Damerval C, Vartanian N (2002) Identification of proteins regulated by cross-talk between drought and hormone pathways in Arabidopsis wild-type and auxin-insensitive mutants, axr1 and axf2. Funct Plant Biol 29
Blokhina O, Virolainen E, Fagerstedt KV (2003) Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: a review. Ann Bot 91:179–194
Boyer JS (1982) Plant productivity and environment. Science 218:443–448
Chandra Sanyal S, Liljas A (2000) The end of the beginning: structural studies of ribosomal proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 10:633–636
Cutler J, Rains D (1978) Effects of water stress and hardening on the internal water relations and osmotic constituents of cotton leaves. Physiol Plant 42:261–268
Davies KJ (2001) Degradation of oxidized proteins by the 20 S proteasome. Biochimie 83:301–310
Diray-Arce J, Clement M, Gul B, Khan MA, Nielsen BL (2015) Transcriptome assembly, profiling and differential gene expression analysis of the halophyte Suaeda fruticosa provides insights into salt tolerance. BMC Genom 16
Epstein E, Norlyn JD, Rush DW, Kingsbury RW, Kelley DB, Cunningham GA, Wrona AF (1980) Saline culture of crops: a genetic approach. Science 210:399–404
Farago S, Brunold C, Kreuz K (1994) Herbicide safeners and glutathione metabolism. Physiol Plant 91:537–542
Ferri A, Lluch C, Ocana A (2000) Effect of salt stress on carbon metabolism and bacteroid respiration in root nodules of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Biol 2:396–402
Grune T, Merker K, Sandig G, Davies KJ (2003) Selective degradation of oxidatively modified protein substrates by the proteasome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 305:709–718
Guo JY, Shi GY, Guo XY, Zhang LW, Xu WY, Wang YM, Su Z, Hua JP (2015) Transcriptome analysis reveals that distinct metabolic pathways operate in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive upland cotton varieties subjected to salinity stress. Plant Sci 238:33–45
Hanna J, Meides A, Zhang DP, Finley D (2007) A ubiquitin stress response induces altered proteasome composition. Cell 129:747–759
Hsiao TC (1973) Plant responses to water stress. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 24:519–570
Huang LY, Zhang F, Zhang F, Wang WS, Zhou YL, Fu BY, Li ZK (2014) Comparative transcriptome sequencing of tolerant rice introgression line and its parents in response to drought stress. BMC Genom 15:1026
JahngenHodge J, Obin MS, Gong X, Shang F, Nowell TR, Gong JX, Abasi H, Blumberg J, Taylor A (1997) Regulation of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes by glutathione following oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 272:28218–28226
Jiang Y, Yang B, Harris NS, Deyholos MK (2007) Comparative proteomic analysis of NaCl stress-responsive proteins in Arabidopsis roots. J Exp Bot 58:3591–3607
Jiang YQ, Deyholos MK (2006) Comprehensive transcriptional profiling of NaCl-stressed Arabidopsis roots reveals novel classes of responsive genes. BMC Plant Biol 6:25
Jin HC, Sun Y, Yang QC, Chao YH, Kang JM, Jin H, Li Y, Margaret G (2010) Screening of genes induced by salt stress from Alfalfa. Mol Biol Rep 37:745–753
Jorrin JV, Maldonado AM, Castillejo MA (2007) Plant proteome analysis: a 2006 update. Proteomics 7:2947–2962
Jung T, Grune T (2008) The proteasome and its role in the degradation of oxidized proteins. IUBMB Life 60:743–752
Kerepesi I, Galiba G (2000) Osmotic and salt stress-induced alteration in soluble carbohydrate content in wheat seedlings. Crop Sci 40:482–487
Kinraide TB (1998) Three mechanisms for the calcium alleviation of mineral toxicities. Plant Physiol 118:513–520
Komatsu S, Tanaka N (2005) Rice proteome analysis: a step toward functional analysis of the rice genome. Proteomics 5:938–949
Kurepa J, Smalle JA (2008) To misfold or to lose structure?: detection and degradation of oxidized proteins by the 20 S proteasome. Plant Signal Behav 3:386–388
Kurepa J, Wang S, Li Y, Smalle J (2009) Proteasome regulation, plant growth and stress tolerance. Plant Signal Behav 4:924–927
Lee DG, Ahsan N, Lee SH, Lee JJ, Bahk JD, Kang KY, Lee BH (2009) Chilling stress-induced proteomic changes in rice roots. J Plant Physiol 166:1–11
Li XH, Wei YL, Moore KJ, Michaud R, Viands DR, Hansen JL, Acharya A, Brummer EC (2011) Association mapping of biomass yield and stem composition in a tetraploid alfalfa breeding population. Plant Genome-Us 4:24–35
Luttge U, Fischer-Schliebs E, Ratajczak R (2001) The H+-pumping V-ATPase of higher plants: A versatile “eco-enzyme” in response to environmental stress. Cell Mol Biol Lett 6:356–361
Maas E (1986) Salt tolerance of plants. Appl Agric Res 1:12–25
Manaa A, Ben Ahmed H, Valot B, Bouchet JP, Aschi-Smiti S, Causse M, Faurobert M (2011) Salt and genotype impact on plant physiology and root proteome variations in tomato. J Exp Bot 62:2797–2813
Morgan JM (1984) Osmoregulation and water stress in higher plants. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 35:299–319
Munns R, Husain S, Rivelli AR, James RA, Condon AG, Lindsay MP, Lagudah ES, Schachtman DP, Hare RA (2002) Avenues for increasing salt tolerance of crops, and the role of physiologically based selection traits. Plant Soil 247:93–105
Munns R, Termaat A (1986) Whole-plant responses to salinity. Funct Plant Biol 13:143–160
