Abstract
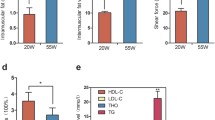
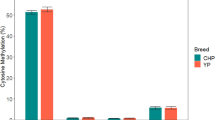
In eukaryotes, DNA methylation is an important epigenetic modification involved in gene expression regulation. Meat quality traits are complicated traits that are controlled by many genes. Changes in the methylation levels of certain genes controlling meat quality traits will inevitably affect their expression levels, thereby affecting meat quality. The objectives of this study were to investigate the differences in the DNA methylation level in pectoral muscle tissues using fluorescent-labeled methylation sensitive amplified polymorphism and their relationships with meat quality traits in three-yellow chickens. The results showed that the differences in the DNA methylation level had a highly significant effect on muscle fiber density and drip loss (P < 0.01). However, no significant correlations were found between the DNA methylation levels and the other investigated traits (P > 0.05).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auclair G, Weber M (2012) Mechanisms of DNA methylation and demethylation in mammals. Biochimie 94:2202–2211
Yin H, Blanchard KL (2000) DNA methylation represses the expression of the human erythropoietin gene by two different mechanisms. Blood 95:111–119
Bell JT, Pai AA, Pickrell JK, Gaffney DJ, Pique-Regi R, Degner JF, Gilad Y, Pritchard JK (2011) DNA methylation patterns associate with genetic and gene expression variation in HapMap cell lines. Genome Biol 12:R10
Nica AC, Parts L, Glass D, Nisbet J, Barrett A, Sekowska M, Travers M, Potter S, Grundberg E, Small KNica AC (2011) The architecture of gene regulatory variation across multiple human tissues: the MuTHER study. PLoS Genet 7:e1002003
Xu Q, Zhang Y, Sun D, Wang Y, Yu Y (2007) Analysis on DNA methylation of various tissues in chicken. Anim Biotechnol 18:231–241
Grunau C, Hindermann W, Rosenthal A (2000) Large-scale methylation analysis of human genomic DNA reveals tissue-specific differences between the methylation profiles of genes and pseudogenes. Hum Mol Genet 9:2651–2663
Yeivin A, Razin A (1993) Gene methylation patterns and expression. EXS 64:523–568
Jiang C, Deng C, Xiong Y (2005) Relationship between individual DNA methylation percentage difference and carcass traits in pig. J Agri Biotechnol China 13:179–185
Rehfeldt C, Kuhn G (2006) Consequences of birth weight for postnatal growth performance and carcass quality in pigs as related tomyogenesis. J Anim Sci 84:113–123
Yang Chun, Zhang Mingjun, Niu Weiping, Yang Runjun, Zhang Yonghong, Qiu Zhengyan, Sun Boxing, Zhao Zhihui (2011) Analysis of DNA methylation in various swine tissues. PLoS ONE 6:e16229
Frommer M, McDonald LE, Millar DS, Collis CM, Watt F, Grigg GW, Molloy PL, Paul CL (1992) A genomic sequencing protocol that yields a positive display of 5-methylcytosine residues in individual DNA strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:1827–1831
Cottrell SE (2004) Molecular diagnostic applications of DNA methylation technology. Clin Biochem 37:595–604
Shan XH, Li YD, Liu XM, Wu Y, Zhang MZ, Guo WL, Liu B, Yuan YP (2012) Comparative analyses of genetic/epigenetic diversities and structures in a wild barley species (Hordeum brevisubulatum) using MSAPSSAP and AFLP. Genet Mol Res 11:2749–2759
Mastan SG, Rathore MS, Bhatt VD, Yadav P, Chikara J (2012) Assessment of changes in DNA methylation by methylation-sensitive amplification polymorphism in Jatropha curcas L. subjected to salinity stress. Gene 508:125–129
Shiraishi M, Sekiguchi A, Oates AJ, Terry MJ, Miyamoto Y, Sekiya T (2004) Methyl-CpG binding domain column chromatography as a tool for the analysis of genomic DNA methylation. Anal Biochem 329:1–10
Suzuki MM, Bird A (2008) DNA methylation landscapes: provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat Rev Genet 9:465–476
Wilson IM, Davies JJ, Weber M, Brown CJ, Alvarez CE, MacAulay C, Schübeler D, Lam WL (2006) Epigenomics: mapping the methylome. Cell Cycle 5:155–158
Auclair Ghislain, Weber Michael (2012) Mechanisms of DNA methylation and demethylation in mammals. Biochimie 94:2202–2211
Cedar H (1988) DNA methylation and gene activity. Cell 53:3–4
Gama-Sosa MA, Midgett RM, Slagel VA, Githens S, Kuo KC, Gehrke CW, Ehrich M (1983) Tissue-specific differences in DNA methylation in various mammals. Biochim Biophys Acta 740:212–219
Mohandas T, Sparkes RS, Shapiro LJ (1981) Reactivation of an inactive human X chromosome:evidence for X inactivation by DNA methylation. Science 211:393–396
Li E, Beard C, Jaenisch R (1993) Role for DNA methylation in genomic imprinting. Nature 366:362–365
