Abstract
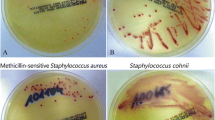
For the past decade, a number of chromogenic media for methicillin-resistance Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) detection have been developed and applied, including Oxoid Brilliance™ MRSA, CHROMagar™ MRSA, BBL™ CHROMagar™ MRSA, MRSASelect and chromID MRSA. The advantages of these chromogenic media offers direct detection of visible staphylococcal colonies, coupled with the use of chromogenic enzymatic substrates that can be hydrolyzed by S. aureus to confirm species or strain identification. BBL™ CHROMagar™ MRSA and MRSASelect are designed for detection of nasal colonization by MRSA, while CHROMagar™ MRSA, Oxoid Brilliance™ MRSA and chromID MRSA are readily applied in bacterial screening. This review summarizes the characteristics, principles and capacities of these selective media, and focuses on comparison of different chromogenic media.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duerden BI (2012) MRSA: why have we got it and can we do anything about it. Eye (Lond) 26:218–221
Samra Z, Ofir O, Bahar J (2004) Optimal detection of Saphylococcus aureus from clinical specimens using a new chromogenic medium. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 49:243–247
Alonzo F III, Torres VJ (2013) A lesson in surival: S. aureus versus the skin. Cell Host Microbe 13:3–5
Liu GY (2009) Molecular pathogensis of Staphylococcus aureus infection. Prediatr Res 65:71R–77R
Collins J, Rudkin J, Recker M, Pozzi C, O’Gara JP et al (2010) Offsetting virulence and antibiotic resistance costs by MRSA. ISME J 4:557–584
Prosper M, Veras N, Azarian T, Rathore M, Nolan D et al (2013) Molecular epidemiology of community-assicuated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the genomic era: a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep 3:1–8
Pateerson GK, Harrison EW, Holmes MA (2014) The emergence of mecC methicillin-resistant Stapylococcus aureus. Trends Microbiol 22:42–47
van Hal SJ, Jemsem SO, Vaska VL, Espedido BA, Paterson DL (2012) Predictors of mortality in Staphylcoccus aureus bacteremia. Clin Microbiol Rev 25:362–386
Otto M (2014) Staphylococcus aureus toxins. Curr Opin Microbiol 17:32–37
Feng Y, Chen CJ, Su LH, Hu S, Yu J et al (2008) Evolution and pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus: lessons larned from genotyping and comparative genomics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:23–37
Lyon BR, Skurray R (1987) Antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus: genetic basis. Microbiol Rev 51:88–134
Chambers HF (1988) Methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Clin Microbiol Rev 1:173–186
Roemer T, Schneider T, Pinho MG (2013) Auxiliary factors: a chink in the armor of MRSA resistance to β-lactam antibiotics. Curr Opin Microbiol 16:538–548
Zapun A, Contereas-Martel C, Vernet T (2008) Penicillin-bingding proteins and β-lactam resistance. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:361–385
David MZ, Daum RS (2010) Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: epidemiology and clinical consequences of an emerging epidemic. Clin Microbiol Rev 23:616–687
Fitzgerald JR (2012) Livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus: origin evolution and public health threat. Trends Microbiol 20:192–198
Huang H, Flynn NM, King JH, Monchaud C et al (2006) Comparisons of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and hospital-associated MRSA infections in Sacramento, California. J Clin Microbiol 44:2423–2427
Riedel S, Dam L, Stamper PD, Shah SA, Carroll KC (2010) Evaluation of bio-rad MRSASelect agar for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus directly from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol 48:2285–2288
Lindsay JA, Holden MTG (2004) Staphylococcus aureus: superbug, super genome? Trends Microbiol 12:378–385
Chopra S, Harjai K, Chhibber S (2015) Antibiotic susceptibility of ica-positive and ica-negative MRSA in different phases of biofilm growth. J Antibiotics 68:15–22
Merlino J, Watson J, Funnell G, Gottlieb T, Bradbury R, Harbour C (2002) New screening medium for detection and identification of methicillin/oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus for nosocomial surveillance. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 21:414–416
Verkade E, Elberts S, Verhulst C, Kluytmans J (2009) Performance of oxoid brilliance MRSA medium for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an in vitro study. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 28:1443–1446
Han Z, Lautenbach E, Fishman N, Nachamkin I (2007) Evaluation of mannitol salt agar, CHROMagar staph aureus and CHROMagar MRSA for detection of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from nasal swab specimens. J Med Microbiol 56:43–46
Veenemans J, Verhulst C, Punselie R, van Keulen PH, Kluytmans JA (2013) Evaluation of brilliance MRSA 2 agar for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in clinical samples. J Clin Microbiol 51:1026–1027
Diederen B, van Duijn I, van Belkum A, Willemse P, van Keulen P et al (2005) Performance of CHROMagar MRSA medium for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 43:1925–1927
