Abstract
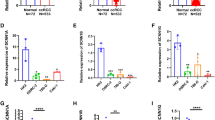
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common tumor arising from the cells in the lining of tubules in the kidney. Some members of the Ca2+-permeable transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) family of channel proteins have demonstrated a role in the proliferation of some types of cancer cells. In this study, we investigated the role of TRPC6 in the development of human RCC. RT-PCR and Western blotting were used to investigate TRPC6 expression in 1932 and ACHN cells. Immunohistochemical techniques were applied to study TRPC6 expression in 60 cases of RCC primary tissue samples and 10 cases of corresponding normal renal tissues. To inhibit TRPC6 activity or expression, RNA interference was used. The effects of TRPC6 channels on RCC cell viability and cell cycle progression were investigated by MTT and flow cytometry. TRPC6 was expressed in 1932 and ACHN cells. TRPC6 protein was detected in 73.3 % of RCC samples, and there was a significant difference compared with the normal renal samples (30 %) (p < 0.05). Moreover the level of TRPC6 expression was associated with RCC Fuhrman grade (p < 0.01). Blockade of TRPC6 channels in ACHN cells suppressed basal cell proliferation and partially inhibited HGF-induced cell proliferation. Furthermore, inhibition of TRPC6 channels expression prolonged the transition through G2/M phase in ACHN cells. In summary, expression of TRPC6 is markedly increased in RCC specimens and associated with RCC histological grade. TRPC6 plays an important role in ACHN cells proliferation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vogelzang NJ, Stadler WM (1998) Kidney cancer. Lancet 352:1691–1696
Chen H, Nicol TL, Udelsman R (1999) Clinically significant, isolated metastatic disease to the thyroid gland. World J Surg 23:177–180
Cohen HT, McGovern FJ (2005) Renal cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 353:2477–2790
Clapham DE (2007) Calcium signaling. Cell 131:1047–1058
Roderick HL, Cook SJ (2008) Ca2+ signaling checkpoints in cancer: remodeling Ca2+ for cancer cell proliferation and survival. Nat Rev Cancer 8:361–375
Yu Y, Sweeney M, Zhang S et al (2003) PDGF stimulates pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by upregulating TRPC6 expression. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 284(2):C316–C330
Thilo F, Liu Y, Loddenkemper C et al (2012) VEGF regulates TRPC6 channels in podocytes. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27(3):921–929
Heeringa SF, Möller CC, Du J et al (2009) A novel TRPC6 mutation that causes childhood FSGS. PLoS ONE 4:e7771
Yue D, Wang Y, Xiao JY et al (2009) Expression of TRPC6 in benign and malignant human prostate tissues. Asian J Androl 11(5):541–547
Thebault S, Flourakis M, Vanoverberghe K et al (2006) Differential role of transient receptor potential channels in Ca2+ entry and proliferation of prostate cancer epithelial cells. Cancer Res 66(4):2038–2047
Aydar E, Yeo S, Djamgoz M et al (2009) Abnormal expression, localization and interaction of canonical transient receptor potential ion channels in human breast cancer cell lines and tissues: a potential target for breast cancer diagnosis and therapy. Cancer Cell Int 9:23
El Boustany C, Bidaux G, Enfissi A et al (2008) Capacitative calcium entry and transient receptor potential canonical 6 expression control human hepatoma cell proliferation. Hepatology 47(6):2068–2077
Boros P, Miller CM (1995) Hepatocyte growth factor: a multifunctional cytokine. Lancet 345(8945):293–295
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E et al (2003) Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4(12):915–925
Williams MJ, Clark P (2003) Microscopic analysis of the cellular events during scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor-induced epithelial tubulogenesis. J Anat 203(5):483–503
Horie S, Aruga S, Kawamata H et al (1999) Biological role of HGF/MET pathway in renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 161(3):990–997
Tanimoto S, Fukumori T, El-Moula G et al (2008) Prognostic significance of serum hepatocyte growth factor in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: comparison with serum vascular endothelial growth factor. J Med Invest 55(1–2):106–111
Wang Y, Yue D, Li K et al (2010) The role of TRPC6 in HGF-induced cell proliferation of human prostate cancer DU145 and PC3 cells. Asian J Androl 12:841–852
Rampino T, Gregorini M, Guidetti C et al (2007) KCNA1 and TRPC6 ion channels and NHE1 exchanger operate the biological outcome of HGF/scatter factor in renal tubular cells. Growth Factors 25:382–391
Fuhrman SA, Lasky LC, Limas C (1982) Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 6(7):655–663
Kahl CR, Means AR (2003) Regulation of cell cycle progression by calcium/calmodulin-dependent pathways. Endocr Rev 24(6):719–736
Ding X, He Z, Zhou K et al (2010) Essential role of TRPC6 channels in G2/M Phase transition and development of human glioma. J Natl Cancer Inst 102(14):1052–1068
Cai R, Ding X, Zhou K et al (2009) Blockade of TRPC6 channels induced G2/M phase arrest and suppressed growth in human gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer 125(10):2281–2287
Shi Y, Ding X, He ZH et al (2009) Critical role of TRPC6 channels in G2 phase transition and the development of human oesophageal cancer. Gut 58:1443–1450
Lobrich M, Jeggo PA (2007) The impact of a negligent G2/M checkpoint on genomic instability and cancer induction. Nat Rev Cancer 7:861–869
Mukohara T, Civiello G, Davis IJ et al (2005) Inhibition of the met receptor in mesothelioma. Clin Cancer Res 11:8122–8130
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants (81202380) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grants (20111202120016) from Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China, Grants (12JCQNJC07800) from Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin and Grants (20110138) from Tianjin Municipal Higher School Science and technology development fund program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jiayin Song and Yong Wang both authors contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Wang, Y., Li, X. et al. Critical role of TRPC6 channels in the development of human renal cell carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep 40, 5115–5122 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2613-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2613-4