Ndimba BK, Chivasa S, Simon WJ, Slabas AR (2005) Identification of Arabidopsis salt and osmotic stress responsive proteins using two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Proteomics 5:4185–4196
Parker R, Flowers TJ, Moore AL, Harpham NVJ (2006) An accurate and reproducible method for proteome profiling of the effects of salt stress in the rice leaf lamina. J Exp Bot 57:1109–1118
Peel MD, Waldron BL, Jensen KB, Chatterton NJ, Horton H, Dudley LM (2004) Screening for salinity tolerance in alfalfa: a repeatable method. Crop Sci 44:2049–2053
Poppek D, Grune T (2006) Proteasomal defense of oxidative protein modifications. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:173–184
Rawlings ND, Tolle DP, Barrett AJ (2004) Evolutionary families of peptidase inhibitors. Biochem J 378:705–716
Requejo R, Tena M (2006) Maize response to acute arsenic toxicity as revealed by proteome analysis of plant shoots. Proteomics 6:S156–S162
Riccardi F, Gazeau P, de Vienne D, Zivy M (1998) Protein changes in response to progressive water deficit in maize—quantitative variation and polypeptide identification. Plant Physiol 117:1253–1263
Rizhsky L, Liang HJ, Shuman J, Shulaev V, Davletova S, Mittler R (2004) When defense pathways collide. The response of Arabidopsis to a combination of drought and heat stress. Plant Physiol 134:1683–1696
Ruegsegger A, Brunold C (1992) Effect of Cadmium on gamma-Glutamylcysteine Synthesis in Maize Seedlings. Plant Physiol 99:428–433
Singh BN, Mishra RN, Agarwal PK, Goswami M, Nair S, Sopory SK, Reddy MK (2004) A pea chloroplast translation elongation factor that is regulated by abiotic factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 320:523–530
Spiro RG (1966) [1] Analysis of sugars found in glycoproteins. Methods Enzymol 8:3–26
VanCamp W, Capiau K, VanMontagu M, Inze D, Slooten L (1996) Enhancement of oxidative stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco plants overproducing Fe-superoxide dismutase in chloroplasts. Plant Physiol 112:1703–1714
Verdonk JC, Hatfield RD, Sullivan ML (2012) Proteomic analysis of cell walls of two developmental stages of alfalfa stems. Front Plant Sci 3:279
Voges D, Zwickl P, Baumeister W (1999) The 26 S proteasome: a molecular machine designed for controlled proteolysis. Annu Rev Biochem 68:1015–1068
Wang T, Hou YL, Ding X, Song B, Wang F, Hou WR (2013) Overexpression, purification, molecular characterization and pharmacological evaluation for anticancer activity of ribosomal protein S23 from the giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). Mol Med Rep 7:1875–1882
Wang WY, Hall AE, O’Malley R, Bleecker AB (2003) Canonical histidine kinase activity of the transmitter domain of the ETR1 ethylene receptor from Arabidopsis is not required for signal transmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:352–357
Xiong JB, Yang QC, Kang JM, Sun Y, Zhang TJ, Margaret G, Ding W (2011) Simultaneous isolation of DNA, RNA, and protein from Medicago truncatula L. Electrophoresis 32:321–330
Yacoubi R, Job C, Belghazi M, Chaibi W, Job D (2011) Toward characterizing seed vigor in alfalfa through proteomic analysis of germination and priming. J Proteome Res 10:3891–3903
Yacoubi R, Job C, Belghazi M, Chaibi W, Job D (2013) Proteomic analysis of the enhancement of seed vigour in osmoprimed alfalfa seeds germinated under salinity stress. Seed Sci Res 23:99–110
Yamaguchi T, Blumwald E (2005) Developing salt-tolerant crop plants: challenges and opportunities. Trends Plant Sci 10:615–620
Yan SP, Zhang QY, Tang ZC, Su WA, Sun WN (2006) Comparative proteomic analysis provides new insights into chilling stress responses in rice. Mol Cell Proteomics 5:484–496
Yang G, Komatsu S (2004) Microarray and proteomic analysis of brassinosteroid-and gibberellin-regulated gene and protein expression in rice. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 2:77–83
Yang QC, Wu MS, Wang PQ, Kang JM, Zhou XL (2005) Cloning and expression analysis of a vacuolar Na+/H + antiporter gene from Alfalfa. DNA Seq 16:352–357
Zhang KP, Fang ZJ, Liang Y, Tian JC (2009) Genetic dissection of chlorophyll content at different growth stages in common wheat. J Genet 88:183–189
Zhou GA, Chang RZ, Qiu LJ (2010) Overexpression of soybean ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene GmUBC2 confers enhanced drought and salt tolerance through modulating abiotic stress-responsive gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 72:357–367
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273
Zhu JK (2003) Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:441–445
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31472139), National Science and Technology Supporting Project of China (2011BAD17B01-01-3) and Basic Scientific Research Fund of IAS-CAAS (2014ywf-zd-2). We thank Dr. Hui Shen (Department of Biological Sciences, University of North Texas, USA) for critical comments on the manuscript. The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qiaoli Ma and Junmei Kang have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Q., Kang, J., Long, R. et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of alfalfa revealed new salt and drought stress-related factors involved in seed germination. Mol Biol Rep 44, 261–272 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-017-4104-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-017-4104-5