Abstract
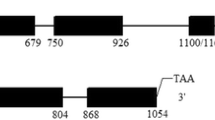
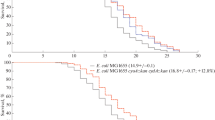
In this study, in silico analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans genome revealed six genes (cah-1, cah-2, cah-3, cah-4, cah-5, and cah-6) possibly encoding α class CAs (carbonic anhydrase). Real-time RT-PCR analysis revealed the temporal expression pattern of each gene, as well as changes in expression levels under different atmospheric conditions (stress). Cah-3 and cah-4 showed the highest levels of transcript accumulation, while most genes responded to the stress conditions. Yeast complementation showed that cah-3 was able to complement the function of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CA (NCE103) in vivo. Recombinant CAH-3, CAH-4a and CAH-5 enzymes, expressed in Escherichia coli were used for in vitro measurement of CA activity. However, in vitro activity was only detectable for CAH-4a. RNAi by feeding was performed on wild-type C. elegans for all genes. The worms were examined for a visible phenotype under normal and stress conditions (pH, CO2/O2). Silencing cah-3 and cah-4 may reduce the life-span of the worms (at 22°C).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Esbaugh AJ, Tufts BL (2006) The structure and function of carbonic anhydrase isozymes in the respiratory system of vertebrates. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 154:185–198
Sterling D, Reithmeier RAF, Casey JR (2001) Carbonic anhydrase: in the driver’s seat for bicarbonate transport. JOP 2:165–170
Liljas A, Laurberg M (2000) A wheel invented three times. EMBO J 1:16–17
Tripp BC, Smith K, Ferry JG (2001) Carbonic anhydrase: new insights for an ancient enzyme. J Biol Chem 276:48615–48618
Sly SW, Hu PY (1995) Human carbonic anhydrases and carbonic anhydrase deficiencies. Annu Rev Biochem 64:375–401
Fasseas MK, Tsikou D, Flemetakis E, Katinakis P (2009) Molecular and biochemical analysis of the β class carbonic anhydrases in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Biol Rep. doi: 10.1007/s11033-009-9857-z
Hall RA, Vullo D, Innocenti A, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT, Klappaa P, Mόhlschlegelt FA (2008) External pH influences the transcriptional profile of the carbonic anhydrase, CAH-4b in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Biochem Parasitol 161:140–149
DeRosa AA, Chirgwin SR, Williams JC, Klei TR (2008) Isolation and characterization of a gene encoding carbonic anhydrase from Ostertagia ostertagi and quantitative measurement of expression during in vivo exsheathment. Vet Parasitol 154:58–66
Simmer F, Moorman C, van der Linden AM, Kuijk E, van den Berghe PVE, Kamath RS, Fraser AG, Ahringer J, Plasterk RHA (2003) Genome-wide RNAi of C. elegans using the hypersensitive rrf-3 strain reveals novel gene functions. PLoS Biol 1:e12
Wormbase (2008) WS193 21. http://ws193.wormbase.org/
Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T (2006) The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22:195–201
Kim G, Lee TH, Wetzel P, Geers C, Robinson MA, Myers TG, Owens JW, Wehr NB, Eckhaus MW, Gros G, Wynshaw-Boris A, Levine RL (2004) Carbonic anhydrase III is not required in the mouse for normal growth, development, and life span. Mol Cell Biol 24:9942–9947
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Guex N, Peitsch MC (1997) SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modelling. Electrophoresis 18:2714–2723
Schwede T, Kopp J, Guex N, Peitsch MC (2003) SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3381–3385
Stiernagle T (2006) Maintenance of C.elegans. In Wormbook (ed) The C. elegans research community. Wormbook, Pasadena. doi:10.1895/wormbook.1.101.1. http://www.wormbook.org
Sasagawa Y, Urano T, Kohara Y, Takahashi H, Higashitani A (2003) Caenorhabditis elegans RBX1 is essential for meiosis, mitotic chromosomal condensation and segregation, and cytokinesis. Genes Cells 8:857–872
Götz R, Gnann A, Zimmermann FK (1999) Deletion of the carbonic anhydrase-like gene NCE103 of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae causes an oxygen-sensitive growth defect. Yeast 15:855–864
Kamath RS, Martinez-Campos M, Zipperlen P, Fraser AG, Ahringer J (2000) Effectiveness of specific RNA-mediated interference through ingested double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genome Biol 2:1–10
Kazuyo N, Kanemori M, Kitagawa M, Yanagi H, Yura T (1998) Chaperone coexpression plasmids: differential and synergistic roles of DnaK-DnaJ-GrpE and GroEL-GroES in assisting folding of an allergen of Japanese cedar pollen, Cryj2, in Escherichia coli. Appl Envirol Microbiol 64:1694–1699
Persson M, Hammarstrom P, Linden M, Jonsson B-H, Svensson M, Carlsson U (1998) EPR mapping of interactions between spin-labeled variants of human carbonic anhydrase II and GroEL: evidence for increased flexibility of the hydrophobic core by the interaction. Biochemistry 38:432–441
Clark D, Rowlett RS, Coleman JR, Klessig DF (2004) Complementation of the yeast deletion mutant ΔNCE103 by members of the β class of carbonic anhydrases is dependent on carbonic anhydrase activity rather that on antioxidant activity. Biochem J 379:609–615
Güzel Ö, Innocenti A, Hall RA, Scozzafava A, Mühlschlegel FA, Supuran CT (2009) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. The nematode a-carbonic anhydrase of Caenorhabditis elegans CAH-4b is highly inhibited by 2-(hydrazinocarbonyl)-3-substituted-phenyl-1H-indole-5-sulfonamides. Bioorg Med Chem 17:3212–3215
Hallem EA, Sternberg PW (2008) Acute carbon dioxide avoidance in Caenorhabditis elegans. PNAS 105:8038–8043
Bretscher AJ, Busch KE, de Bono M (2008) A carbon dioxide avoidance behaviour is integrated with responses to ambient oxygen and food in Caenorhabditis elegans. PNAS 105:8044–8049
Petronijevic T, Rogers WP, Sommerville RI (1985) Carbonic acid as the host signal for the development of parasitic stages of nematodes. Int J Parasitol 15:661–666
Föll RL, Pleyers A, Lewandovski GJ, Wermter C, Hegemann V, Paul RJ (1999) Anaerobiosis in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Comp Biochem Physiol B 124:269–280
Van Voorhies WA, Ward S (2000) Broad oxygen tolerance in the nematode Caerorhabditis elegans. J Exp Biol 203:2467–2478
Mochii M, Yoshida S, Morita K, Kohara Y, Ueno N (1999) Identification of transforming growth factor-β regulated genes in Caenorhabditis elegans by differential hybridization of arrayed cDNAs. PNAS 96:15020–15025
Muller FL, Lustgarten MS, Jang Y, Richardson A, Van Remmen H (2007) Trends in oxidative aging theories. Free Radic Biol Med 43:477–503
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Y. Kohara from the Kohara Laboratory (NIG, Japan) for providing the cDNA clones yk713, yk443, yk1011 and yk794. We also thank Dr. N. Tavernarakis from the Tavernarakis Lab (IMBB, Greece) for his assistance and for providing the C. elegans strain N2, the E. coli strains OP50 and HT115 and the pL4440 vector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fasseas, M.K., Tsikou, D., Flemetakis, E. et al. Molecular and biochemical analysis of the α class carbonic anhydrases in Caenorhabditis elegans . Mol Biol Rep 38, 1777–1785 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0292-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0292-y