Abstract
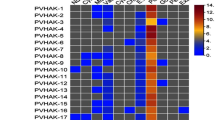
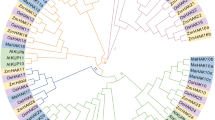
The high-affinity K+ (HAK) transporter gene family constitutes the largest family that functions as potassium transporter in plant and is important for various cellular processes of plant life. In spite of their physiological importance, systematic analyses of ZmHAK genes have not yet been investigated. In this paper, we indicated the isolation and characterization of ZmHAK genes in whole-genome wide by using bioinformatics methods. A total of 27 members (ZmHAK1–ZmHAK27) of this family were identified in maize genome. ZmHAK genes were distributed in all the maize 10 chromosomes. These genes expanded in the maize genome partly due to tandem and segmental duplication events. Multiple alignment and motif display results revealed major maize ZmHAK proteins share all the three conserved domains. Phylogenetic analysis indicated ZmHAK family can be divided into six subfamilies. Putative cis-elements involved in Ca2+ response, abiotic stress adaption, light and circadian rhythms regulation and seed development were observed in the promoters of ZmHAK genes. Expression data mining suggested maize ZmHAK genes have temporal and spatial expression pattern. In all, these results will provide molecular insights into the potassium transporter research in maize.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GA3 :
-
Gibberellin
- HAK:
-
High-affinity K+
- NAA:
-
Naphthaleneacetic acid
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- KCO:
-
K+ channel openers
- KT:
-
Cytokinin
References
Glass ADM (1983) Regulation of ion-transport. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 34:311–326
Schroeder JI, Ward JM, Gassmann W (1994) Perspectives in the physiology and structure of inward rectifying K+ channels in higher-plants: biophysical implications for K+ uptake. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 23:441–471. doi:10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.002301
Maathuis FJ, Sanders D (1999) Plasma membrane transport in context: making sense out of complexity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:236–243. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(99)80041-7
Santa-Maria GE, Rubio F, Dubcovsky J, Rodriguez-Navarro A (1997) The HAK1 gene of barley is a member of a large gene family and encodes a high-affinity potassium transporter. Plant Cell 9:2281–2289. doi:10.1105/tpc.9.12.2281
Gierth M, Mäser P, Schroeder JI (2005) The potassium transporter AtHAK5 functions in K+ deprivation-induced high-affinity K+ uptake and AKT1K+ channel contribution to K+ uptake kinetics in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol 137:1105–1114. doi:10.1104/pp.104.057216
Ashley MK, Grant M, Grabov A (2006) Plant responses to potassium deficiencies: a role for potassium transport proteins. J Exp Bot 57:425–436. doi:10.1093/jxb/erj034
Zimmerman S, Sentenac H (1999) Plant ion channel: from molecular structures to physiological functions. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:477–482. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(99)00020-5
Véry AA, Sentenac H (2003) Molecular mechanisms and regulation of K+ transport in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:575–603. doi:10.1146/annurev.plant.54.031902.134831
Maathuis FJM, Sanders D (1997) Regulation of K+ absorption in plant root cells by external K+: interplay of different K+ transporters. J Exp Bot 48:451–458. doi:10.1093/jxb/48.Special_Issue.451
Maathuis FJM, Sanders D (1994) Mechanism of high-affinity potassium uptake in roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:9272–9276
Mäser P, Thomine S, Schroeder JI, Ward JM, Hirschi K, Sze H, Talke IN, Amtmann A, Maathuis FJ, Sanders D, Harper JF, Tchieu J, Gribskov M, Persans MW, Salt DE, Kim SA, Guerinot ML (2001) Phylogenetic relationships within cation transporter families of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126:1646–1667. doi:10.1104/pp.126.4.1646
Gupta M, Qiu X, Wang L, Xie W, Zhang C, Xiong LZ, Lian XM, Zhang QF (2008) KT/HAK/KUP potassium transporters gene family and their whole-life cycle expression profile in rice (Oryza sativa). Mol Genet Genomics 280:437–452. doi:10.1007/s00438-008-0377-7
Ahn SJ, Shin R, Schachtman DP (2004) Expression of KT/KUP genes in Arabidopsis and the role of root hairs K+ uptake. Plant Physiol 134:1135–1145. doi:10.1104/pp.103.034660
Epstein W, Kim BS (1971) Potassium transport loci in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 108:639–644
Martínez-Cordero M, Martínez V, Rubio F (2004) Cloning and functional characterization of the high-affinity K+ transporter HAK1 of pepper. Plant Mol Biol 56:413–421. doi:10.1007/s11103-004-3845-4
