Abstract
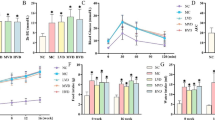
The objective of the present study is to observe the effect of Astragalus polysaccharide (APS) on myocardial glucose and lipid metabolism in diabetes (DM) hamster and to explore its mechanism in intervention of DM cardiomyopathy. Low-dose- streptozotocin-induced hamsters (STZ, 40 mg/kg × 3 days, i.p.) with blood glucose >13.9 mmo/L were considered as type 2 diabetic models. We measure blood glucose, serum lipid, insulin, C-peptide, myocardial enzyme levels, myocardial glycogen staining, myocardial ultrastructure, fluorescence quantitative RT–PCR detection of myocardial PPAR-α and the target genes (FATP, ACS) and GLUT4 mRNA expression in normal control group, DM group and APS treatment group hamsters. There was significant glycolipid metabolic disorders in DM group compared with normal group. Glucose, glycosylated serum protein, myocardial enzymes and lipid levels in APS treatment group decreased significantly than DM group, but insulin and C-peptide levels was no difference. Myocardial glycogen staining and abnormal myocardial ultrastructure in APS treatment group were significantly improved than in DM group. Gene expression of myocardial PPAR-α and its target genes (FATP, ACS) in APS group were significantly lower than in DM group, while gene expression of GLUT4 in APS group was higher than DM group. APS can partially improve myocardial glucose and lipid metabolism disorders in diabetic hamsters and protect myocardium in some extent.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen W, YU M-H, LI Y-M et al (2008) Astragalus polysaccharides: an effective treatment for diabetes prevention in NOD mice. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 116(8):468–474
CHEN W, YU M-H, LI Y-M et al (2007) Effects of Astragalus polysaccharides on chymase, angiotensin-converting enzyme and angiotensin II in diabetic cardiomyopathy in hamsters. J Int Med Res 35(6):873–877
CHEN W, YU M-H, LI Y-M et al (2010) Astragalus polysaccharides inhibited diabetic cardiomyopathy in hamsters depending on suppression of heart chymase activation. J Diabetes Complications 24(3):199–208
Chen W, YU M-H, LI Y-M et al (2009) Beneficial effects of astragalus polysaccharides treatment on cardiac chymase activities and cardiomyopathy in diabetic hamsters. Acta Diabetol 47(suppl 1):535–546
Mohammad A, Sharma V, Mcneill JH (2002) Vanadium increases GLUT4 in diabetic rat skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Biochem 233(1):139–143
Watson RT, Pessin J (2001) Intracellular organization of insulin signaling and GLUT4 translocation. Recent Prog Horm Res 56:175–193
Suden MC, Bulmer K, Gibbons GF et al (2002) Peroxisome-proliferator activated receptor alpha deficiency leads to dysregulation of hepatic lipid and carbohydrate metabolism by fatty acids and insulin. Biochem J 364:361–368
Lee SS, Chan WY, Lo CK et al (2004) Requirement of PPAR-alpha in maintaining phospholipid and triacylglycerol homeostasis during energy deprivation. J Lipid Res 45:2025–2037
Farrell GC, Robertson G, Auwerx J et al (2003) Central role of PPAR-alpha-dependent hepatic lipid turnover in dietary steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 38:123–132
Laukkanen Johanna, Yla-Herruala Seppo (2002) Genes involved in Atherosclerosis. Exp Nephrol 10:150–163
Sundvold H, Lien S (2001) Identification of a novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) promoter in man and transactivation by the nuclear receptor ROR alpha1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 287(2):383–390
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Chinese State Natural Science Funds Commission (NSFC), Grant No: 81001568.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wei Chen and Yan-Ping Xia contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Xia, YP., Chen, WJ. et al. Improvement of myocardial glycolipid metabolic disorder in diabetic hamster with Astragalus polysaccharides treatment. Mol Biol Rep 39, 7609–7615 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1595-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1595-y