Abstract
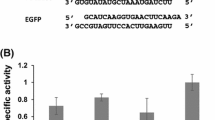
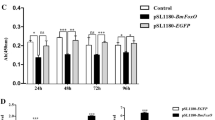
β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (GlcNAcase) is a key enzyme in the chitin decomposition process. In this study, we investigated the gene expression profile of GlcNAcases and the regulation mechanism for one of these genes, BmGlcNAcase1, in the silkworm. We performed sequence analysis of GlcNAcase. Using dual-spike-in qPCR method, we examined the expression of Bombyx β-N-acetylglucosaminidases (BmGlcNAcases) in various tissues of silkworm as well as expression changes after stimulation with ecdysone. Using Bac-to-Bac system and luciferase reporter vectors, we further analyzed the promoter sequence of BmGlcNAcase1. The results showed that these proteins have a highly conserved catalytic domain. The expression levels of the BmGlcNAcase genes varied in different tissues, and were increased 48 h after exposure to ecdysone. BmGlcNAcase1 gene promoter with 5′-end serial deletions showed different levels of activity in various tissues, higher in the blood, skin and fat body. Deletion of the region from −347 to −223 upstream of BmGlcNAcase-1 gene abolished its promoter activity. This region contains the binding sites for key transcription factors including Hb, BR–C Z, the HSF and the typical TATA-box element. These results indicate that BmGlcNAcases are expressed at different levels in different tissues of the silkworm, but all are subjected to the regulation by ecdysone. BmGlcNAcase1 promoter analysis has paved a foundation for further study of the gene expression patterns.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen E (2010) Chitin biochemistry: synthesis, hydrolysis and inhibition, chap. 2. In: Jérôme C, Stephen JS (eds) Advances in Insect Physiology. Academic Press, London, pp 5–74
Wagner G, Lo J, Laine R, Almeder M (1993) Chitin in the epidermal cuticle of a vertebrate (Paralipophrys trigloides, blenniidae, teleostei). Cell Mol Life Sci 49(4):317–319
Fernandez CW, Koide RT (2012) The role of chitin in the decomposition of ectomycorrhizal fungal litter. Ecology 93(1):24–28
Van Leeuwen T, Demaeght P, Osborne EJ et al (2012) Population bulk segregant mapping uncovers resistance mutations and the mode of action of a chitin synthesis inhibitor in arthropods. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(12):4407–4412
Kramer KJ, Hopkins TL, Schaefer J (1995) Applications of solids NMR to the analysis of insect sclerotized structures. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 25(10):1067–1080
Kramer KJ, Hopkins TL, Schaefer J (1988) Insect cuticle structure and metabolism. Biotechnology for Crop Protection. American Chemical Society, Washington DC, pp 160–185
Fukamizo T, Kramer KJ (1985) Mechanism of chitin hydrolysis by the binary chitinase system in insect moulting fluid. Insect Biochem 15(2):141–145
Filho BPD, Lemos FJA, Secundino NFC, Páscoa V, Pereira ST, Pimenta PFP (2002) Presence of chitinase and β-N-acetylglucosaminidase in the Aedes aegypti: a chitinolytic system involving peritrophic matrix formation and degradation. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 32(12):1723–1729
Fukamizo T, Kramer KJ (1985) Mechanism of chitin oligosaccharide hydrolysis by the binary enzyme chitinase system in insect moulting fluid. Insect Biochem 15(1):1–7
Kramer KJ, Koga D (1986) Insect chitin: physical state, synthesis, degradation and metabolic regulation. Insect Biochem 16(6):851–877
Zen KC, Choi HK, Krishnamachary N, Muthukrishnan S, Kramer KJ (1996) Cloning, expression, and hormonal regulation of an insect beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase gene. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 26(5):435–444
Xia QY, Zhou ZY, Lu C et al (2004) A draft sequence for the genome of the domesticated silkworm (Bombyx mori). Science 306(5703):1937–1940
Consortium TISG (2008) The genome of a lepidopteran model insect, the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol 38(12):1036–1045
Xia Q, Guo Y, Zhang Z et al (2009) Complete resequencing of 40 genomes reveals domestication events and genes in silkworm (Bombyx). Science 326(5951):433–436
Nagamatsu Y, Yanagisawa I, Kimoto M, Okamoto E, Koga D (1995) Purification of a chitooligosaccharidolytic beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Bombyx mori larvae during metamorphosis and the nucleotide sequence of its cDNA. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59(2):219–225
Okada T, Ishiyama S, Sezutsu H et al (2007) Molecular cloning and expression of two novel β-N-acetylglucosaminidases from silkworm Bombyx mori. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71(7):1626–1635