Quintero FJ, Blatt MR (1997) A new family of K+ transporters from Arabidopsis that are conserved across phyla. FEBS Lett 415:206–211. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(97)01125-3
Fu H-H, Luan S (1998) AtKUP1: a dual-affinity K+ transporter from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10:63–74. doi:10.1105/tpc.10.1.63
Kim EJ, Kwak JM, Uozumi N, Schroeder JI (1998) AtKUP1: an Arabidopsis gene encoding high-affinity potassium transport activity. Plant Cell 10:51–62. doi:10.1105/tpc.10.1.51
Wang YH, Garvin DF, Kochian LV (2002) Rapid induction of regulatory and transporter genes in response to phosphorus, potassium, and iron deficiencies in tomato roots: evidence for cross talk and root/rhizosphere-mediated signals. Plant Physiol 130:1361–1370. doi:10.1104/pp.008854
Nieves-Cordones M, Martínez-Cordero MA, Martínez V, Rubio F (2007) An NH4 +-sensitive component dominates high-affinity K+ uptake in tomato plants. Plant Sci 172:273–280. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2006.09.003
Desbrosses G, Kopka C, Ott T, Udvardi MK (2004) Lotus japonicus LjKUP is induced late during nodule development and encodes a potassium transporter of the plasma membrane. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17:789–797. doi:10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.7.789
Davies C, Shin R, Liu W, Thomas MR, Schachtman DP (2006) Transporters expressed during grape berry (Vitis vinifera L.) development are associated with an increase in berry size and berry potassium accumulation. J Exp Bot 57:3209–3216. doi:10.1093/jxb/erl091
Garciadeblas B, Benito B, Rodríguez-Navarro A (2002) Molecular cloning and functional expression in bacteria of the potassium transporters CnHAK1 and CnHAK2 of the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa. Plant Mol Biol 50:623–633. doi:10.1023/A:1019951023362
Baňuelos MA, Garciadeblas B, Cubero B, Rodríguez-Navarro A (2002) Inventory and functional characterization of the HAK potassium transporters of rice. Plant Physiol 130:784–795. doi:10.1104/pp.007781
Qi Z, Hampton CR, Shin R, Barkla BJ, White PJ, Schachtman DP (2008) The high affinity K+ transporter AtHAK5 plays a physiological role in planta at very low K+ concentrations and provides a caesium uptake pathway in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 59:595–607. doi:10.1093/jxb/erm330
Rubio F, Santa-María GE, Rodríguez-Navarro A (2000) Cloning of Arabidopsis and barley cDNA sencoding HAK potassium transporters in root and shoot cells. Physiol Plant 109:34–43. doi:10.1034/j.1399-3054.2000.100106.x
Su H, Golldack D, Zhao CS, Bohnert HJ (2002) The expression of HAK-type K+ transporters is regulated in response to salinity stress in common ice plant. Plant Physiol 129:1482–1493. doi:10.1104/pp.001149
Elumalai RP, Nagpal P, Reed JW (2002) A mutation in the Arabidopsis KT2/KUP2 potassium transporter gene affects shoot cell expansion. Plant Cell 14:119–131. doi:10.1105/tpc.010322
Rigas S, Debrosses G, Haralampidis K, Vicente-Agullo F, Feldmann KA, Grabov A, Dolan L, Hatzopoulos P (2001) TRH1 encodes a potassium transporter required for tip growth in Arabidopsis root hairs. Plant Cell 13:139–151. doi:10.1105/tpc.13.1.139
Vicente-Agullo F, Rigas S, Desbrosses G, Dolan L, Hatzopoulos P, Grabov A (2004) Potassium carrier TRH1 is required for auxin transport in Arabidopsis roots. Plant J 40:523–535. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02230.x
Maathuis FJM (2006) The role of monovalent cation transporters in plant responses to salinity. J Exp Bot 57:1137–1147. doi:10.1093/jxb/erj001
Takahashi R, Nishio T, Ichizen N, Takano T (2007) High-affinity K+ transporter PhaHAK5 is expressed only in salt-sensitive reed plants and shows Na+ permeability under NaCl stress. Plant Cell Rep 26:1673–1679. doi:10.1007/s00299-007-0364-1
Schnable PS, Ware D, Fulton RS et al (2009) The B73 maize genome: complexity, diversity, and dynamics. Science 326(5956):1112–1115. doi:10.1126/science.1178534
Yang ZF, Gao QS, Sun CS, Li WJ, Gu SL, Xu CW (2009) Molecular evolution and functional divergence of HAK potassium transporter gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Genet Genomics 36:161–172. doi:10.1016/S1673-8527(08)60103-4
Sonnhammer EL, Eddy SR, Durbin R (1997) Pfam: a comprehensive database of protein domain families based on seed alignments. Proteins 28:405–420
Guo AY, Zhu QH, Chen X, Luo JC (2007) GSDS: a gene structure display server. Yi Chuan 29(8):1023–1026. doi:10.1360/yc-007-1023
Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA et al (2009) MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucl Acids Res 37:202–208. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp335