Nahimana I, Francioli P, Blanc DS (2006) Evaluation of three chromogenic media (MRSA-ID, MRSA-Select and CHROMagar MRSA) and ORSAB for surveillance cultures of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Microbiol Infect 12:1168–1174
Compernolle V, Verschraegen G, Claeys G (2007) Combined use of pastorex staph-plus and either of two new chromogenic agars, MRSA ID and CHROMagar MRSA, for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 45:154–158
Flayhart D, Hindler JF, Bruckner DA, Hall G, Shrestha RK et al (2005) Multicenter evaluation of BBL CHROMagar MRSA medium for direct detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from surveillance cultures of the anterior nares. J Clin Microbiol 43:5536–5540
Van VK, Cartuyvels R, Coppens G, Frans J, Van AM (2010) Performance of a new chromogenic medium, BBL CHROMagar MRSA II (BD), for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in screening samples. J Clin Microbiol 48:1450–1451
Pape J, Wadlin J, Nachamkin I (2006) Use of BBL CHROMagar MRSA medium for identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus directly from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol 44:2575–2576
Wendt C, Havill NL, Chapin KC, Boyce JM, Dickenson R et al (2010) Evaluation of a new selective medium, BD BBL CHROMagar MRSA II, for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in different specimens. J Clin Microbiol 48:2223–2227
Louie L, Soares D, Meaney H, Vearncombe M, Simor AE (2006) Evaluation of a new chromogenic medium, MRSASelect, for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 44:4561–4563
Nsira SB, Dupuis M, Leclercq R (2006) Evaluation of MRSASelect, a new chromogenic medium for the detection of nasal carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Antimicrob Agents 27:561–564
van Loo IHM, van DS, Verbakel-Schelle IA, Buiting AG (2007) Evaluation of a chromogenic agar (MRSASelect) for the detection of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with clinical samples in The Netherlands. J Clin Microbiol 56(4):491–494
Diederen BM, van Leest ML, van Duijn I, Willemse P, van Keulen PH et al (2006) Performance of MRSA ID, a new chromogenic medium for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 44:586–588
Perry JD, Davies A, Butterworth LA, Hopley AL, Nicholson A et al (2004) Development and evaluation of a chromogenic agar medium for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 42:4519–4523
Micheel V, Hogan B, Koller T, Warnke P, Crusius S et al (2015) Screening agars for MRSA: evaluation of a stepwise diagnostic approach with two different selective agars for the screening for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Mil Med Res 2:1–8
Denys GA, Renzi PB, Koch KM, Wissel CM (2013) Three-way comparison of BBL CHROMagar MRSA II, MRSASelect, and spectra MRSA for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in nasal surveillance cultures. J Clin Microbiol 51:202–205
Stoakes L, Reyes R, Daniel J, Lennox G, John MR (2006) Prospective comparison of a new chromogenic medium, MRSASelect, to CHROMagar MRSA and mannitol-salt medium supplemented with oxacillin or cefoxitin for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 44:637–639
Malhotra-Kumar S, Abrahantes JC, Sabiiti W, Lammens C, Vercauteren G et al (2010) Evaluation of chromogenic media for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 48:1040–1046
Yamada K, Ohkura T, Okamoto A, Ohta M, Inuzuka K et al (2010) Evaluation of selection media for the detection of borderline MRSA. J Infect Chemother 16:19–24
Nonhoff C, Denis O, Brenner A, Buidin P, Legros N et al (2009) Comparison of three chromogenic media and enrichment broth media for the detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from mucocutaneous screening specimens: comparison of MRSA chromogenic media. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 28:363–369
Lagace-Wiens P, Alfa M, Manickam K, Harding GK (2008) Reductions in workload and reporting time by use of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus screening with MRSASelect medium compared to mannitol-salt medium supplemented with oxacillin. J Clin Microbiol 46:1174–1177
Faron ML, Buchan BW, Vismara C, Lacchini C, Bielli A et al (2016) Automated scoring of chromogenic media for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by use of WASPLab image analysis software. J Clin Microbiol 54:620–624
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National 973-Plan of China (2012CB720800), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31201362 & 31101278), International Science & Technology Cooperation Program (2013B051000014), National Outstanding Doctoral Dissertation Funding (201459), Guangdong Outstanding Doctoral Dissertation Funding (K3140030), Open Project Program of State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology, Jiangnan University (SKLF-KF-201513) and Open Project Program of Key Laboratory for Green Chemical Process of Ministry of Education in Wuhan Institute of Technology (GCP201506).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Hou, Y., Peters, B.M. et al. Chromogenic media for MRSA diagnostics. Mol Biol Rep 43, 1205–1212 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4062-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4062-3