Kokuho T, Yasukochi Y, Watanabe S, Inumaru S (2010) Molecular cloning and expression profile analysis of a novel β-d-N-acetylhexosaminidase of domestic silkworm (Bombyx mori). Genes Cells 15(5):525–536
Nomura T, Ikeda M, Ishiyama S et al (2010) Cloning and characterization of a β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (BmFDL) from silkworm Bombyx mori. J Biosci Bioeng 110(4):386–391
Zhang Y, Wei Z, Li Y–Y, Chen Y, Shen W, Lu C (2009) Transcription level of messenger RNA per gene copy determined with dual-spike-in strategy. Anal Biochem 394(2):202–208
Peng R, Zhai Y, Ding H et al (2012) Analysis of reference gene expression for real-time PCR based on relative quantitation and dual spike-in strategy in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 44(7):614–622
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22(22):4673–4680
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Zhang Y, Wei Z, Li YY, Chen Y, Shen W, Lu C (2009) Transcription level of messenger RNA per gene copy determined with dual-spike-in strategy. Anal Biochem 394(2):202–208
Léonard R, Rendić D, Rabouille C, Wilson IBH, Préat T, Altmann F (2006) The Drosophila fused lobes gene encodes an N-acetylglucosaminidase involved in N-glycan processing. J Biol Chem 281(8):4867–4875
Hogenkamp DG, Arakane Y, Kramer KJ, Muthukrishnan S, Beeman RW (2008) Characterization and expression of the β-N-acetylhexosaminidase gene family of Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38(4):478–489
Koga D, Funakoshi T, Fujimoto H, Kuwano E, Eto M, Ide A (1991) Effects of 20-hydroxyecdysone and KK-42 on chitinase and β-N-acetylglucosaminidase during the larval-pupal transformation of Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem 21(3):277–284
Perotti ME, Cattaneo F, Pasini ME, Vernì F, Hackstein JHP (2001) Male sterile mutant casanova gives clues to mechanisms of sperm–egg interactions in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Reprod Dev 60(2):248–259
Cattaneo F, Ogiso M, Hoshi M, Perotti ME, Pasini ME (2002) Purification and characterization of the plasma membrane glycosidases of Drosophila melanogaster spermatozoa. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 32(8):929–941
Cattaneo F, Pasini M, Intra J et al (2006) Identification and expression analysis of Drosophila melanogaster genes encoding β-hexosaminidases of the sperm plasma membrane. Glycobiology 16(9):786–800
Lehmann R, Nüsslein-Volhard C (1987) Hunchback, a gene required for segmentation of an anterior and posterior region of the Drosophila embryo. Dev Biol 119(2):402
Fernandes M, Xiao H, Lis JT (1994) Fine structure analyses of the Drosophila and Saccharomyces heat shock factor-heat shock element interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 22(2):167–173
Morton EA, Lamitina T (2012) Caenorhabditis elegans HSF‐1 is an essential nuclear protein that forms stress granule-like structures following heat shock. Aging Cell 12(1):112–120
Dottorini T, Persampieri T, Palladino P, Spaccapelo R, Crisanti A (2012) Silencing of the Hsf gene, the transcriptional regulator of A. gambiae male accessory glands, inhibits the formation of the mating plug in mated females and disrupts their monogamous behaviour. Pathogens Glob Health 106(7):405–412
Emery IF, Bedian V, Guild GM (1994) Differential expression of Broad-Complex transcription factors may forecast tissue-specific developmental fates during Drosophila metamorphosis. Development 120(11):3275–3287
Talbot WS, Swyryd EA, Hogness DS (1993) Drosophila tissues with different metamorphic responses to ecdysone express different ecdysone receptor isoforms. Cell 73(7):1323–1337
Tzolovsky G, Deng WM, Schlitt T, Bownes M (1999) The function of the broad-complex during Drosophila melanogaster oogenesis. Genetics 153(3):1371–1383
Roeder R (1998) Role of general and gene-specific cofactors in the regulation of eukaryotic transcription. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, pp 201–218
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the foundation of post scientist in National Sericultural System (CARS-22-ZJ0305).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yuan-fen Zhai and Ming-xia Huang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, Yf., Huang, Mx., Wu, Y. et al. The expression profile and promoter analysis of β-N-acetylglucosaminidases in the silkworm Bombyx mori . Mol Biol Rep 41, 6667–6678 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3550-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3550-6