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP et al (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23(21):2947–2948. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24(8):1596–1599. doi:10.1093/molbev/msm092
Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T (1999) Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database. Nucl Acids Res 27(1):297–300. doi:10.1093/nar/27.1.297
Wang YJ, Deng DX, Bian YL, Lv YP, Xie Q (2010) Genome-wide analysis of primary auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene family in maize (Zea mays. L.). Mol Biol Rep 37:3991–4001. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0058-6
Maher C, Stein L, Ware D (2006) Evolution of Arabidopsis microRNA families through duplication events. Genome Res 16:510–519. doi:10.1101/gr.4680506
Nakano M, Nobuta K, Vemaraju K, Tej SS, Skogen JW, Meyers BC (2006) Plant MPSS databases: signature-based transcriptional resources for analyses of mRNA and small RNA. Nucl Acids Res 34:731–735. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj077
Mulder N, Apweiler R (2007) InterPro and InterProScan: tools for protein sequence classification and comparison. Methods Mol Biol 396:59–70
Grabova (2007) Plant KT/KUP/HAK potassium transporters: single family-multiple functions. Ann Bot 99:1035–1041. doi:10.1093/aob/mcm066
Schleyer M, Bakker EP (1993) Nucleotide sequence and 3’-end deletion studies indicate that the K+-uptake protein Kup from Escherichia coli is composed of a hydrophobic core linked to a large and partially essential hydrophilic C terminus. J Bacteriol 175:6925–6931
Baňuelos MA, Klein RD, Alexander-Bowman SJ, Rodríguez-Navarro A (1995) A potassium transporter of the yeast Schwanniomyces occidentalis homologous to the Kup system of Escherichia coli has a high concentrative capacity. EMBO J 14:3021–3027
Greiner T, Ramos J, Alvarez MC, Gurnon JR, Kang M, Etten JLV, Moroni A, Thiell G (2011) Functional HAK/KUP/KT-like potassium transporter encoded by chlorella viruses. Plant J 68:977–986. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04748.x
Amrutha RN, Sekhar PN, Varshney RK, Kishor PBK (2007) Genome-wide analysis and identification of genes related to potassium transporter families in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci 172:708–721. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2006.11.019
Qiu D, Xiao J, Xie W, Cheng H, Li X, Wang S (2009) Exploring transcriptional signalling mediated by OsWRKY13, a potential regulator of multiple physiological processes in rice. BMC Plant Biol 9:74. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-9-74
Vornam B, Gailing O, Derory J, Plomion C, Kremer A, Finkeldey R (2011) Characterisation and natural variation of a dehydrin gene in Quercus petraea (Matt.) Liebl. Plant Biol 13:881–887. doi:10.1111/j.1438-8677.2011.00446.x
Bratić AM, Majić DB, Samardžić JT, Maksimović VR (2009) Functional analysis of the buckwheat metallothionein promoter: tissue specificity pattern and up-regulation under complex stress stimuli. J Plant Physiol 166:996–1000. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2008.12.002
Yazaki J, Shimatani Z, Hashimoto A, Nagata Y, Fujii F, Kojima K, Suzuki K, Taya T, Tonouchi M, Nelson C et al (2004) Transcriptional profiling of genes responsive to abscisic acid and gibberellin in rice: phenotyping and comparative analysis between rice and Arabidopsis. Physiol Genom 17:87–100. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00201.2003
Guo L, Yu Y, Xia X, Yin W (2010) Identification and functional characterisation of the promoter of the calcium sensor gene CBL1 from the xerophyte Ammopiptanthus mongolicus. BMC Plant Biol 10:18. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-10-18
Piechulla B, Merforth N, Rudolph B (1998) Identification of tomato Lhc promoter regions necessary for circadian expression. Plant Mol Biol 38:655–662. doi:10.1023/A:1006094015513
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to editors and reviewers for their helpful comments. This work was supported partly by the International Science and Technology Cooperation Project (ISTCP) in China (No. 2010DFB33740) and the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission (No. Z111100066111005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Zhang, J., Chen, Y. et al. Genome-wide analysis and identification of HAK potassium transporter gene family in maize (Zea mays L.). Mol Biol Rep 39, 8465–8473 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1700-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1700-2