Abstract
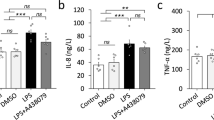
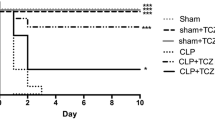
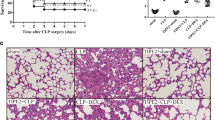
Penehyclidine hydrochloride (PHC) is a new anticholinergic drug. PHC has been shown to have a good curative effect for sepsis. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) has recently been considered to play an important role in sepsis. In this study, the role of MAPK signal pathways in protective effects of PHC preconditioning on acute lung injury in cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced sepsis was investigated. Healthy female mice were randomly divided into 4 groups: sham control, CLP, and 0.3 or 0.45 mg/kg PHC. At 12 h after surgery, arterial blood was drawn for blood gas analysis, and lung tissue samples were collected to examine pulmonary microvascular permeability, IL-6 levels and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity. MAPK protein expressions were measured using western blot technique. Compared with sham control mice, acute lung injury was induced in CLP group, which was indicated by decreased PaO2/FiO2, increased pulmonary microvascular permeability, IL-6 levels and MPO activity. Furthermore, mice’ exposure to CLP induced the increased protein levels of MAPK. Treatment of 0.45 mg/kg PHC markedly improved PaO2/FiO2, decreased pulmonary microvascular permeability, IL-6 levels and MPO activity, and inhibited expressions of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2) and p38 MAPK. Taken together, these results suggest that PHC ameliorated acute lung injury through the inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2) and p38 MAPK activation in septic mice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muenzer JT, Davis CG, Dunne BS, Unsinger J, Dunne WM, Hotchkiss RS (2006) Pneumonia after cecal ligation and puncture: a clinically relevant “two-hit” model of sepsis. Shock 26:565–570
Ma X, Xu D, Ai Y, Ming G, Zhao S (2009) Fas inhibition attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and cytokine release of rat type II alveolar epithelial cells. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9876-9
Xiaozhi Chen (2003) Penehyclidine hydrochloride. Central South Pharmacy 1:188–189
Han XY, Liu H, Liu CH, Wu B, Chen LF, Zhong BH, Liu KL (2005) Synthesis of the optical isomers of a new anticholinergic drug, penehyclidine hydrochloride (8018). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:1979–1982
Li A, Duan ML, Weng YB, Hu B (2006) Clinical study on penehyclidine hydrochloride on treatment of septic shock. J Emerg Med 15:742–744
Shen W, Gan J, Xu S, Jiang G, Wu H (2009) Penehyclidine hydrochloride attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury involvement of NF-kappaB pathway. Pharmacol Res 60:296–302
Zhan J, Wang Y, Wang C, Li J, Zhang Z, Jia B (2007) Protective effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride on septic mice and its mechanism. Shock 28:727–732
Ruimi N, Petrova RD, Agbaria R, Sussan S, Wasser SP, Reznick AZ, Mahajna J (2010) Inhibition of TNFalpha-induced iNOS expression in HSV-tk transduced 9L glioblastoma cell lines by Marasmius oreades substances through NF-kappaB- and MAPK-dependent mechanisms. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0035-0
Li Y, Du X, Li F, Deng Y, Yang Z, Wang Y, Pen Z, Wang Z, Yuan W, Zhu C, Wu X (2006) A novel zinc-finger protein ZNF436 suppresses transcriptional activities of AP-1 and SRE. Mol Biol Rep 33:287–294
Raman M, Chen W, Cobb MH (2007) Differential regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene 26:3100–3112
Obata K, Yamanaka H, Kobayashi K, Dai Y, Mizushima T, Katsura H, Fukuoka T, Tokunaga A, Noguchi K (2004) Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in injured and intact primary afferent neurons for mechanical and heat hypersensitivity after spinal nerve ligation. J Neurosci 24:l0211–10222
Thirunavukkarasu C, Watkins SC, Gandhi CR (2006) Mechanisms of endotoxin-induced NO, IL-6, and TNF-alpha production in activated rat hepatic stellate cells: role of p38 MAPK. Hepatology 44:389–398
Ying B, Yang T, Song X, Hu X, Fan H, Lu X, Chen L, Cheng D, Wang T, Liu D, Xu D, Wei Y, Wen F (2009) Quercetin inhibits IL-1 beta-induced ICAM-1 expression in pulmonary epithelial cell line A549 through the MAPK pathways. Mol Biol Rep 36:1825–1832
Maniatis NA, Orfanos SE (2008) The endothelium in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Curr Opin Crit Care 14:22–30
Zongze Z, Jia Z, Chang C, Kai C, Yanlin W (2009) Protective effects of remifentanil on septic mice. Mol Biol Rep 37(6):2803–2808. doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9828-4
Krens SF, Spaink HP, Snaar-Jagalska BE (2006) Functions of the MAPK family in vertebrate-development. FEBS Lett 580:4984–4990
Nash SP, Heuertz RM (2005) Blockade of p38 map kinase inhibits complement-induced acute lung injury in a murine model. Int Immunopharmacol 5:1870–1880
Matthiesen S, Bahulayan A, Holz O, Racké K (2007) MAPK pathway mediates muscarinic receptor-induced human lung fibroblast proliferation. Life Sci 80:2259–2262
Kim JY, Yang MS, Oh CD, Kim KT, Ha MJ, Kang SS, Chun JS (1999) Signalling pathway leading to an activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by stimulating M3 muscarinic receptor. Biochem J 337:275–280
Caulfield MP, Birdsall NJ (1998) International union of pharmacology. XVII. Classification of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 50:279–290
Hamilton SE, Nathanson NM (2001) The M1 receptor is required for muscarinic activation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in murine cerebral cortical neurons. J Biol Chem 276:15850–15853
Yagle K, Lu H, Guizzetti M, Möller T, Costa LG (2001) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by muscarinic receptors in astroglial cells: role in DNA synthesis and effect of ethanol. Glia 35:111–120
Acknowledgments
This stydy was supported by a grant from Hubei Provincial Health Department (No. 2005JX2C61).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jia Zhan and Yongpan Liu were co-authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, J., Liu, Y., Zhang, Z. et al. Effect of penehyclidine hydrochloride on expressions of MAPK in mice with CLP-induced acute lung injury. Mol Biol Rep 38, 1909–1914 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0310-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0310-0