Zhang D, Li S, Tan Q, Pang Z (2012) Twin-based DNA methylation analysis takes the center stage of studies of human complex diseases. J Genet Genomics 39:581–586
Spisák S, Kalmár A, Galamb O, Wichmann B, Sipos F, Péterfia B, Csabai I, Kovalszky I, Semsey S, Tulassay Z, Molnár B (2012) Genome-wide screening of genes regulated by DNA methylation in colon cancer development. PLoS ONE 7:e46215
Buchheit T, Van de Ven T, Shaw A (2012) Epigenetics and the transition from acute to chronic pain. Pain Med 13:1474–1490
Razin A (1998) CpG methylation, chromatin structure and gene silencing—a three-way connection. EMBO J 17:4905–4908
Gokul G, Khosla S (2012) DNA methylation and cancer. Subcell Biochem. 61:597–625
Gopalakrishnan S, van Emburgh BO, Robertson KD (2011) DNA methylation in development and human disease. Mutat Res 647:30–38
Esteller M (2005) Aberrant DNA methylation as a cancer-inducing mechanism. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 45:629–656
Okano M, Bell DW, Haber DA, Li E (1999) DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development. Cell 99:247–257
Rlehardson BC (2002) Role of DNA methylation in the regulation of cell function: autoimmunity, agingandeaneer. J Nutr 132:2401S–2405S
Rönn T, Poulsen P, Hansson O, Holmkvist J, Almgren P, Nilsson P, Tuomi T, Isomaa B, Groop L, Vaag A, Ling C (2008) Age influenees DNA methylation and gene expression of COX7A1 in homan skeletal muscle. Diabetologia 51:1159–1168
Bollati V, Schwartz J, Wright R, Litonjua A, Tarantini L, Suh H, Sparrow D, Vokonas P, Baccarelli A (2009) Decline in genomic DNA methylation through aging in a cohort of elderly subjects. Mech Ageing Dev 130:234–239
Jang HJ, Lee MO, Kim S, Kim TH, Kim SK, Song G, Womack JE, Han JY (2013) Biallelic expression of the l-arginine:glycine amidinotransferase gene with different methylation status between male and female primordial germ cells in chickens. Poult Sci 92:760–769
Penaloza CG, Estevez B, Han DM, Norouzi M, Lockshin RA, Zakeri Z (2014) Sex-dependent regulation of cytochrome P450 family members Cyp1a1, Cyp2e1, and Cyp7b1 by methylation of DNA. FASEB J 28:966–977
Haggarty P (2012) Nutrition and the epigenome. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 108:427–446
Bottinelli R, Reggiani C (2000) Human skeletal muscle fibres: molecular and functional diversity. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 73:195–262
Seideman SC, Crouse JD (1986) The effects of sex condition, genotype and diet on bovine muscle characteristics. Meat Sci 17:55–72
Renand G, Picard B, Touraille C, Berge P, Lepetit J (2001) Relationships between muscle characteristics and meat quality traits of young Charolais bulls. Meat Sci 59:49–60
Lengerken G, Wicke M, Maak S (1997) Stress susceptibility and meat quality-situation and prospects in animal breeding and research. Arch Tierz 40:163–171
Lahbib-Mansais Y, Yerle M, Pinton P, Gellin J (1996) Chromosomal localization of homeobox genes and associated markers on porcine chromosomes 3,5,12,15,16 and 18: comparative mapping study with human and mouse. Mamm Genome 7:174–179
Goureau A, Garrigues A, Tosser-Klopp G, Lahbib-Mansais Y, Chardon P, Yerle M (2001) Conserved synteny and gene order difference between human chromosome 12 and pig chromosome 5. Cytogenet Cell Genet 94:49–54
Bertani GR, Johnson RK, Robic A, Pomp D (2003) Mapping of porcine ESTs obtained from the anterior pituitary. Anim Genet 34:132–134
Fontanesi L, Davoli R, Nanni Costa L, Scotti E, Russo V (2003) Study of candidate genes for glycolytic potential of porcine skeletal muscle: identification and analysis of mutations, linkage and physical mapping and association with meat quality traits in pigs. Cytogenet Genome Res 102:145–151
Cepica S, Yerle M, Stratil A, Schroffel J, Redl B (1999) Regional localization of porcine MYOD1, MYF5, LEP, UCP3 and LCN1 genes. Anim Genet 30:476–478
Vykoukalova Z, Knoll A, Dvorak J, Rohrer GA, Cepica S (2003) Linkage and radiation hybrid mapping of the porcine MYF6 gene to chromosome 5. Anim Genet 34:238–240
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (30972085) and Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (PCSIRT, No. IRT1248). We also appreciate and gratefully acknowledge the Jilin Academy of Agricultural Sciences for providing three-yellow chickens.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Guo, J., Gao, Y. et al. Genome-wide methylation changes are associated with muscle fiber density and drip loss in male three-yellow chickens. Mol Biol Rep 41, 3509–3516 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3214-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3214-6